Korean J Radiol.
2013 Apr;14(2):384-388. 10.3348/kjr.2013.14.2.384.
Pulmonary Mucinous Cystadenocarcinoma: Report a Case and Review of CT Findings
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiology and Center for Imaging Science, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul 135-710, Korea. hoyunlee96@gmail.com
- 2Department of Nuclear Medicine, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul 135-710, Korea.
- 3Department of Pathology, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul 135-710, Korea.
- 4Department of Thoracic & Cardiovascular Surgery, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul 135-710, Korea.
- 5Division of Respiratory and Critical Medicine of the Department of Internal Medicine, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul 135-710, Korea.
- KMID: 1482803
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2013.14.2.384
Abstract
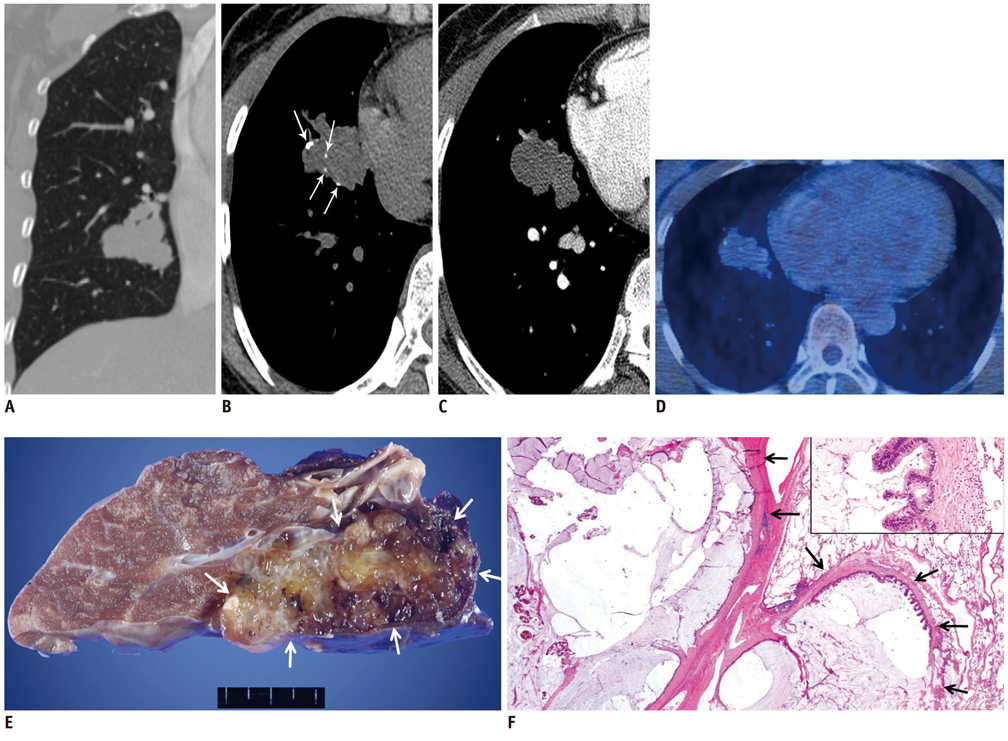
- A pulmonary mucinous cystadenocarcinoma is an extremely rare tumor that is considered to be a cystic variant of mucin-producing lung adenocarcinoma. We present a case of pulmonary mucinous cystadenocarcinoma in a 54-year-old woman. Chest CT scans showed a 4.3-cm-sized, lobulated, well-defined, and homogeneous mass in the right middle lobe with peripheral stippled calcifications that demonstrated low-attenuation with no enhancement after contrast administration; 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) PET/CT demonstrated mild heterogeneous FDG uptake. The mass was diagnosed as adenocarcinoma with mucin production by transbronchial lung biopsy. Right middle lobectomy was performed, and the pathologic examination disclosed a pulmonary mucinous cystadenocarcinoma.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Cystadenocarcinoma, Mucinous/pathology/*radiography/surgery
Diagnosis, Differential
Female
Fluorodeoxyglucose F18/diagnostic use
Humans
Lung Neoplasms/pathology/*radiography/surgery
Middle Aged
Positron-Emission Tomography and Computed Tomography
Radiopharmaceuticals/diagnostic use
Tomography, X-Ray Computed/*methods
Radiopharmaceuticals
Fluorodeoxyglucose F18
Figure
Reference
-
1. Chhieng DC. Fine-needle aspiration cytology of pulmonary mucinous cystadenocarcinoma. Diagn Cytopathol. 2008. 36:581–585.2. Beasley MB, Brambilla E, Travis WD. The 2004 World Health Organization classification of lung tumors. Semin Roentgenol. 2005. 40:90–97.3. Tsuta K, Ishii G, Nitadori J, Murata Y, Kodama T, Nagai K, et al. Comparison of the immunophenotypes of signet-ring cell carcinoma, solid adenocarcinoma with mucin production, and mucinous bronchioloalveolar carcinoma of the lung characterized by the presence of cytoplasmic mucin. J Pathol. 2006. 209:78–87.4. Gao ZH, Urbanski SJ. The spectrum of pulmonary mucinous cystic neoplasia: a clinicopathologic and immunohistochemical study of ten cases and review of literature. Am J Clin Pathol. 2005. 124:62–70.5. Iwasaki T, Kawahara K, Nagano T, Nakagawa K. Pulmonary mucinous cystadenocarcinoma: an extremely rare tumor presenting as a cystic lesion of the lung. Gen Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2007. 