J Korean Med Sci.
2006 Dec;21(6):1041-1047. 10.3346/jkms.2006.21.6.1041.
Analysis of Endoscopic Electronic Image of Intramucosal Gastric Carcinoma Using a Software Program for Calculating Hemoglobin Index
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Pusan National University College of Medicine, 1-10 Ami-dong, Seo-gu, Busan, Korea. gasong@pusan.ac.kr
- 2Department of Pathology, Pusan National University College of Medicine and Medical Research Institute, Korea.
- 3School of Computer Engineering, Pusan National University, Busan, Korea.
- 4Department of Computer Engineering, Silla University, Busan, Korea.
- KMID: 1713116
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2006.21.6.1041
Abstract
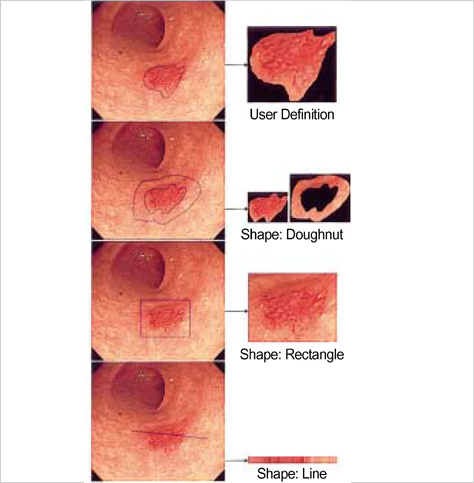
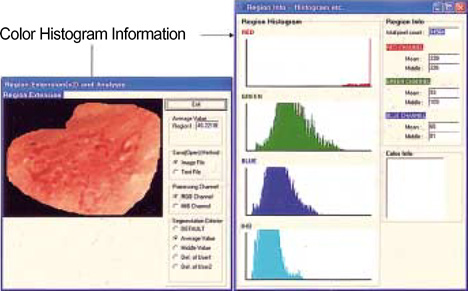
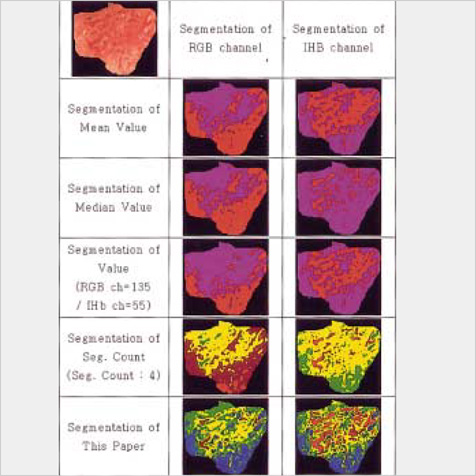
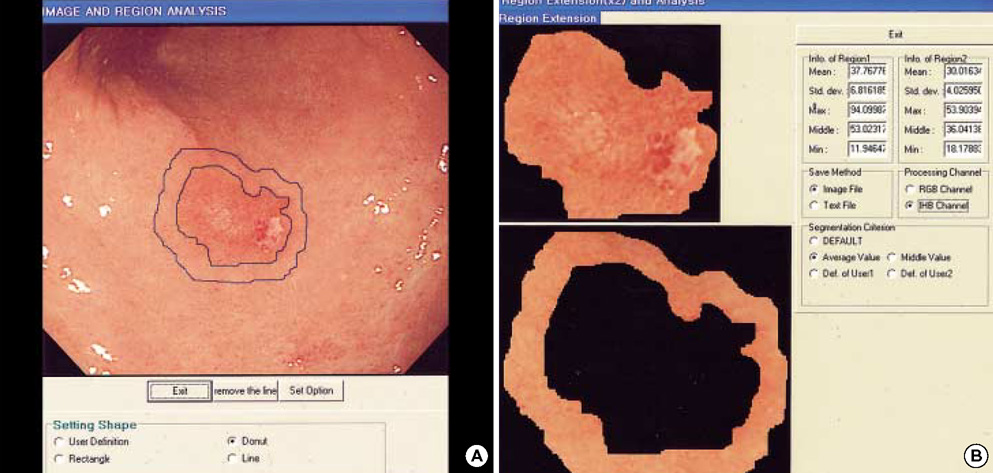
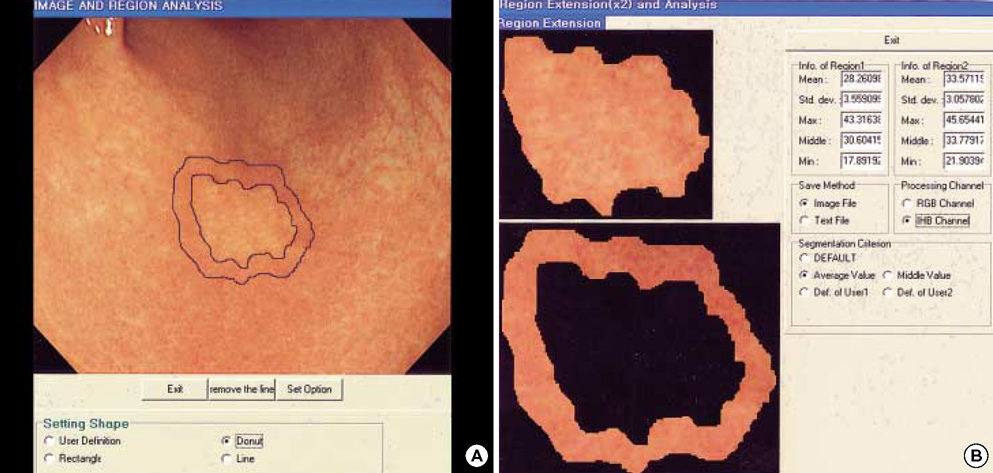
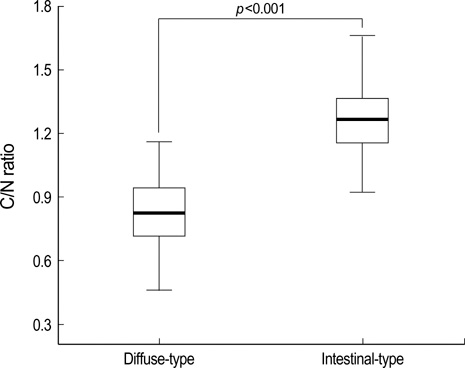
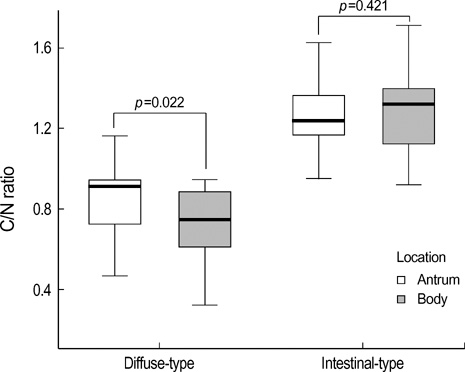
- Hemoglobin is the predominent pigment in the gastrointestinal mucosa, and the development of electronic endoscopy has made it possible to quantitatively measure the mucosal hemoglobin volume, by using a hemoglobin index (IHb). The aims of this study were to make a software program to calculate the IHb and then to investigate whether the mucosal IHb determined from the electronic endoscopic data is a useful marker for evaluating the color of intramucosal gastric carcinoma with regard to its value for discriminating between the histologic types. We made a software program for calculating the IHb in the endoscopic images. By using this program, the mean values of the IHb for the carcinoma (IHb-C) and