J Korean Bone Joint Tumor Soc.
2014 Jun;20(1):14-21. 10.5292/jkbjts.2014.20.1.14.
Treatment Outcome of Langerhans Cell Histocytosis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Kosin University Gospel Hospital, Busan, Korea. shchung@kosin.ac.kr
- KMID: 1707760
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5292/jkbjts.2014.20.1.14
Abstract
- PURPOSE
To analyze the clinical features and treatment outcome of Langerhans' cell histocytosis.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
From August 1996 to June 2013, 28 patients who histologically proven with LCH were analyzed of medical records, radiography, pathologic character retrospectively.
RESULTS
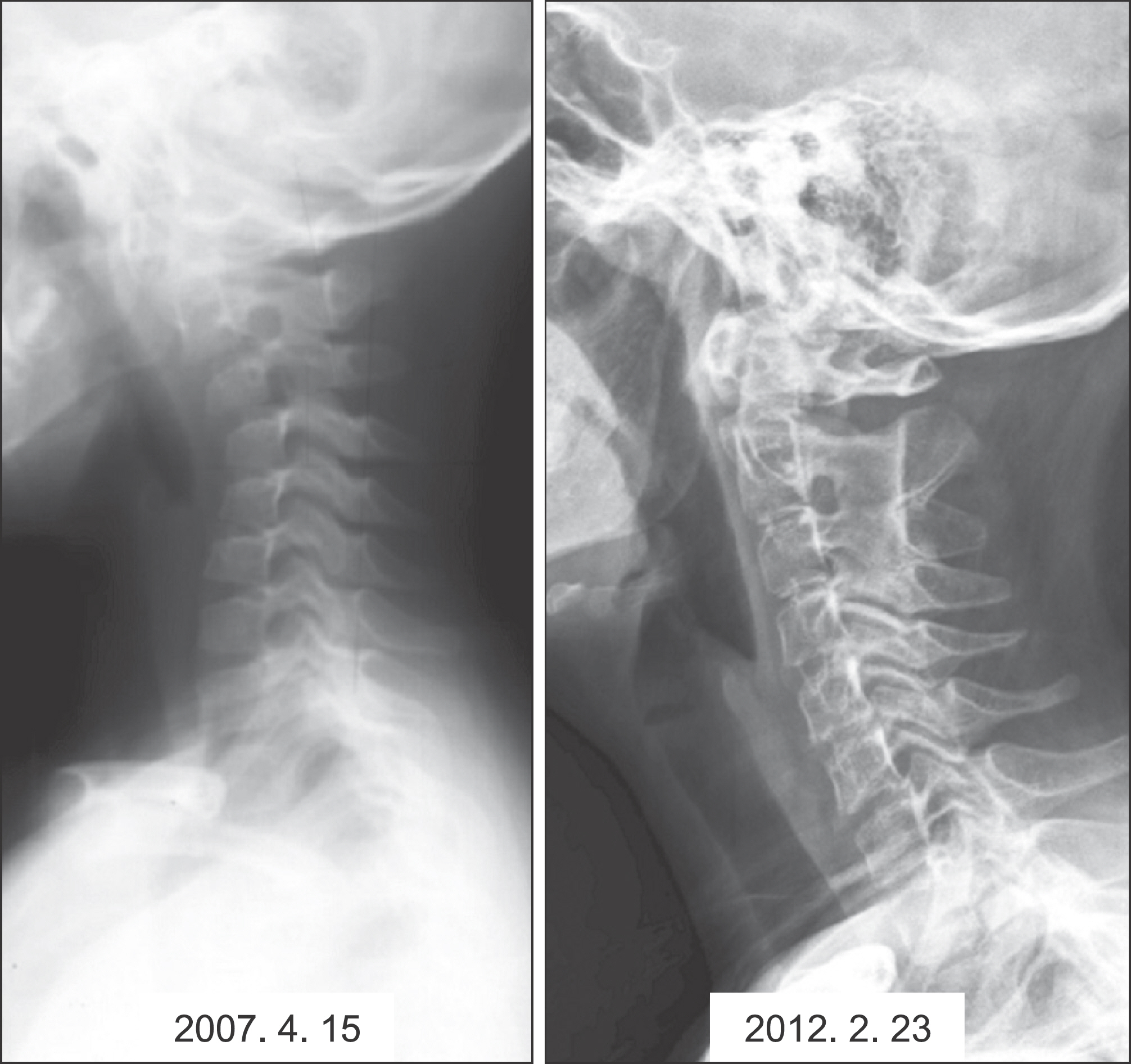
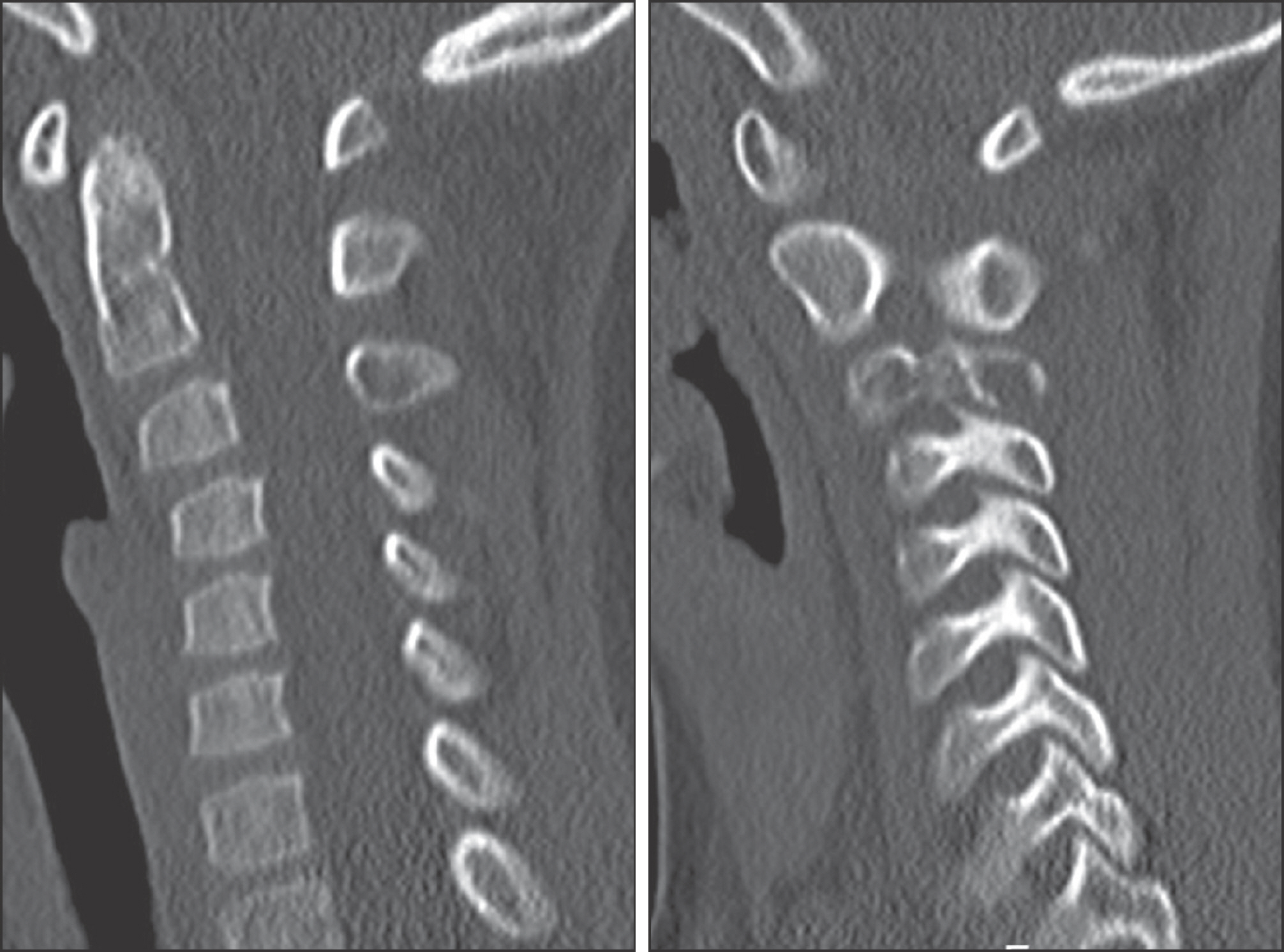
