J Korean Soc Spine Surg.
2008 Mar;15(1):18-22. 10.4184/jkss.2008.15.1.18.
The Usefulness of Bone Scan in the Osteoporotic Vertebral Compression Fracture Patients Treated With Kyphoplasty
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Gil Medical Center, Gacheon Medical University, Korea. shinwj72@gilhospital.com
- KMID: 1482839
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4184/jkss.2008.15.1.18
Abstract
-
STUDY DESIGN: Retrospective study.
OBJECTIVES
To compare the clinical results of kyphoplasty between osteoporotic patients with compression fractures and rib hot uptake on bone scan and patients without rib hot uptake. SUMMARY OF LITERATURE REVIEW: The incidence of osteoporotic rib fractures is 0.3% in postmenopausal women.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Between July 2005 and July 2006, 72 kyphoplasties for osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures were performed, and all patients had a bone scan study. On bone scan study, 41 patients (57.7%) had hot uptake in their ribs. Results were assessed by visual analog scale (VAS).
RESULTS
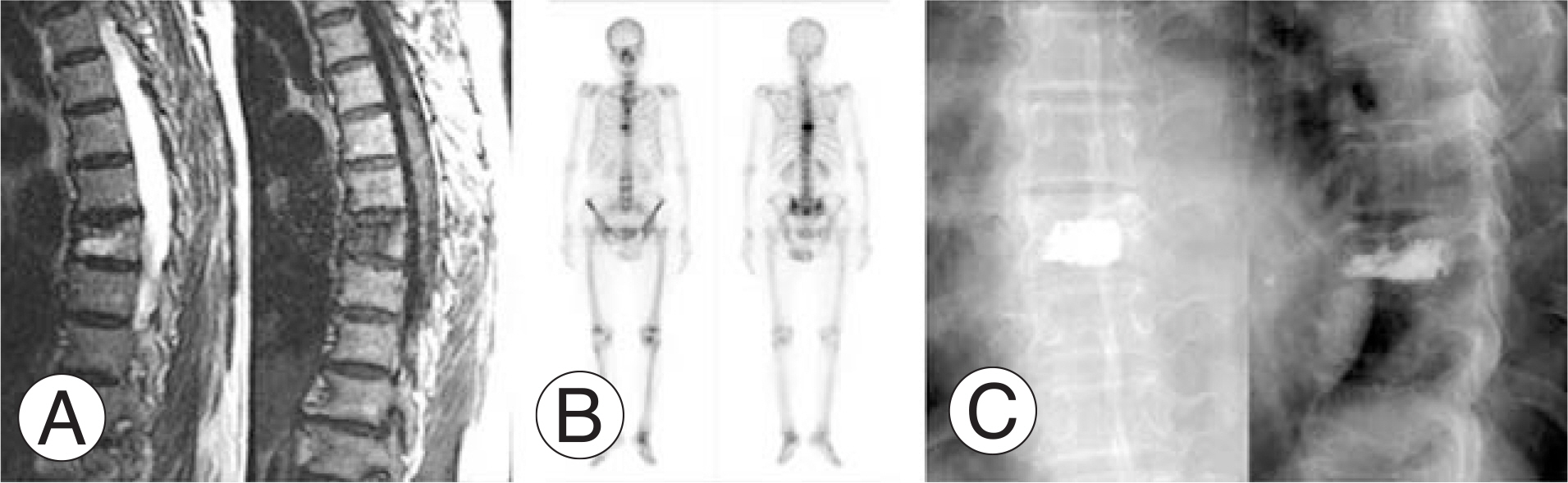
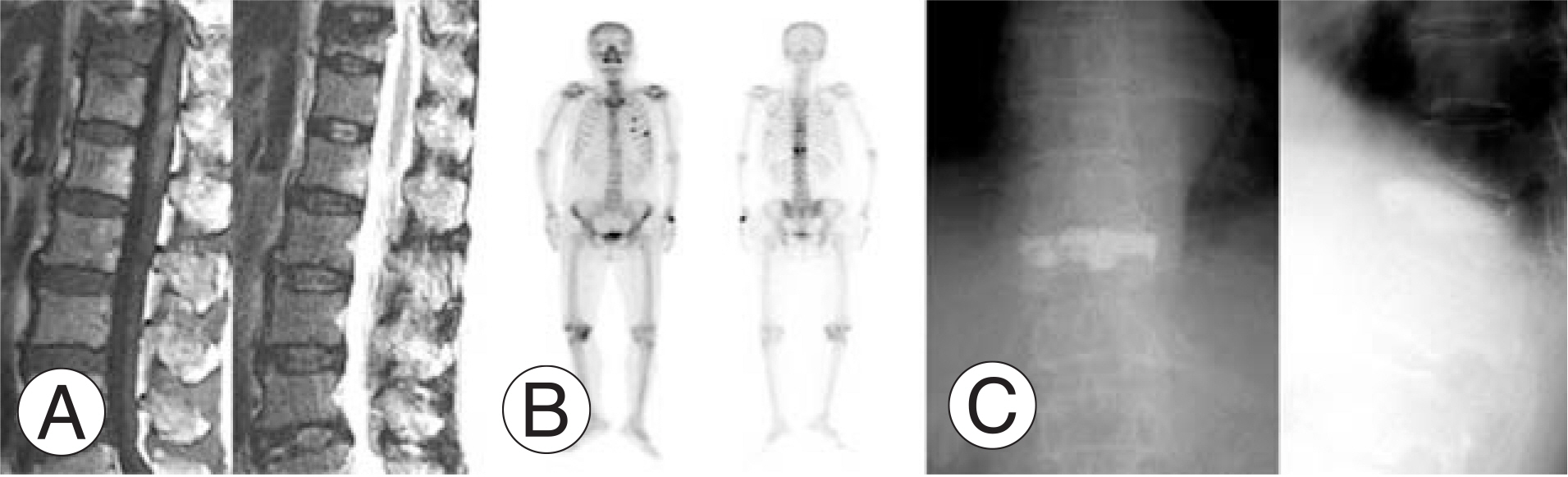
The incidence of hot uptake was 67.8% in thoracic fractures, 40.0% in lumbar fractures, and 72.7% in thoracolumbar fractures. Hot uptake was significantly more common with thoracic and thoracolumbar fractures than with lumbar fractures (p<0.05). The incidence of hot uptake was 49.1% in one- and two-level fractures and 84.6% in over three-level fractures. This finding demonstrated significant difference between the two groups (p<0.05). The mean VAS scores for all cases were 8.2/3.4/3.2 at preoperative/immediate postoperative/after 3 months, respectively. In thoracic fractures, they were 8.2/3.9/3.1; lumbar fractures 8.0/3.2/3.1; and thoracolumbar fractures 8.3/3.7/3.0, respectively. The immediate postoperative VAS score in lumbar fractures was better than in thoracic fractures (p<0.05). The VAS scores in thoracic fractures with hot uptake were 8.3/4.1/3, and those without hot uptake were 7.8/2.8/3.0. The immediate VAS score in thoracic fractures without hot uptake was better than in those with hot uptake (p>0.05).
CONCLUSIONS
Thoracic and multiple osteoporotic compression fractures are often accompanied by rib fractures. Bone scan is a useful tool to detect rib fractures and predict the prognosis of kyphoplasty.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Vertebral Recompression after Vertebroplasty or Kyphoplasty
Deuk Soo Jun, Do Hyun Moon, Young Kyu Ko, Jang Seok Choi, Byoung Keun An, Je Won Paik, Min Ho Park
