J Korean Soc Spine Surg.
2007 Mar;14(1):17-24. 10.4184/jkss.2007.14.1.17.
A Comparison of Bone Mineral Density between Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis and Neuromuscular Scoliosis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Korea. haksunkim@yumc.yonsei.ac.kr
- 2Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Cha University College of Medicine, Korea.
- 3Department of Orthopaedic Surgery#, National Health Insurance Corporation Ilsan Hospital, Korea.
- KMID: 1527139
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4184/jkss.2007.14.1.17
Abstract
-
STUDY DESIGN: A Cross-sectional study
OBJECTIVE
This study evaluated the degree of osteoporosis of adolescent idiopathic scoliosis (AIS) and neuromuscular scoliosis (NMS) and compared bone mineral density. LITERATURE REVIEW: In osteoporosis, bone mineral density was not as dense even in the outer layer, and the cortex was thinner than normal. A larger screw doss not enhance the screw stability and can break the thin cortex in osteoporotic vertebrae.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
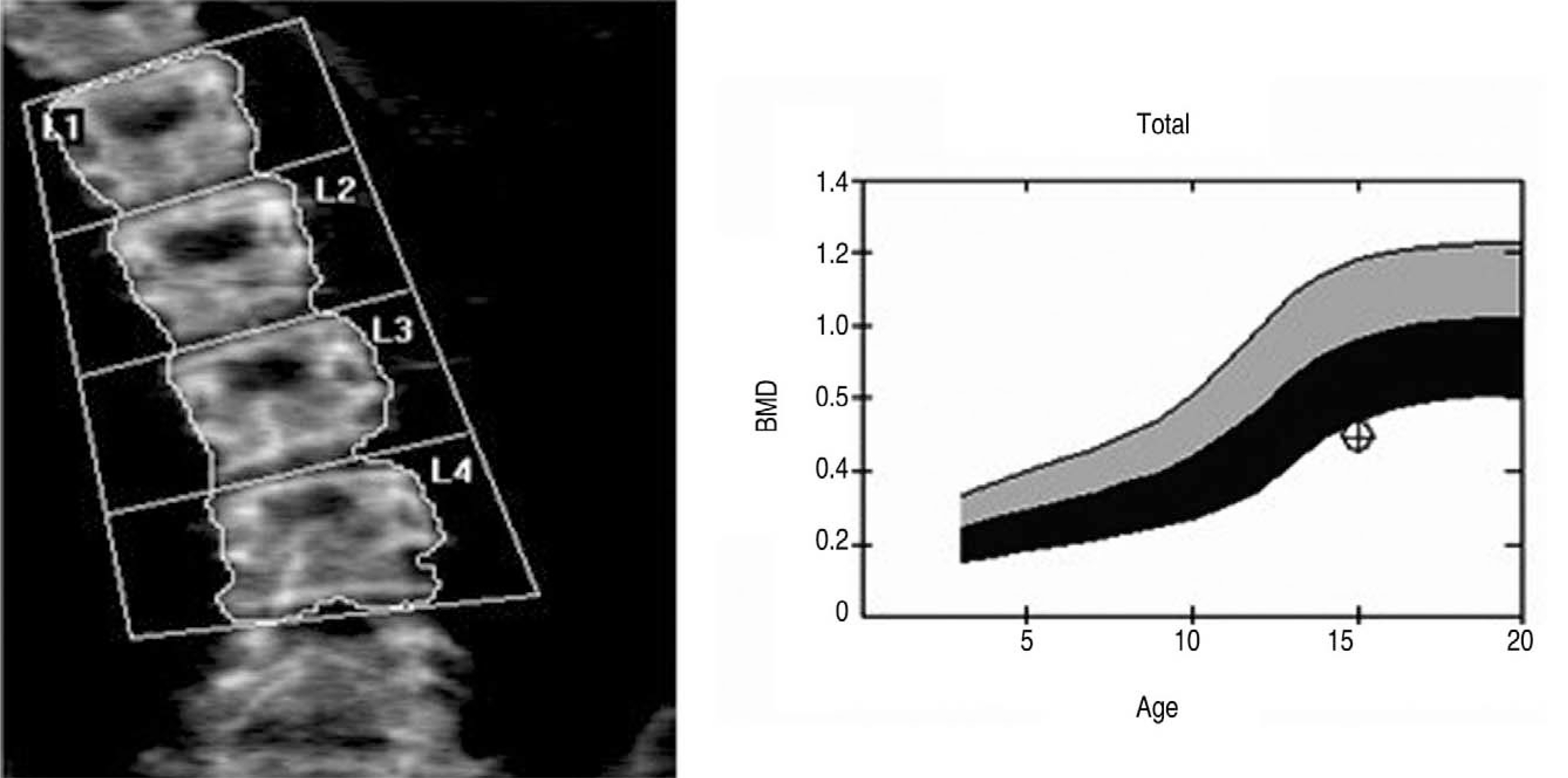
This study reviewed the cases of consecutive patients with scoliosis, who underwent an osteoporosis examination before surgery between August 2004 and June 2006. The osteoporosis examination included DEXA in lumbar vertebrae and proximal femur. The mean osteoporotic degree of both femurs was recorded. The data was analyzed using the BMD(bone mineral density, g/cm(2)) and Z value of the BMD according to age, gender, and ethnicity.