55:143–146.6. Sánchez-Carpintero Abad M, Tamura Ezcurra MA, de Torres Tajes JP. Primary pulmonary mucinous cystadenocarcinoma: presentation of a case and a review of the literature. Arch Bronconeumol. 2011. 47:216–217.7. Sezer O, Hoffmeier A, Bettendorf O, Franzius C, Semik M, Schmid C, et al. Mucinous cystadenocarcinoma--an extremely rare tumor in a young patient. Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2006. 54:216–217.8. Efstathiou A, Asteriou C, Barbetakis N, Miliaras D, Kleontas A, Karvelas C, et al. Primary pulmonary mucinous cystadenocarcinoma: a case report. Case Rep Med. 2011. 2011:562026.9. Raza SA, Alexakis C, Creagh M, Lawrence DR, Wood M. Primary pulmonary mucinous cystadenocarcinoma presenting as a complex bronchocele: a case report. J Med Case Rep. 2009. 3:8581.10. Berger KL, Nicholson SA, Dehdashti F, Siegel BA. FDG PET evaluation of mucinous neoplasms: correlation of FDG uptake with histopathologic features. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2000. 174:1005–1008.11. Rossi G, Murer B, Cavazza A, Losi L, Natali P, Marchioni A, et al. Primary mucinous (so-called colloid) carcinomas of the lung: a clinicopathologic and immunohistochemical study with special reference to CDX-2 homeobox gene and MUC2 expression. Am J Surg Pathol. 2004. 28:442–452.12. Wynveen C, Behmaram B, Haasler G, Rao N. Diverse histologic appearances in pulmonary mucinous cystic neoplasia: a case report. J Med Case Rep. 2008. 2:312.13. Maeda R, Isowa N, Onuma H, Miura H. Primary pulmonary mucinous (colloid) adenocarcinoma. Gen Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2008. 56:195–198.14. Lee HY, Lee KS, Han J, Kim BT, Cho YS, Shim YM, et al. Mucinous versus nonmucinous solitary pulmonary nodular bronchioloalveolar carcinoma: CT and FDG PET findings and pathologic comparisons. Lung Cancer. 2009. 65:170–175.15. Ishibashi H, Moriya T, Matsuda Y, Sado T, Hoshikawa Y, Chida M, et al. Pulmonary mucinous cystadenocarcinoma: report of a case and review of the literature. Ann Thorac Surg. 2003. 76:1738–1740.16. Butnor KJ, Sporn TA, Dodd LG. Fine needle aspiration cytology of mucinous cystadenocarcinoma of the lung: report of a case with radiographic and histologic correlation. Acta Cytol. 2001. 45:779–783.17. Tangthangtham A, Chonmaitri I, Tungsagunwattana S, Charupatanapongse U. Mucinous cystadenocarcinoma of the lung. J Med Assoc Thai. 1998. 81:794–798.18. Gaeta M, Blandino A, Scribano E, Ascenti G, Minutoli F, Pandolfo I. Mucinous cystadenocarcinoma of the lung: CT-pathologic correlation in three cases. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 1999. 23:641–643.19. Mann GN, Wilczynski SP, Sager K, Grannis FW Jr. Recurrence of pulmonary mucinous cystic tumor of borderline malignancy. Ann Thorac Surg. 2001. 71:696–697.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumor of the Appendix Mimicking a Mucinous Cystadenocarcinoma: A Case Report
- Primary Retroperitoneal Mucinous Cystadenocarcioma Involving the Splenic Hilum
- Mucinous cystadenocarcinoma of ovary with metastasis in 14-year-old girl
- A case of small cell carcinoma of pulmonary type of ovary associated with huge mucinous cystadenocarcinoma
- A Case of Ovarian Mucinous Cystadenocarcinoma with Mural Nodule of Anaplastic Carcinoma