those of the IHb for the surrounding non-cancerous mucosa (IHb-N) were calculated in 75 intestinal-type and 34 diffuse-type intramucosal gastric carcinomas. We then analyzed the ratio of the IHb-C to the IHb-N (C/N ratio). The C/N ratio in the intestinal-type carcinoma group was higher than that in the diffuse-type carcinoma group (p<0.001). In the diffuse-type carcinoma group, the C/N ratio in the body was lower than that in the antrum (p=0.022). The accuracy rate, sensitivity, specificity, and the positive and negative predictive values for the differential diagnosis of the diffuse-type carcinoma from the intestinal-type carcinoma were 94.5%, 94.1%, 94.7%, 88.9% and 97.3%, respectively. IHb is useful for making quantitative measurement of the endoscopic color in the intramucosal gastric carcinoma, and the C/N ratio by using the IHb would be helpful for distinguishing the diffuse-type carcinoma from the intestinal-type carcinoma.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Tumor Markers, Biological/*analysis
Stomach Neoplasms/classification/*diagnosis
*Software
Sensitivity and Specificity
Reproducibility of Results
Neoplasm Proteins/analysis
Male
Image Interpretation, Computer-Assisted/*methods
Humans
Hemoglobins/*analysis
Gastroscopy/*methods
Gastric Mucosa/metabolism/*pathology
Female
Colorimetry/methods
Figure
Reference
-
1. Misumi A, Misumi K, Murakami A, Harada K, Honmyo U, Akagi M. Endoscopic diagnosis of minute, small, and flat early gastric cancers. Endoscopy. 1989. 21:159–164.2. Honmyo U, Misumi A, Murakami A, Mizumoto S, Yoshinaka I, Maeda M, Yamamoto S, Shimada S. Mechanisms producing color change in flat early gastric cancers. Endoscopy. 1997. 29:366–371.
