Korean J Radiol.
2013 Oct;14(5):781-785. 10.3348/kjr.2013.14.5.781.
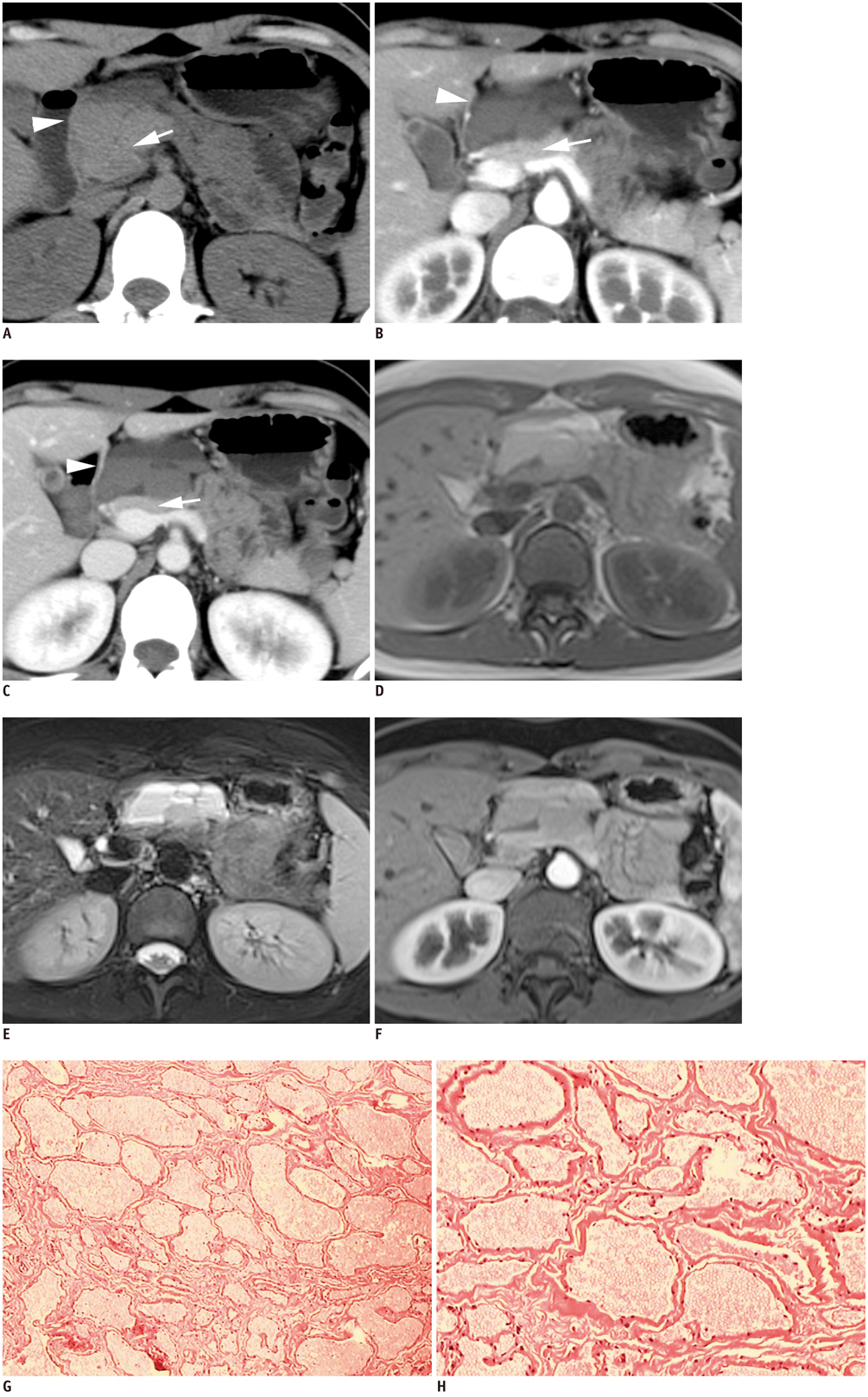
Unusual Features in an Adult Pancreatic Hemangioma: CT and MRI Demonstration
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiology, Changshu Hospital of Soochow University, Jiangsu 215500, China. luzhihua79@yahoo.com.cn
- 2Department of Pathology, Changshu Hospital of Soochow University, Jiangsu 215500, China.
- KMID: 1711433
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2013.14.5.781
Abstract
- Hemangiomas in the pancreas are very rare and only a few cases in adulthood have been reported in the literature. We describe a case of pancreatic hemangiomas in an adult with unique imaging findings. A 23-year-old woman visited the hospital for an incidentally detected pancreatic mass. CT and MRI revealed a multilocular cyst with fluid-fluid levels and no obvious enhancement. The patient underwent surgery and the mass was confirmed as a pancreatic hemangioma. The radiological features and differential diagnosis of this rare lesion are discussed.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Kobayashi H, Itoh T, Murata R, Tanabe M. Pancreatic cavernous hemangioma: CT, MRI, US, and angiography characteristics. Gastrointest Radiol. 1991; 16:307–310.2. Chang WT, Lee KT, Yang SF. Cavernous hemangioma of the pancreas: report of a case. Pancreas. 2003; 26:310–312.3. Mundinger GS, Gust S, Micchelli ST, Fishman EK, Hruban RH, Wolfgang CL. Adult pancreatic hemangioma: case report and literature review. Gastroenterol Res Pract. 2009; 2009:839730.4. Jarboui S, Salem A, Gherib BS, Ben Moussa M, Rajhi H, Mnif N, et al. Hemangioma of the pancreas in a 60-year-old woman: a report of a new case. Gastroenterol Clin Biol. 2010; 34:569–571.5. Lee J, Raman K, Sachithanandan S. Pancreatic hemangioma mimicking a malignant pancreatic cyst. Gastrointest Endosc. 2011; 73:174–176.6. Weidenfeld J, Zakai BB, Faermann R, Barshack I, Aviel-Ronen S. Hemangioma of pancreas: a rare tumor of adulthood. Isr Med Assoc J. 2011; 13:512–514.7. Mulliken JB, Fishman SJ, Burrows PE. Vascular anomalies. Curr Probl Surg. 2000; 37:517–584.8. Soyer P, Bluemke DA, Fishman EK, Rymer R. Fluid-fluid levels within focal hepatic lesions: imaging appearance and etiology. Abdom Imaging. 1998; 23:161–165.9. Ehara S, Sone M, Tamakawa Y, Nishida J, Abe M, Hachiya J. Fluid-fluid levels in cavernous hemangioma of soft tissue. Skeletal Radiol. 1994; 23:107–109.10. Buck JL, Hayes WS. From the Archives of the AFIP. Microcystic adenoma of the pancreas. Radiographics. 1990; 10:313–322.11. Kim HC, Yang DM, Kim HJ, Lee DH, Ko YT, Lim JW. Computed tomography appearances of various complications associated with pancreatic pseudocysts. Acta Radiol. 2008; 49:727–734.12. Cho HW, Choi JY, Kim MJ, Park MS, Lim JS, Chung YE, et al. Pancreatic tumors: emphasis on CT findings and pathologic classification. Korean J Radiol. 2011; 12:731–739.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Differential Diagnosis of Pancreatic Cancer and its Mimicking Lesions
- Benign Vascular Hepatic Tumor
- Acinar Cell Cystadenoma (Acinar Cystic Transformation) of the Pancreas: the Radiologic-Pathologic Features
- A Case of Cavernous Hemangioma of the Cervix and Vagina
- A Clinical Experience with Pancreatic Cavernous Hemangioma