Korean J Radiol.
2013 Oct;14(5):754-763. 10.3348/kjr.2013.14.5.754.
Pretreatment Evaluation with Contrast-Enhanced Ultrasonography for Percutaneous Radiofrequency Ablation of Hepatocellular Carcinomas with Poor Conspicuity on Conventional Ultrasonography
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiology and Center for Imaging Science, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul 135-710, Korea. leeminwoo0@gmail.com
- 2Department of Radiology, Kangwon National University College of Medicine, Chuncheon 200-722, Korea.
- KMID: 1711429
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2013.14.5.754
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
To determine whether pretreatment evaluation with contrast-enhanced ultrasonography (CEUS) is effective for percutaneous radiofrequency ablation (RFA) of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) with poor conspicuity on conventional ultrasonography (US).
MATERIALS AND METHODS
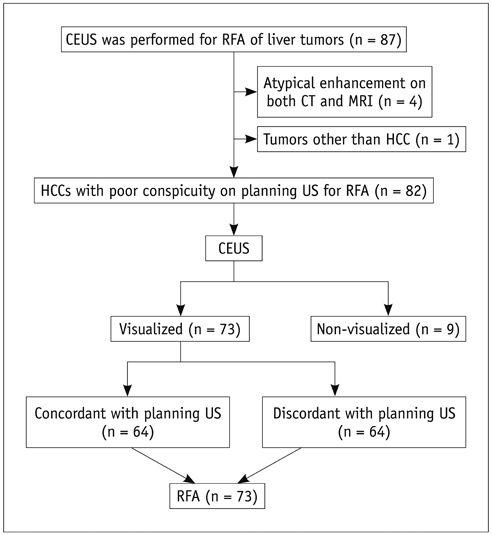
This retrospective study was approved by the institutional review board and informed consent was waived. From June 2008 to July 2011, 82 patients having HCCs (1.2 +/- 0.4 cm) with poor conspicuity on planning US for RFA were evaluated with CEUS prior to percutaneous RFA. We analyzed our database, radiologic reports, and US images in order to determine whether the location of HCC candidates on planning US coincide with that on CEUS. To avoid incomplete ablation, percutaneous RFA was performed only when HCC nodules were identified on CEUS. The rate of technical success was assessed. The cumulative rate of local tumor progression was estimated with the use of the Kaplan-Meier method (mean follow-up: 24.0 +/- 13.0 months).
RESULTS
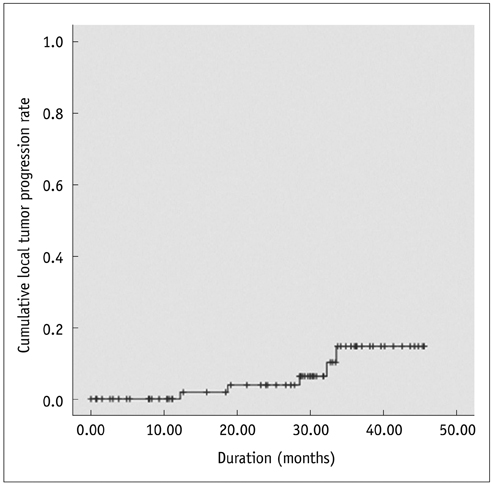
Among 82 patients, 73 (89%) HCCs were identified on CEUS, whereas 9 (11%) were not. Of 73 identifiable HCCs on CEUS, the location of HCC on planning US corresponded with that on CEUS in 64 (87.7%), whereas the location did not correspond in 9 (12.3%) HCCs. Technical success was achieved for all 73 identifiable HCCs on CEUS in a single (n = 72) or two (n = 1) RFA sessions. Cumulative rates of local tumor progression were estimated as 1.9% and 15.4% at 1 and 3 years, respectively.