RESULTS
The mean degree of the coronal deformity was 48.4 in AIS and 62.9 in NMS. A comparison of both groups revealed a significantly lower BMD and Z value of Femur, and BMD of the vertebra in the NMS patients (p<0.05). A comparison between AIS and non-ambulant NMS showed that all parameters were significantly lower in the non-ambulant NMS (p<0.05). Neither the BMD and Z value of the AIS nor the NMS were associated with the severity of the spinal deformity.
CONCLUSION
A lower BMD was measured in patients with non ambulant NMS than AIS. The degree of the osteoporosis, particularly of the non ambulant NMS patients need to be considered before undergoing surgery.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1). Suk SI, Kim WJ, Lee SM, Kim JH, Chung ER. Thoracic pedicle screw fixation in spinal deformities: are they really safe? Spine. 2001; 26:2049–2057.2). Suk SI, Lee CK, Kim WJ, Chung YJ, Park YB. Segmental pedicle screw fixation in the treatment of thoracic idiopathic scoliosis. Spine. 1995; 20:1399–1405.
Article3). Teli M, Elsebaie H, Biant L, Noordeen H. Neuromuscular scoliosis treated by segmental third-generation instrumented spinal fusion. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2005; 18:430–438.
Article4). Wimmer C, Wallnofer P, Walochnik N, Krismer M, Saraph V. Comparative evaluation of luque and isola instrumentation for treatment of neuromuscular scoliosis. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2005; 439:181–192.
Article5). Cheng JC, Qin L, Cheung CS, et al. Generalized low areal and volumetric bone mineral density in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. J Bone Miner Res. 2000; 15:1587–1595.
Article6). Cheng JC, Guo X, Sher AH. Persistent osteopenia in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis: a longitudinal followup study. Spine. 1999; 24:1218–1222.7). Aparicio LF, Jurkovic M, DeLullo J. Decreased bone density in ambulatory patients with duchenne muscular dystrophy. J Pediatr Orthop. 2002; 22:179–181.
Article8). Vestergaard P, Glerup H, Steffensen BF, Rejnmark L, Rahbek J, Moseklide L. Fracture risk in patients with muscular dystrophy and spinal muscular atrophy. J Rehabil Med. 2001; 33:150–155.
Article9). Quinlivan R, Roper H, Davie M, Shaw NJ, McDonagh J, Bushby K. Report of a Muscular Dystrophy Campaign funded workshop Birmingham, UK, January 16th 2004. Osteoporosis in Duchenne muscular dystrophy; its prevalence, treatment and prevention. Neuromuscul Disord. 2005; 15:72–79.
Article10). Tan JS, Kwon BK, Dvorak MF, Fisher CG, Oxland TR. Pedicle screw motion in the osteoporotic spine after augmentation with laminar hooks, sublaminar wires, or calcium phosphate cement: a comparative analysis. Spine. 2004; 29:1723–1730.
Article11). Hasegawa K, Takahashi HE, Uchiyama S, et al. An experimental study of a combination method using a pedicle screw and laminar hook for the osteoporotic spine. Spine. 1997; 22:958–962.
Article12). Velis KP, Healey JH, Schneider R. Peak skeletal mass assessment in young adults with idiopathic scoliosis. Spine. 1989; 14:706–711.
Article13). Doyle F, Brown J, Lachance C. Relation between bone mass and muscle weight. Lancet. 1970; 21:391–393.
Article14). Larson CM, Henderson RC. Bone mineral density and fractures in boys with Duchenne muscular dystrophy. J Pediatr Orthop. 2000; 20:71–74.
Article15). McDonald DG, Kinali M, Gallagher AC, et al. Fracture prevalence in Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Dev Med Child Neurol. 2002; 44:695–698.
Article16). Hirano T, Hasegawa K, Takahashi HE, et al. Structural characteristics of the pedicle and its role in screw stability. Spine. 1997; 22:2504–2509.
Article17). Brantley AGU, Mayfield JK, Koeneman JB, Clark KR. The effects of pedicle screw fit. Spine. 1994; 19:1752–1758.
Article18). Halvorson TL, Kelley LA, Thomas KA, Whitecloud TS 3rd, Cook SD. Effects of bone mineral density on pedicle screw fixation. Spine. 1994; 19:2415–2420.
Article19). Kim NH, Lee HM, Lee WS. The effect of bone mineral density on instrumented spine fusion. J Kor Soc Spine Surg. 1994; 1:133–139.20). Okuyama K, Abe E, Suzuki T, Tamura Y, Chiba M, Sato K. Influence of bone mineral density on pedicle screw fixation: a study of pedicle screw fixation augmenting posterior lumbar interbody fusion in elderly patients. Spine J. 2001; 1:402–407.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Body Mass Index and Bone Mineral Densityin Patients with Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis
- Evaluation of Bone Mineral Status in Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis
- The Classification of Idiopathic Scoliosis
- Medical genomic approach to early-onset scoliosis
- Etiology of Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis: A Literature Review