Tuberc Respir Dis.
2013 Apr;74(4):177-180. 10.4046/trd.2013.74.4.177.
Bronchogenic Cyst Rupture and Pneumonia after Endobronchial Ultrasound-Guided Transbronchial Needle Aspiration: A Case Report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine, Department of Medicine, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. sangwonum@skku.edu
- 2Division of Pulmonary Medicine, Department of Medicine, Samsung Changwon Hospital, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Changwon, Korea.
- KMID: 1495858
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4046/trd.2013.74.4.177
Abstract
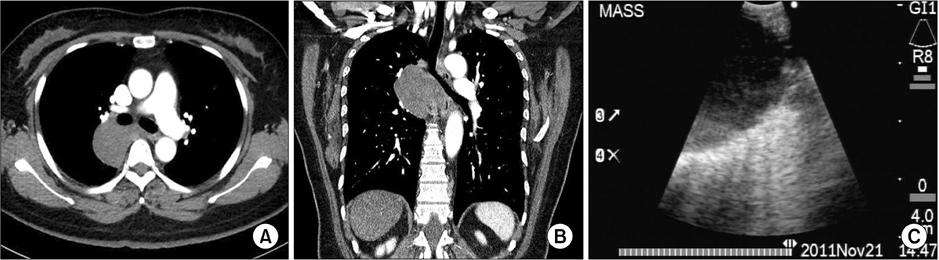
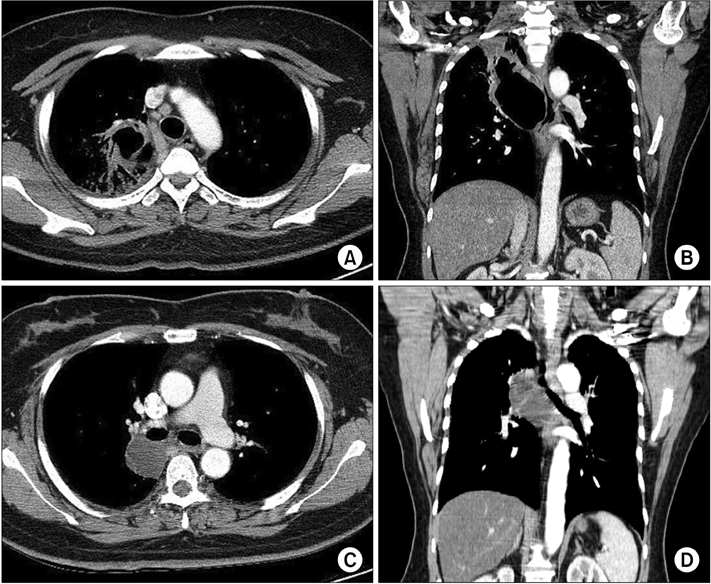
- We report a 54-year-old woman who presented with a well-defined, homogeneous, and non-enhancing mass in the retrobronchial region of the bronchus intermedius. The patient underwent endobronchial ultrasound-guided transbronchial needle aspiration (EBUS-TBNA) for histological confirmation. Serous fluid was aspirated by EBUS-TBNA. Cytological examination identified an acellular smear with negative microbiological cultures. The patient was finally diagnosed with bronchogenic cysts by chest computed tomography (CT) and EBUS-TBNA findings. However, 1 week after EBUS-TBNA, the patient developed bronchogenic cyst rupture and pneumonia. Empirical antibiotics were administered, and pneumonia from the bronchogenic cyst rupture had resolved on follow-up chest CT. To our knowledge, this is the first reported case of pneumonia from bronchogenic cyst rupture after EBUS-TBNA.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Varela-Lema L, Fernandez-Villar A, Ruano-Ravina A. Effectiveness and safety of endobronchial ultrasound-transbronchial needle aspiration: a systematic review. Eur Respir J. 2009. 33:1156–1164.2. Takeda S, Miyoshi S, Minami M, Ohta M, Masaoka A, Matsuda H. Clinical spectrum of mediastinal cysts. Chest. 2003. 124:125–132.3. St-Georges R, Deslauriers J, Duranceau A, Vaillancourt R, Deschamps C, Beauchamp G, et al. Clinical spectrum of bronchogenic cysts of the mediastinum and lung in the adult. Ann Thorac Surg. 1991. 52:6–13.4. Suen HC, Mathisen DJ, Grillo HC, LeBlanc J, McLoud TC, Moncure AC, et al. Surgical management and radiological characteristics of bronchogenic cysts. Ann Thorac Surg. 1993. 55:476–481.5. Kanemitsu Y, Nakayama H, Asamura H, Kondo H, Tsuchiya R, Naruke T. Clinical features and management of bronchogenic cysts: report of 17 cases. Surg Today. 1999. 29:1201–1205.6. Sarper A, Ayten A, Golbasi I, Demircan A, Isin E. Bronchogenic cyst. Tex Heart Inst J. 2003. 30:105–108.7. Aktogu S, Yuncu G, Halilcolar H, Ermete S, Buduneli T. Bronchogenic cysts: clinicopathological presentation and treatment. Eur Respir J. 1996. 9:2017–2021.8. McAdams HP, Kirejczyk WM, Rosado-de-Christenson ML, Matsumoto S. Bronchogenic cyst: imaging features with clinical and histopathologic correlation. Radiology. 2000. 217:441–446.9. Anantham D, Phua GC, Low SY, Koh MS. Role of endobronchial ultrasound in the diagnosis of bronchogenic cysts. Diagn Ther Endosc. 2011. 2011:468237.10. Nakajima T, Yasufuku K, Shibuya K, Fujisawa T. Endobronchial ultrasound-guided transbronchial needle aspiration for the treatment of central airway stenosis caused by a mediastinal cyst. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2007. 32:538–540.11. Galluccio G, Lucantoni G. Mediastinal bronchogenic cyst's recurrence treated with EBUS-FNA with a long-term follow-up. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2006. 29:627–629.12. Haas AR. Infectious complications from full extension endobronchial ultrasound transbronchial needle aspiration. Eur Respir J. 2009. 33:935–938.13. Parker KL, Bizekis CS, Zervos MD. Severe mediastinal infection with abscess formation after endobronchial ultrasound-guided transbrochial needle aspiration. Ann Thorac Surg. 2010. 89:1271–1272.14. Moffatt-Bruce SD, Ross P Jr. Mediastinal abscess after endobronchial ultrasound with transbronchial needle aspiration: a case report. J Cardiothorac Surg. 2010. 5:33.15. Huang CT, Chen CY, Ho CC, Yu CJ. A rare constellation of empyema, lung abscess, and mediastinal abscess as a complication of endobronchial ultrasound-guided transbronchial needle aspiration. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2011. 40:264–265.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Technical Aspects of Endobronchial Ultrasound-Guided Transbronchial Needle Aspiration
- Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma Diagnosed by Endobronchial Ultrasound-Guided Transbronchial Needle Aspiration
- Is there enough support for endobronchial ultrasound-guided transbronchial needle aspiration as an initial diagnostic tool?
- The First Pediatric Case of Intrathoracic Tuberculosis Lymphadenitis Diagnosed by Endobronchial Ultrasound Guided Transbronchial Needle Aspiration
- A Case of Pulmonary Cryptococcosis Mimicking Bronchogenic Lung Cancer in an Immunocompetent Patient: A Review of the Literature