CONCLUSION
Pretreatment evaluation with CEUS is effective for percutaneous RFA of HCCs with poor conspicuity on conventional US.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Forner A, Llovet JM, Bruix J. Hepatocellular carcinoma. Lancet. 2012; 379:1245–1255.2. European Association For The Study Of The Liver. European Organisation For Research And Treatment Of Cancer. EASL-EORTC clinical practice guidelines: management of hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatol. 2012; 56:908–943.3. Bruix J, Sherman M. American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases. Management of hepatocellular carcinoma: an update. Hepatology. 2011; 53:1020–1022.4. Lee MW, Kim YJ, Park HS, Yu NC, Jung SI, Ko SY, et al. Targeted sonography for small hepatocellular carcinoma discovered by CT or MRI: factors affecting sonographic detection. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2010; 194:W396–W400.5. Meloni MF, Goldberg SN, Livraghi T, Calliada F, Ricci P, Rossi M, et al. Hepatocellular carcinoma treated with radiofrequency ablation: comparison of pulse inversion contrastenhanced harmonic sonography, contrast-enhanced power Doppler sonography, and helical CT. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2001; 177:375–380.6. Goldberg SN, Gazelle GS, Compton CC, Mueller PR, Tanabe KK. Treatment of intrahepatic malignancy with radiofrequency ablation: radiologic-pathologic correlation. Cancer. 2000; 88:2452–2463.7. Min JH, Lee MW, Rhim H, Choi D, Kim YS, Kim YJ, et al. Recurrent hepatocellular carcinoma after transcatheter arterial chemoembolization: planning sonography for radio frequency ablation. J Ultrasound Med. 2011; 30:617–624.8. Lee MW, Lim HK, Kim YJ, Choi D, Kim YS, Lee WJ, et al. Percutaneous sonographically guided radio frequency ablation of hepatocellular carcinoma: causes of mistargeting and factors affecting the feasibility of a second ablation session. J Ultrasound Med. 2011; 30:607–615.9. Minami Y, Kudo M, Kawasaki T, Chung H, Ogawa C, Shiozaki H. Treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma with percutaneous radiofrequency ablation: usefulness of contrast harmonic sonography for lesions poorly defined with B-mode sonography. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2004; 183:153–156.10. Masuzaki R, Shiina S, Tateishi R, Yoshida H, Goto E, Sugioka Y, et al. Utility of contrast-enhanced ultrasonography with Sonazoid in radiofrequency ablation for hepatocellular carcinoma. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2011; 26:759–764.11. Kudo M, Hatanaka K, Maekawa K. Newly developed novel ultrasound technique, defect reperfusion ultrasound imaging, using sonazoid in the management of hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncology. 2010; 78:Suppl 1. 40–45.12. Bruix J, Sherman M. Practice Guidelines Committee, American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases. Management of hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology. 2005; 42:1208–1236.13. Omata M, Lesmana LA, Tateishi R, Chen PJ, Lin SM, Yoshida H, et al. Asian Pacific Association for the Study of the Liver consensus recommendations on hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatol Int. 2010; 4:439–474.14. Makuuchi M, Kokudo N, Arii S, Futagawa S, Kaneko S, Kawasaki S, et al. Development of evidence-based clinical guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma in Japan. Hepatol Res. 2008; 38:37–51.15. Rhim H, Choi D, Kim YS, Lim HK, Choe BK. Ultrasonography-guided percutaneous radiofrequency ablation of hepatocellular carcinomas: a feasibility scoring system for planning sonography. Eur J Radiol. 2010; 75:253–258.16. Song I, Rhim H, Lim HK, Kim YS, Choi D. Percutaneous radiofrequency ablation of hepatocellular carcinoma abutting the diaphragm and gastrointestinal tracts with the use of artificial ascites: safety and technical efficacy in 143 patients. Eur Radiol. 2009; 19:2630–2640.17. Rhim H, Lim HK. Radiofrequency ablation for hepatocellular carcinoma abutting the diaphragm: the value of artificial ascites. Abdom Imaging. 2009; 34:371–380.18. Goldberg SN, Grassi CJ, Cardella JF, Charboneau JW, Dodd GD 3rd, Dupuy DE, et al. Image-guided tumor ablation: standardization of terminology and reporting criteria. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2009; 20:7 Suppl. S377–S390.19. Liu F, Yu X, Liang P, Cheng Z, Han Z, Dong B. Contrastenhanced ultrasound-guided microwave ablation for hepatocellular carcinoma inconspicuous on conventional ultrasound. Int J Hyperthermia. 2011; 27:555–562.20. Solbiati L, Ierace T, Tonolini M, Cova L. Guidance and monitoring of radiofrequency liver tumor ablation with contrast-enhanced ultrasound. Eur J Radiol. 2004; 51:Suppl. S19–S23.21. Wakui N, Takayama R, Kanekawa T, Ichimori M, Otsuka T, Shinohara M, et al. Usefulness of arrival time parametric imaging in evaluating the degree of liver disease progression in chronic hepatitis C infection. J Ultrasound Med. 2012; 31:373–382.22. Minami Y, Kudo M, Hatanaka K, Kitai S, Inoue T, Hagiwara S, et al. Radiofrequency ablation guided by contrast harmonic sonography using perfluorocarbon microbubbles (Sonazoid) for hepatic malignancies: an initial experience. Liver Int. 2010; 30:759–764.23. Moriyasu F, Itoh K. Efficacy of perflubutane microbubbleenhanced ultrasound in the characterization and detection of focal liver lesions: phase 3 multicenter clinical trial. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2009; 193:86–95.24. Hatanaka K, Kudo M, Minami Y, Ueda T, Tatsumi C, Kitai S, et al. Differential diagnosis of hepatic tumors: value of contrastenhanced harmonic sonography using the newly developed contrast agent, Sonazoid. Intervirology. 2008; 51:Suppl 1. 61–69.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Fusion imaging of real-time ultrasonography with CT or MRI for hepatic intervention
- Radiofrequency Ablation of Liver Cancer: Early Evaluation of Therapeutic Response with Contrast-Enhanced Ultrasonography
- Radiofrequency ablation of very-early-stage hepatocellular carcinoma inconspicuous on fusion imaging with B-mode US: value of fusion imaging with contrast-enhanced US
- Local ablation therapy with contrast-enhanced ultrasonography for hepatocellular carcinoma: a practical review
- Sonography Guided Percutaneous Radiofrequency Ablation of Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Effect of Cooperative Training on the Pretreatment Assessment of the Operation's Feasibility