Korean J Radiol.
2014 Apr;15(2):218-225. 10.3348/kjr.2014.15.2.218.
Hepatic Sinusoidal Obstruction Syndrome Caused by Herbal Medicine: CT and MRI Features
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiology, The First Affiliated Hospital, Zhejiang University School of Medicine, Hangzhou 310003, China.
- 2Department of Imaging and Interventional Radiology, The Chinese University of Hong Kong, Prince of Wales Hospital, Hong Kong SAR 999077, China.
- 3Department of Radiology, The Second Affiliated Hospital, Zhejiang University School of Medicine, Hangzhou 310009, China. zhangminming@zju.edu.cn
- KMID: 1705576
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2014.15.2.218
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
To describe the CT and MRI features of hepatic sinusoidal obstruction syndrome (HSOS) caused by herbal medicine Gynura segetum.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
The CT and MRI features of 16 consecutive Gynura segetum induced HSOS cases (12 men, 4 women) were analyzed. Eight patients had CT; three patients had MRI, and the remaining five patients had both CT and MRI examinations. Based on their clinical presentations and outcomes, the patients were classified into three categories: mild, moderate, and severe. The severity of the disease was also evaluated radiologically based on the abnormal hepatic patchy enhancement in post-contrast CT or MRI images.
RESULTS
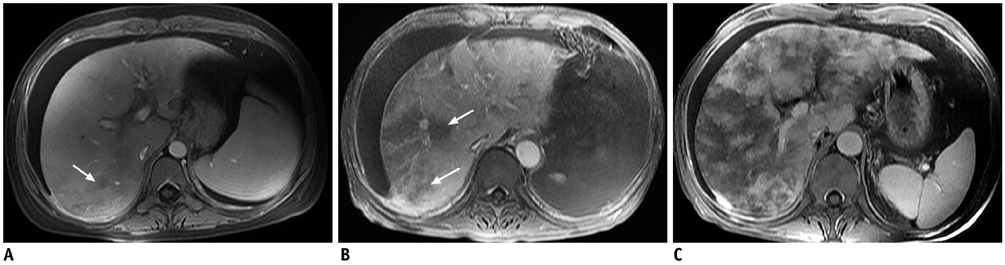
Ascites, patchy liver enhancement, and main right hepatic vein narrowing or occlusion were present in all 16 cases. Hepatomegaly and gallbladder wall thickening were present in 14 cases (87.5%, 14/16). Periportal high intensity on T2-weighted images was present in 6 cases (75%, 6/8). Normal liver parenchymal enhancement surrounding the main hepatic vein forming a clover-like sign was observed in 4 cases (25%, 4/16). The extent of patchy liver enhancement was statistically associated with clinical severity classification (kappa = 0.565).
CONCLUSION
Ascites, patchy liver enhancement, and the main hepatic veins narrowing were the most frequent signs of herbal medicine induced HSOS. The grade of abnormal patchy liver enhancement was associated with the clinical severity.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Adult
Aged
Ascites/diagnosis
Asteraceae/chemistry
Cholecystography
Female
Gallbladder/pathology
Hepatic Veins/pathology/radiography
Hepatic Veno-Occlusive Disease/chemically induced/*diagnosis
Hepatomegaly/diagnosis
Humans
*Magnetic Resonance Imaging
Male
Middle Aged
Phytotherapy/*adverse effects
Pyrrolizidine Alkaloids/adverse effects
Severity of Illness Index
*Tomography, X-Ray Computed
Young Adult
Pyrrolizidine Alkaloids
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Two Cases of Hepatic Sinusoidal Dilatation Mimicking Hepatic Metastases
Jong-Hoon Hyun, Yoo-Kyung Cho, Hyun-Joo Song, Eun-Kwang Choi, Chang-Lim Hyun, Jung-Mi Kwon, Bong-Soo Kim, Byung-Cheol Song
Korean J Gastroenterol. 2014;64(4):239-245. doi: 10.4166/kjg.2014.64.4.239.
Reference
-
1. Helmy A. Review article: updates in the pathogenesis and therapy of hepatic sinusoidal obstruction syndrome. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2006; 23:11–25.2. Wilmot FC, Robertson GW. Senecio disease, or cirrhosis of the liver due to senecio poisoning. Lancet. 1920; 196:848–849.3. Zuckerman M, Steenkamp V, Stewart MJ. Hepatic veno-occlusive disease as a result of a traditional remedy: confirmation of toxic pyrrolizidine alkaloids as the cause, using an in vitro technique. J Clin Pathol. 2002; 55:676–679.4. Kakar F, Akbarian Z, Leslie T, Mustafa ML, Watson J, van Egmond HP, et al. An outbreak of hepatic veno-occlusive disease in Western afghanistan associated with exposure to wheat flour contaminated with pyrrolizidine alkaloids. J Toxicol. 2010; 2010:313280.5. Ortiz Cansado A, Crespo Valadés E, Morales Blanco P, Sáenz de Santamaría J, González Campillejo JM, Ruiz Téllez T. [Veno-occlusive liver disease due to intake of Senecio vulgaris tea]. Gastroenterol Hepatol. 1995; 18:413–416.6. Kumar S, DeLeve LD, Kamath PS, Tefferi A. Hepatic veno-occlusive disease (sinusoidal obstruction syndrome) after hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Mayo Clin Proc. 2003; 78:589–598.7. Alpert LI. Veno-occlusive disease of the liver associated with oral contraceptives: case report and review of literature. Hum Pathol. 1976; 7:709–718.8. Fajardo LF, Colby TV. Pathogenesis of veno-occlusive liver disease after radiation. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 1980; 104:584–588.9. Lin G, Wang JY, Li N, Li M, Gao H, Ji Y, et al. Hepatic sinusoidal obstruction syndrome associated with consumption of Gynura segetum. J Hepatol. 2011; 54:666–673.10. Dai HF, Gao Y, Yang M, Yu CH, Gu ZY, Chen WX. Hepatic veno-occlusive disease induced by Gymura segetum: report of two cases. Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int. 2006; 5:406–408.11. Chen Z, Huo JR. Hepatic veno-occlusive disease associated with toxicity of pyrrolizidine alkaloids in herbal preparations. Neth J Med. 2010; 68:252–260.12. Jones RJ, Lee KS, Beschorner WE, Vogel VG, Grochow LB, Braine HG, et al. Venoocclusive disease of the liver following bone marrow transplantation. Transplantation. 1987; 44:778–783.13. McDonald GB, Sharma P, Matthews DE, Shulman HM, Thomas ED. Venocclusive disease of the liver after bone marrow transplantation: diagnosis, incidence, and predisposing factors. Hepatology. 1984; 4:116–122.14. Wu XW, Wang WQ, Liu B, Xu JM, Yu YQ, Zhang S, et al. Hepatic veno-occlusive disease after taking Gynura Rhizome: the value of multidetector computed tomography in diagnosing the disease and evaluating the clinical therapeutic effect. Hepatol Res. 2012; 42:304–309.15. van den Bosch MA, van Hoe L. MR imaging findings in two patients with hepatic veno-occlusive disease following bone marrow transplantation. Eur Radiol. 2000; 10:1290–1293.16. Dumont Ch, Lambert M, Van Beers BE. MR imaging findings in a patient with hepatic veno-occlusive disease. Acta Gastroenterol Belg. 2004; 67:236–238.17. Mortelé KJ, Van Vlierberghe H, Wiesner W, Ros PR. Hepatic veno-occlusive disease: MRI findings. Abdom Imaging. 2002; 27:523–526.18. Gao H, Li N, Wang JY, Zhang SC, Lin G. Definitive diagnosis of hepatic sinusoidal obstruction syndrome induced by pyrrolizidine alkaloids. J Dig Dis. 2012; 13:33–39.19. DeLeve LD, Valla DC, Garcia-Tsao G. Vascular disorders of the liver. Hepatology. 2009; 49:1729–1764.20. Danan G, Benichou C. Causality assessment of adverse reactions to drugs--I. A novel method based on the conclusions of international consensus meetings: application to drug-induced liver injuries. J Clin Epidemiol. 1993; 46:1323–1330.21. McDonald GB, Hinds MS, Fisher LD, Schoch HG, Wolford JL, Banaji M, et al. Veno-occlusive disease of the liver and multiorgan failure after bone marrow transplantation: a cohort study of 355 patients. Ann Intern Med. 1993; 118:255–267.22. Mahgerefteh SY, Sosna J, Bogot N, Shapira MY, Pappo O, Bloom AI. Radiologic imaging and intervention for gastrointestinal and hepatic complications of hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Radiology. 2011; 258:660–671.23. Gray H, Williams PL, Bannister LH. Gray's anatomy: the anatomical basis of medicine and surgery. 38th ed. New York: Churchill Livingstone;1995. p. 1902–1903.24. Sharma D, Deshmukh A, Raina VK. Surgical anatomy of retrohepatic inferior vena cava and hepatic veins: a quantitative assessment. Indian J Gastroenterol. 2001; 20:136–139.25. DeLeve LD, McCuskey RS, Wang X, Hu L, McCuskey MK, Epstein RB, et al. Characterization of a reproducible rat model of hepatic veno-occlusive disease. Hepatology. 1999; 29:1779–1791.26. Méresse V, Hartmann O, Vassal G, Benhamou E, Valteau-Couanet D, Brugieres L, et al. Risk factors for hepatic veno-occlusive disease after high-dose busulfan-containing regimens followed by autologous bone marrow transplantation: a study in 136 children. Bone Marrow Transplant. 1992; 10:135–141.27. Ayash LJ, Hunt M, Antman K, Nadler L, Wheeler C, Takvorian T, et al. Hepatic venoocclusive disease in autologous bone marrow transplantation of solid tumors and lymphomas. J Clin Oncol. 1990; 8:1699–1706.28. Erturk SM, Mortelé KJ, Binkert CA, Glickman JN, Oliva MR, Ros PR, et al. CT features of hepatic venoocclusive disease and hepatic graft-versus-host disease in patients after hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2006; 186:1497–1501.29. Ward J, Guthrie JA, Sheridan MB, Boyes S, Smith JT, Wilson D, et al. Sinusoidal obstructive syndrome diagnosed with superparamagnetic iron oxide-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging in patients with chemotherapy-treated colorectal liver metastases. J Clin Oncol. 2008; 26:4304–4310.30. Shin NY, Kim MJ, Lim JS, Park MS, Chung YE, Choi JY, et al. Accuracy of gadoxetic acid-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging for the diagnosis of sinusoidal obstruction syndrome in patients with chemotherapy-treated colorectal liver metastases. Eur Radiol. 2012; 22:864–871.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case Report of Localized Hepatic Sinusoidal Dilatation: The Diagnostic Usefulness of the Hepatobiliary Phase of Gd-EOB-DTPA-Enhanced Magnetic Resonance Imaging
- Budd-Chiari syndrome by membranous obstruction of inferior vena cava: comparison of sonography and computed tomography
- Budd-Chiari Syndrome: Right hepatic vein obstruction and incomplete IVC obstruction with azygos continuation of IVC
- Biomarkers for hepatic sinusoidal obstruction syndrome after hematopoietic cell transplantation
- Two Cases of Hepatic Sinusoidal Dilatation Mimicking Hepatic Metastases