J Korean Med Sci.
2007 Oct;22(5):928-931. 10.3346/jkms.2007.22.5.928.
Proteinuria in a Boy with Infectious Mononucleosis, C1q Nephropathy, and Dent's Disease
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatrics, Chungang University Yongsan Hospital, Seoul, Korea. inseok@cau.ac.kr
- 2Department of Pathology, Seoul National University Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Pediatrics, Seoul National University Children's Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 1713307
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2007.22.5.928
Abstract
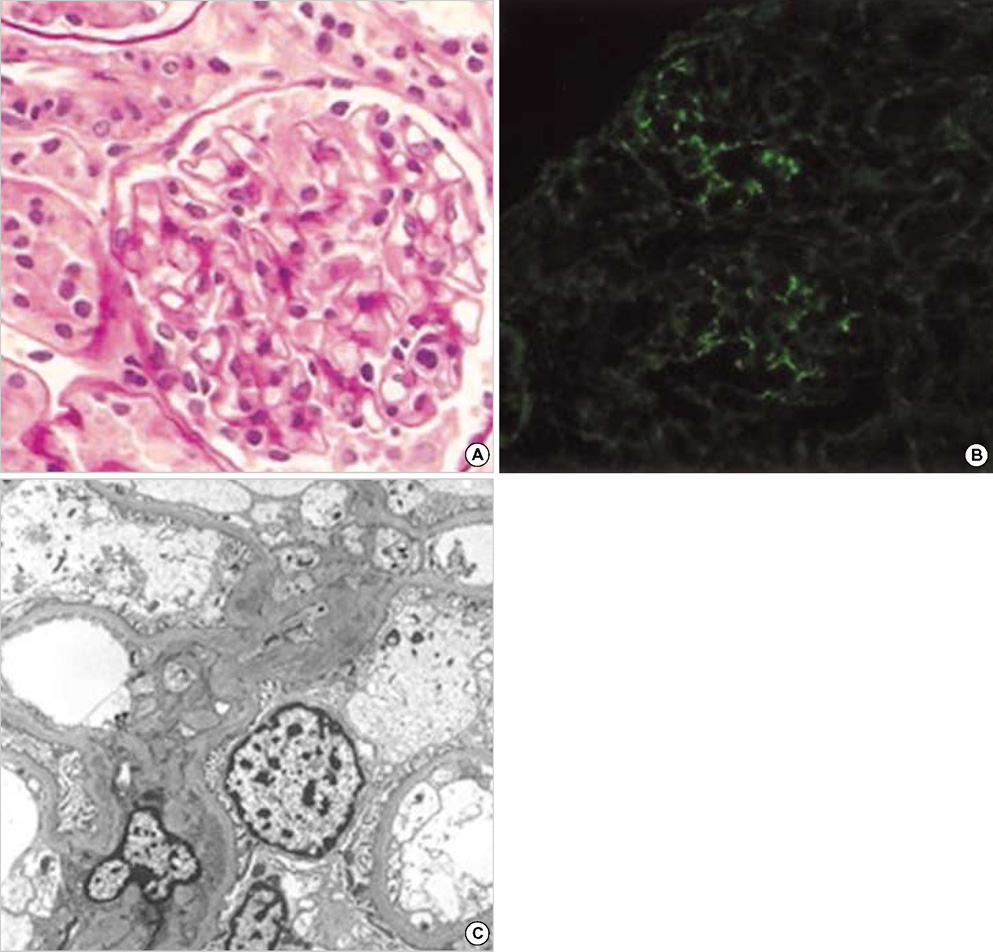
- C1q nephropathy is a proliferative glomerulopathy with extensive mesangial deposition of C1q. A three-year old boy presented with a nephrotic-range proteinuria during an acute phase of Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) infection, and he had a family history of Dent's disease. The renal biopsy findings were compatible with C1q nephropathy. However, EBV in situ hybridization was negative. The CLCN5 gene analysis revealed an R637X hemizygous mutation, which was the same as that detected in his maternal cousin, the proband of the family. The causal relationship between EBV infection and C1q nephropathy remains to be determined. Moreover, the effects of underlying Dent's disease in the process of C1q nephropathy has to be considered.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Biopsy
Child, Preschool
Epstein-Barr Virus Infections/metabolism
Glomerulonephritis/pathology
Humans
In Situ Hybridization
Infectious Mononucleosis/*complications/*diagnosis
Kidney Diseases/*complications/*diagnosis
Kidney Tubules/*pathology
Male
Membrane Glycoproteins/*chemistry
Mutation
Nephrosis
Proteinuria/*complications/*diagnosis
Receptors, Complement/*chemistry
Treatment Outcome
Figure
Reference
-
1. Jennette JC, Hipp CG. C1q nephropathy: a distinct pathologic entity usually causing nephrotic syndrome. Am J Kidney Dis. 1985. 6:103–110.2. Macsween KF, Crawford DH. Epstein-Barr virus-recent advances. Lancet Infect Dis. 2003. 3:131–140.
