J Korean Med Sci.
2007 Feb;22(1):167-169. 10.3346/jkms.2007.22.1.167.
Generalized Pustular Psoriasis and Hepatic Dysfunction Associated with Oral Terbinafine Therapy
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Dermatology, Pusan National University College of Medicine, Busan, Korea, Korea. hsjang@pusan.ac.kr
- 2Laboratory of Immunopathology, National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Disease, National Institute of Health, Bethesda, M.D., U.S.A.
- KMID: 1713261
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2007.22.1.167
Abstract
- We report a case of 61-yr-old man with stable psoriasis who progressively developed generalized pustular eruption, erythroderma, fever, and hepatic dysfunction following oral terbinafine. Skin biopsy was compatible with pustular psoriasis. After discontinuation of terbinafine and initiating topical corticosteroid and calcipotriol combination with narrow band ultraviolet B therapy, patient's condition slowly improved until complete remission was reached 2 weeks later. The diagnosis of generalized pustular psoriasis (GPP) induced by oral terbinafine was made. To our knowledge, this is the first report of GPP accompanied by hepatic dysfunction associated with oral terbinafine therapy.
MeSH Terms
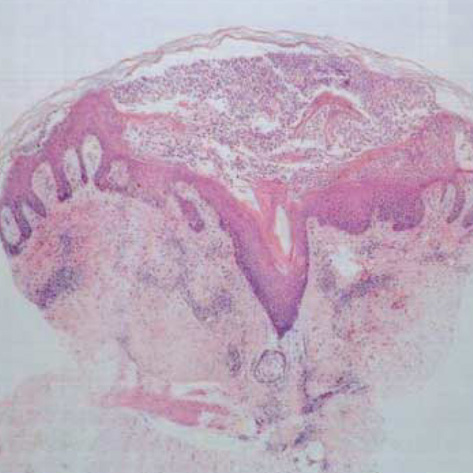
Figure
Reference
-
1. Hall M, Monka C, Krupp P, O'Sullivan D. Safety of oral terbinafine: results of a postmarketing surveillance study in 25,884 patients. Arch Dermatol. 1997. 133:1213–1219.
Article2. Kempinaire A, De Raeve L, Merckx M, De Coninck A, Bauwens M, Roseeuw D. Terbinafine-induced acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis confirmed by a positive patch-test result. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1997. 37:653–655.
Article3. Ham SH, Ha SJ, Park YM, Cho SH, Kim JW. Acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis induced by terbinafine. J Asthma Allergy Clin Immunol. 1998. 18:330–334.4. Hall AP, Tate B. Acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis associated with oral terbinafine. Australas J Dermatol. 2000. 41:42–45.
Article5. Carstens J, Wendelboe P, Sogaard H, Thestrup-Pedersen K. Toxic epidermal necrolysis and erythema multiforme following therapy with terbinafine. Acta Derm Venereol. 1994. 74:391–392.6. Gupta AK, Lynde CW, Lauzon GJ, Mehlmauer MA, Braddock SW, Miller CA, Del Rosso JQ, Shear NH. Cutaneous adverse effects associated with terbinafine therapy: 10 case reports and a review of the literature. Br J Dermatol. 1998. 138:529–532.
Article7. Rzany B, Mockenhaupt M, Gehring W, Schopf E. Stevens-Johnson syndrome after terbinafine therapy. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1994. 30:509.
Article8. Gupta AK, Sibbald RG, Knowles SR, Lynde CW, Shear NH. Terbinafine therapy may be associated with the development of psoriasis de novo or its exacerbation: four case reports and a review of drug-induced psoriasis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1997. 36:858–862.
Article9. Wilson NJ, Evans S. Severe pustular psoriasis provoked by oral terbinafine. Br J Dermatol. 1998. 139:168.10. Spencer JM, Silvers DN, Grossman ME. Pustular eruption after drug exposure: is it pustular psoriasis or a pustular drug eruption? Br J Dermatol. 1994. 13:514–519.
Article11. Roujeau JC, Bioulac-Sage P, Bourseau C, Guillaume JC, Bernard P, Lok C, Plantin P, Claudy A, Delavierre C, Vaillant L, Wechsler J, Danan G, Benichou C, Beylot C. Acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis. Analysis of 63 cases. Arch Dermatol. 1991. 127:1333–1338.
Article12. Wach F, Stolz W, Hein R, Landthaler M. Severe erythema anulare centrifugum-like psoriatic drug eruption induced by terbinafine. Arch Dermatol. 1995. 131:960–961.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Two Cases of Combined Geographic Tongue and Fissured Tongue in Generalized Pustular Psoriasis
- A Case of Generalized Pustular Psoriasis Improved with Isotretinoin
- Oral Treatment of Generalized Pustular Psoriasis in a Child with an Aromatic Retinoid (Ro 10 - 9359)
- Generalized Pustular Psoriasis: Report of a Case
- A Case of Annular Pustular Psoriasis Showing Features of Subcorneal Pustular Dermatosis