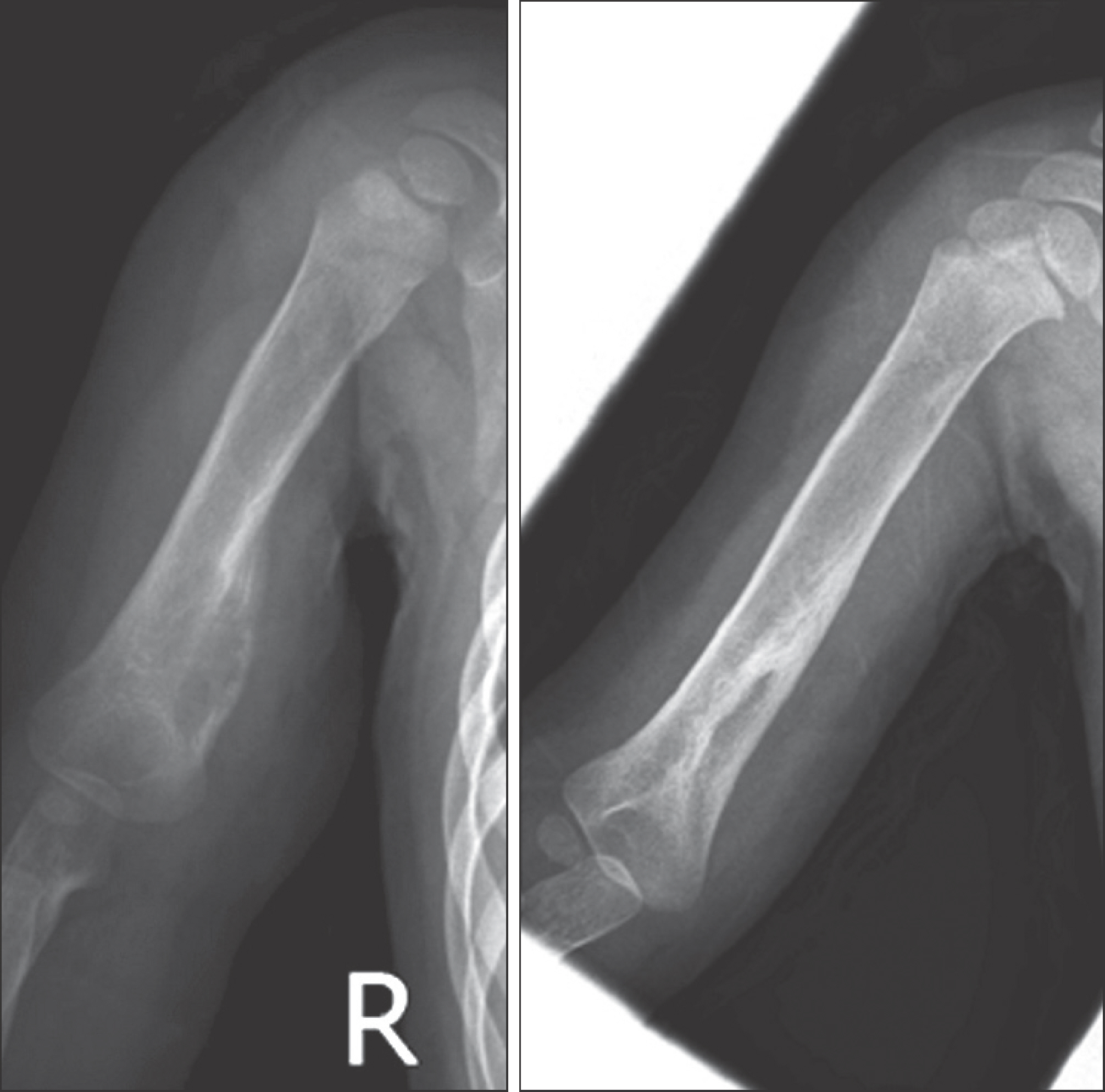
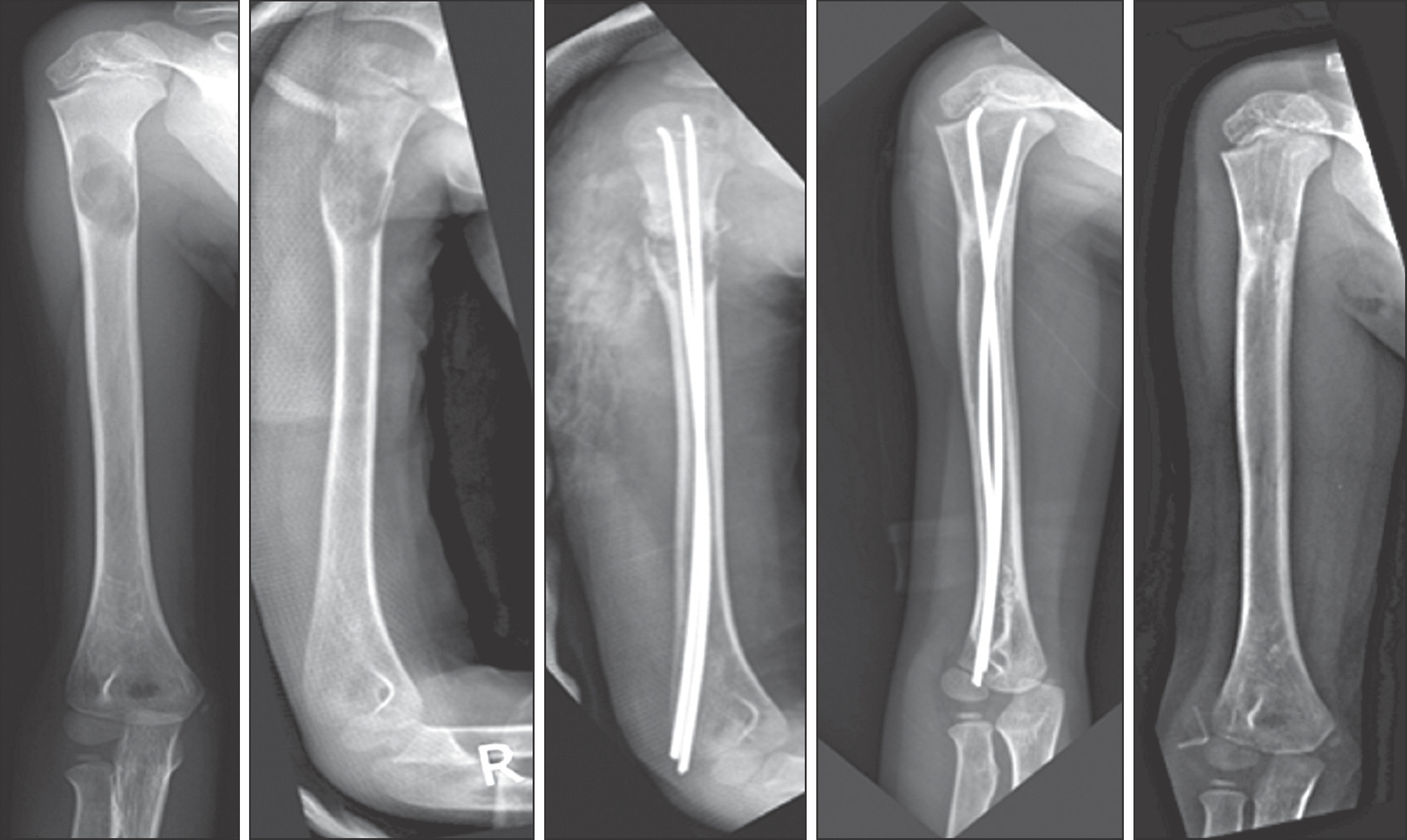
A total of 28 cases of LCH including 22 child has been reported. Onset age was 0.6 to 51 years old, occurred in the average age was 14.8 years. Follow-up period was 6 months to 134 months average was 44.6 months. The M:F ratio was 2.5:1. The initial symptoms was pain in 18 cases, 5 cases of pathologic fracture, 3 case of palpable mass, 1 case of discovered by accident in radiography, 1 case of torticollis. In radiological examination osteolysis was seen all cases, 7 cases showed a periosteal reaction, 1 case showed soft tissue extension. Clinical type of all cases were eosinophilic granuloma. 25 cases were classified as unifocal disease and 3 cases were multifocal single systemic diseases. In all cases, incisional biopsy was performed. After histologic confirmed, 14 cases was treated with curettage or surgical excision of the lesion and the other 14 cases were followed up without treatment. There is no death during follow up period. 11 cases has no radiological improvement after 3-6 months observation, intralesional steroid injection was performed.
CONCLUSION
Patients with LCH who has rapid systemic onset is very rare, so if you meet the young children who suspected LCH, you shoulder avoid the examination which cause excessive radiation exposure to the young patient. In order to confirm the diagnosis of disease, biopsy is needed. Close observation after confirmed by histological method will bring the satisfactory results. But the patients who had pathologic fracture or wide bone destruction already may need curettage and bone grafting to lesion or internal fixation. The lesion which has no radiological improvement after 3-6 months observation or appear with pain interferes daily life may need local steroid injection as a good treatment.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Leikin SL. Immunobiology of histiocytosis-X. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am. 1987; 1:49–61.
Article2. Ryu Y, Lee H, Lee S, et al. Pathological characteristics of 20 cases of langerhans cell histiocytosis and specificity of immunohistochemical stain of langerin (CD207). Korean J Pathol. 2009; 43:113–9.