Article3. Cataudella JA, Young ID, Iliescu EA. Epstein-Barr virus-associated acute interstitial nephritis: infection or immunologic phenomenon? Nephron. 2002. 92:437–439.
Article4. Kano K, Yamada Y, Sato Y, Arisaka O, Ono Y, Ueda Y. Glomerulonephritis in a patient with chronic active Epstein-Barr virus infection. Pediatr Nephrol. 2005. 20:89–92.
Article5. Cheong HI, Lee JW, Zheng SH, Lee JH, Kang JH, Kang HG, Ha IS, Lee SJ, Choi Y. Phenotype and genotype of Dent's disease in three Korean boys. Pediatr Nephrol. 2005. 20:455–459.
Article6. Iskandar SS, Browning MC, Lorentz WB. C1q nephropathy: a pediatric clinicopathologic study. Am J Kidney Dis. 1991. 18:459–465.7. Lau KK, Gaber LW, Delos Santos NM, Wyatt RJ. C1q nephropathy: features at presentation and outcome. Pediatr Nephrol. 2005. 20:744–749.
Article8. Markowitz GS, Schwimmer JA, Stokes MB, Nasr S, Seigle RL, Valeri AM, D'Agati VD. C1q nephropathy: a variant of focal segmental glomerulosclerosis. Kidney Int. 2003. 64:1232–1240.
Article9. Fukuma Y, Hisano S, Segawa Y, Niimi K, Tsuru N, Kaku Y, Hatae K, Kiyoshi Y, Mitsudome A, Iwasaki H. Clinicopathologic correlation of C1q nephropathy in children. Am J Kidney Dis. 2006. 47:412–418.
Article10. Isaac J, Shihab FS. De Novo C1q nephropathy in the renal allograft of a kidney pancreas transplant recipient: BK virus induced nephropathy? Nephron. 2002. 92:431–436.11. Lee JW, Cho SJ, Lee SJ, Sung SH. A case of C1q nephropathy in steroid-dependent nephrotic syndrome. J Korean Soc Pediatr Nephrol. 2001. 5:206–209.12. Verma N, Arunabh S, Brady TM, Charytan C. Acute interstitial nephritis secondary to infectious mononucleosis. Clin Nephrol. 2002. 58:151–154.
Article13. Nadasdy T, Park CS, Peiper SC, Wenzl JE, Oates J, Silva FG. Epstein-Barr virus infection-associated renal disease: diagnostic use of molecular hybridization technology in patients with negative serology. J Am Soc Nephrol. 1992. 2:1734–1742.
Article14. Davenport A, Maciver AG, Mackenzie JC. C1q nephropathy: do C1q deposits have any prognostic significance in the nephrotic syndrome? Nephrol Dial Transplant. 1992. 7:391–396.15. Shappell SB, Myrthil G, Fogo A. An adolescent with relapsing nephrotic syndrome: minimal-change disease versus focal-segmental glomerulosclerosis versus C1q nephropathy. Am J Kidney Dis. 1997. 29:966–970.
Article16. Thakker RV. Pathogenesis of Dent's disease and related syndromes of X-linked nephrolithiasis. Kidney Int. 2000. 57:787–793.
Article17. Igarashi T, Inatomi J, Ohara T, Kuwahara T, Shimadzu M, Thakker RV. Clinical and genetic studies of CLCN5 mutations in Japanese families with Dent's disease. Kidney Int. 2000. 58:520–527.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Complete Remission from C1q Nephropathy with Disappearance of C1q Deposition after Steroid Therapy
- A Case of C1q Mediated Glomerulonephritis Manifested by Asymptomatic Hematuria
- Two Cases of C1q Nephropathy in Siblings
- Skin Rash in A Patient with Infectious Mononucleosis after the Intake of Ampicillin
- A case of infectious mononucleosis