Electrolyte Blood Press.
2011 Jun;9(1):32-37. 10.5049/EBP.2011.9.1.32.
Orthorexia Nervosa with Hyponatremia, Subcutaneous Emphysema, Pneumomediastimum, Pneumothorax, and Pancytopenia
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Nephrology, Department of Internal Medicine, Korea University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. yjkwon@korea.ac.kr
- KMID: 1497140
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5049/EBP.2011.9.1.32
Abstract
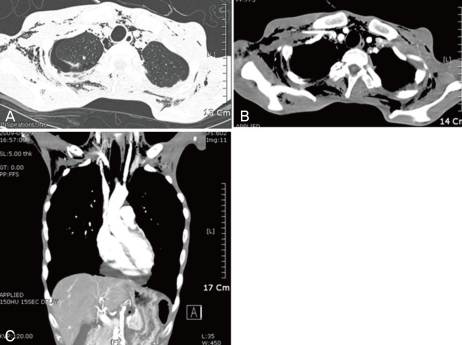
- 30-year-old male was admitted with general weakness and drowsy mental status. He had eaten only 3-4 spoons of brown rice and fresh vegetable without salt for 3 months to treat his tic disorder, and he had been in bed-ridden state. He has had weight loss of 14 kg in the last 3 months. We report a patient with orthorexia nervosa who developed hyponatremia, metabolic acidosis, subcutaneous emphysema, mediastinal emphysema, pneumothorax, and pancytopenia and we will review the literature. Also, we mention to prevent refeeding syndrome, and to start and maintain feeding in malnourished patients.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Kummer A, Dias FM, Teixeira AL. On the concept of orthorexia nervosa. Scand J Med Sci Sports. 2008; 18:395–396. author reply 397. PMID: 18435688.
Article2. Bahia A, Chu ES, Mehler PS. Polydipsia and hyponatremia in a woman with anorexia nervosa. Int J Eat Disord. 2011; 44:186–188. PMID: 20127934.
Article3. Luthra M, Davids MR, Shafiee MA, Halperin ML. Anorexia nervosa and chronic renal insufficiency: a prescription for disaster. QJM. 2004; 97:167–178. PMID: 14976274.
Article4. Danzer G, Mulzer J, Weber G, Lembke A, Kocalevent R, Klapp BF. Advanced anorexia nervosa, associated with pneumomediastinum, pneumothorax, and soft-tissue emphysema without esophageal lesion. Int J Eat Disord. 2005; 38:281–284. PMID: 16211634.
Article5. Fukudo S, Tanaka A, Muranaka M, et al. Case report: reversal of severe leukopenia by granulocyte colony-stimulating factor in anorexia nervosa. Am J Med Sci. 1993; 305:314–317. PMID: 7683451.
Article6. Marinella MA. Refeeding syndrome: an important aspect of supportive oncology. J Support Oncol. 2009; 7:11–16. PMID: 19278172.7. Miller KK, Grinspoon SK, Ciampa J, Hier J, Herzog D, Klibanski A. Medical findings in outpatients with anorexia nervosa. Arch Intern Med. 2005; 165:561–566. PMID: 15767533.
Article8. Amann B, Schafer M, Sterr A, Arnold S, Grunze H. Central pontine myelinolysis in a patient with anorexia nervosa. Int J Eat Disord. 2001; 30:462–466. PMID: 11746309.
Article9. Trimarchi H, Gonzalez J, Olivero J. Hyponatremia-associated rhabdomyolysis. Nephron. 1999; 82:274–277. PMID: 10396001.
Article10. Mehanna HM, Moledina J, Travis J. Refeeding syndrome: what it is, and how to prevent and treat it. BMJ. 2008; 336:1495–1498. PMID: 18583681.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Pneumoperitoneum Associated with Pneumomediastinum, Pneumothorax, Subcutaneous Empysema during Intubation and Positive Ventilation
- A Facial Subcutaneous Emphysema after Using a Fish Cake Skewer: Case Report
- Spontaneous Pneumomediastinum: An Unusual Pulmonary Complication in Anorexia Nervosa
- Pneumothorax, Pneumomediastinum, Subcutaneous Emphysema, Pneumoretroperitoneum Secondary to Colonoscopic Perforation
- Pneumoperitoneum from Subcutaneous Emphysema after Blunt Chest Injury