Article3. Park BM, Shin KH, Kim HW, Kim HJ. Treatment of langerhans cell histiocytosis. J Korean Orthop Assoc. 1996; 31:1218–27.
Article4. Favara BE, Feller AC, Pauli M, et al. Contemporary classification of histiocytic disorders. The WHO Committee On Histiocytic/Reticulum Cell Proliferations. Reclassification Working Group of the Histiocyte Society. Med Pediatr Oncol. 1997; 29:157–66.5. Hicks J, Flaitz CM. Langerhans cell histiocytosis: current insights in a molecular age with emphasis on clinical oral and maxillofacial pathology practice. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2005; 100(2 Suppl):S42–66.
Article6. Seo JJ. Recent advances in histiocytic disorders. Korean J Pediatr. 2007; 50:524–30.
Article7. Lampert F. Langerhans cell histiocytosis. Historical perspectives. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am. 1998; 12:213–9.8. Komp DM. Historical perspectives of Langerhans cell histiocytosis. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am. 1987; 1:9–21.
Article9. Lichtenstein L. Histiocytosis X (eosinophilic granuloma of bone, letterer-siwe disease, and schueller-christian disease). Further observations of pathological and clinical importance. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1964; 46:76–90.10. Lichtenstein L. Histiocytosis X; integration of eosinophilic granuloma of bone, Letterer-Siwe disease, and SchÜller-Christian disease as related manifestations of a single nosologic entity. AMA Arch Pathol. 1953; 56:84–102.11. Chung YG, Kim YS, Rhee SK, et al. Langerhans' cell histiocytosis in patients younger than 2 years. J Korean Orthop Assoc. 2006; 41:37–42.
Article12. Howarth DM, Gilchrist GS, Mullan BP, Wiseman GA, Edmonson JH, Schomberg PJ. Langerhans cell histiocytosis: diagnosis, natural history, management, and outcome. Cancer. 1999; 85:2278–90.13. Leonidas JC, Guelfguat M, Valderrama E. Langerhans' cell histiocytosis. Lancet. 2003; 361:1293–5.
Article14. Islinger RB, Kuklo TR, Owens BD, et al. Langerhans' cell histiocytosis in patients older than 21 years. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2000; 379:231–5.
Article15. Yasko AW, Fanning CV, Ayala AG, Carrasco CH, Murray JA. Percutaneous techniques for the diagnosis and treatment of localized Langerhans-cell histiocytosis (eosinophilic granuloma of bone). J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1998; 80:219–28.
Article16. Han I, Suh ES, Lee SH, Cho HS, Oh JH, Kim HS. Management of eosinophilic granuloma occurring in the appendicular skeleton in children. Clin Orthop Surg. 2009; 1:63–7.
Article17. Cohen M, Zornoza J, Cangir A, Murray JA, Wallace S. Direct injection of methylprednisolone sodium succinate in the treatment of solitary eosinophilic granuloma of bone: a report of 9 cases. Radiology. 1980; 136:289–93.
Article18. Capanna R, Springfield DS, Ruggieri P, et al. Direct cortisone injection in eosinophilic granuloma of bone: a preliminary report on 11 patients. J Pediatr Orthop. 1985; 5:339–42.19. Egeler RM, Thompson RC Jr, VoÛte PA, Nesbit ME Jr. Intralesional infiltration of corticosteroids in localized Langerhans' cell histiocytosis. J Pediatr Orthop. 1992; 12:811–4.
Article20. Scaglietti O, Marchetti PG, Bartolozzi P. Final results obtained in the treatment of bone cysts with methylprednisolone acetate (depo-medrol) and a discussion of results achieved in other bone lesions. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1982; 165:33–42.
Article21. Arenzana-Seisdedos F, Barbey S, Virelizier JL, Kornprobst M, Nezelof C. Histiocytosis X. Purified (T6+) cells from bone granuloma produce interleukin 1 and prostaglandin E2 in culture. J Clin Invest. 1986; 77:326–9.
Article22. Marusić A, Raisz LG. Cortisol modulates the actions of interleukin-1 alpha on bone formation, resorption, and prostaglandin production in cultured mouse parietal bones. Endocrinology. 1991; 129:2699–706.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Langerhans Cell Histiocytosis Presenting as a Solitary Nodule
- Langerhans Cell Histiocytosis with Pancreatic Involvement: Imaging Findings Including Diffusion-Weighted Imaging
- A Case of Langerhans Cell Sarcoma Presenting as Submandibular Gland Mass
- Isolated Thymic Langerhans Cell Histiocytosis
- A Case of Letterer-Siwe Disease in Adult