Article3. Tsuji S, Sato N, Kawano S, Kamada T. Functional imaging for the analysis of the mucosal blood hemoglobin distribution using electronic endoscopy. Gastrointest Endosc. 1988. 34:332–336.
Article4. Tsuji S, Kawano S, Hayashi N, Tsujii M, Ogihara T, Kamada T, Sato N. Analysis of mucosal blood hemoglobin distribution in gastric ulcers by computerized color display on electronic endoscopy. Endoscopy. 1991. 23:321–324.
Article5. Sato N, Tsuji S, Kawano S, Hayashi N, Tsujii M, Ishigami Y, Ogihara T, Nagano K, Kamada T. Computer-assisted two-dimensional analysis of gastric mucosal hemoglobin distribution using electronic endoscopy. Endoscopy. 1992. 24:Suppl 2. 522–526.
Article6. Yao K, Yao T, Matsui T, Iwashita A, Oishi T. Hemoglobin content in intramucosal gastric carcinoma as a marker of histologic differentiation: a clinical application of quantitative electronic endoscopy. Gastrointest Endosc. 2000. 52:241–245.
Article7. Yao K, Kato M, Fujisaki J. Techniques using the hemoglobin index of the gastric mucosa. Endoscopy. 2005. 37:479–486.
Article8. Japanese Gastric Cancer Association. Japanese Classification of Gastric Carcinoma: 2nd English Edition. Gastric Cancer. 1998. 1:10–24.9. Lauren P. The two histological main types of gastric carcinoma: Diffuse and so-called intestinal-type carcinoma. An attempt at a histoclinical classification. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand. 1965. 64:31–49.10. Browner WS, Newman TB, Cummings SR. Hulley SB, Cummings SR, editors. Designing a new study: III. Diagnostic test. Designing clinical research. 1988. 1st ed. Baltimore: Williams & Wilkins;87–97.11. Sano T, Kobori O, Muto T. Lymph node metastasis from early gastric cancer: endoscopic resection of tumour. Br J Surg. 1992. 79:241–244.
Article12. Soetikno RM, Gotoda T, Nakanishi Y, Soehendra N. Endoscopic mucosal resection. Gastrointest Endosc. 2003. 57:567–569.
Article13. Tada M, Murakami A, Karita M, Yanai H, Okita K. Endoscopic resection of early gastric cancer. Endoscopy. 1993. 25:445–450.
Article14. Muto M, Miyamoto S, Hosokawa A, Doi T, Ohtsu A, Yoshida S, Endo Y, Hosokawa K, Saito D, Shim CS, Gossner L. Endoscopic mucosal resection in the stomach using the insulated-tip needle-knife. Endoscopy. 2005. 37:178–182.
Article15. Sano T, Okuyama Y, Kobori O, Shimizu T, Morioka Y. Early gastric cancer. Endoscopic diagnosis of depth of invasion. Dig Dis Sci. 1990. 35:1340–1344.16. Yanai H, Matsumoto Y, Harada T, Nishiaki M, Tokiyama H, Shigemitsu T, Tada M, Okita K. Endoscopic ultrasonography and endoscopy for staging depth of invasion in early gastric cancer: a pilot study. Gastrointest Endosc. 1997. 46:212–216.
Article17. Akahoshi K, Chijiiwa Y, Hamada S, Sasaki I, Maruoka A, Kabemura T, Nawata H. Endoscopic ultrasonography: a promising method for assessing the prospects of endoscopic mucosal resection in early gastric cancer. Endoscopy. 1997. 29:614–619.
Article18. Akahoshi K, Chijiiwa Y, Hamada S, Sasaki I, Nawata H, Kabemura T, Yasuda D, Okabe H. Pretreatment staging of endoscopically early gastric cancer with a 15 MHz ultrasound catheter probe. Gastrointest Endosc. 1998. 48:470–476.
Article19. Oohara T, Aono G, Ukawa S, Takezoe K, Johjima Y, Kurosaka H, Asakura R, Tohma H. Clinical diagnosis of minute gastric cancer less than 5 mm in diameter. Cancer. 1984. 53:162–165.
Article20. Oiwa T, Mori M, Sugimachi K, Enjoji M. Diagnostics of small gastric carcinoma. J Surg Oncol. 1986. 33:170–175.
Article21. Ohtani H, Nagura H. Differing microvasculature in the two major types of gastric carcinoma: a conventional, ultrastructural and ultrastructural immunolocalization study of von Willebrand factor. Virchows Arch A Pathol Anat Histopathol. 1990. 417:29–35.
Article22. Adachi Y, Mori M, Enjoji M, Sugimachi K. Microvascular architecture of early gastric carcinoma. Microvascular-histopathologic correlates. Cancer. 1993. 72:32–36.
Article