J Korean Fract Soc. 2015;28(2):110-117. doi: 10.12671/jkfs.2015.28.2.110.
Reference
-
1). Delmas PD. Treatment of postmenopausal osteoporosis. Lancet. 2002; 359:2018–2026.
Article2). Carolyn Becker. Clinical evaluation for osteoporosis. Clin Geriatr Med. 2003; 19:299–320.3). Deng HW, Chen WM, Recker S, et al. Genetic determination of Colles' fracture and differential bone mass in women with and without Colles' fracture. J Bone Miner Res. 2000; 15:1243–1252.
Article4). Lindsay R, Silverman SL, Cooper C, et al. Risk of new vertebral fracture in the year following a fracture. JAMA. 2001; 285:320–323.
Article5). Melton III LJ, Atkinson EJ, Cooper C, O'Fallon WM. Rigg BL. Vertebral fractures predict subsequent fractures. Osteoporos Int. 1999; 10:214–221.
Article6). Rho SM, Jung JY, Yoon TL, Lee JJ. An epidemiological study of hip fracture A comparison between 1991 and 2001. Korean Journal of Bone Metabolism. 2003; 10:109.7). Chakravarty D, Sloan J, Brenchley J. Risk reduction through skeletal scintigraphy as a screening tool in suspected scaphoid fracture. Emerg Med J. 2002; 19:507–509.8). Donohoe KJ, Henkin RE, Royal HD, et al. Procedure guideline for bone scintigraphy. J Nucl Med. 1999; 37:1903–1906.9). Phillips FM. Minimally invasive treatments of osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures. Spine. 2003; 28:45–53.
Article10). Ryu KS, Park CK, Kim MC, Kang JK. Dose dependent epidural leakage of polymethylmethacrylate after percutaneous vertebroplasty in patients with osteoporotic vertebral compression fracture. J Neurosurg Spine. 2002; 96:56–61.11). Diamond TH, Champion B, Clark WA. Management of Acute Osteoporotic Vertebral Fractures: A Nonrandom-ized Trial Comparing Percutaneous Vertebroplasty with Conservative Therapy. The American Journal of Medicine. 2003; 114:257–265.
Article12). Kelsey JL, Keegan TH, Prill MM, Quesenberry CP, Sidney S. Risk factors for fracture of the shafts of the tibia and fibula in older individuals. Osteoporos Int. 2006; 17:143–149.
Article13). James Roberts. Clinical Procedures in Emergency Medicine. 4th ed. Saunders: Elsevier;p. 1231. 2004.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Spontaneous Short Term Interval New Developed Multiple Adjacent Osteoporotic Lumbar Compression Fracture after Kyphoplasty
- Acute New Compression Fractures of Consecutive Vertebral Bodies Adjacent to the Previously Augmented Level with Kyphoplasty
- Asymptomatic Pulmonary Embolus Following Percutaneous Kyphoplasty: A Case Report
- Spontaneous Height Restoration of Vertebral Compression Fracture: A Case Report
- Minimally Invasive Treatment of Painful Osteoporotic Vertebral Fractures