J Korean Endocr Soc.
2009 Mar;24(1):17-24. 10.3803/jkes.2009.24.1.17.
Expression of miRNA 146a/b, 221 and 222 in Thyroid Cancer
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Chungnam National University Hospital, Korea.
- 2Department of Surgery, Chungnam National University Hospital, Korea.
- KMID: 1468491
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3803/jkes.2009.24.1.17
Abstract
-
BACKGROUND: miRNAs can be diagnostic markers and therapeutic targets in cancers, but few studies have been conducted in thyroid cancer. We investigated the expression levels of miRNA 146a/b, 221, and 222 which are important miRNAs in papillary thyroid cancers (PTCa), and verified their impact on clinicopathological factors.
METHODS
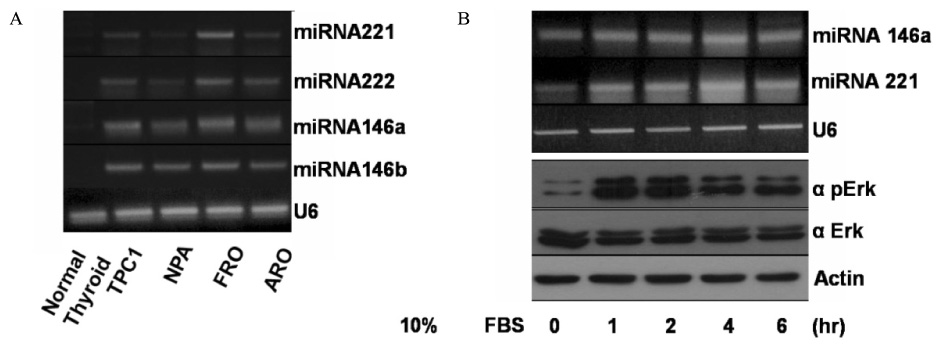
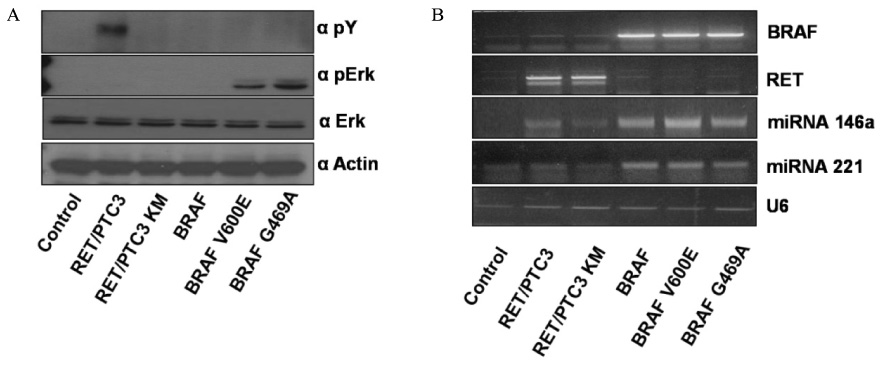
We measured the expression of pre-miRNAs 146a/b, 221, and 222 in NPA cells treated with 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS) or in HEK293T cells transfected with RET/PTC3 or BRAFV600E expression vectors. We also investigated the relationship between miRNA expression levels in thyroid cancer tissue specimens and clinicopathological parameters.
RESULTS
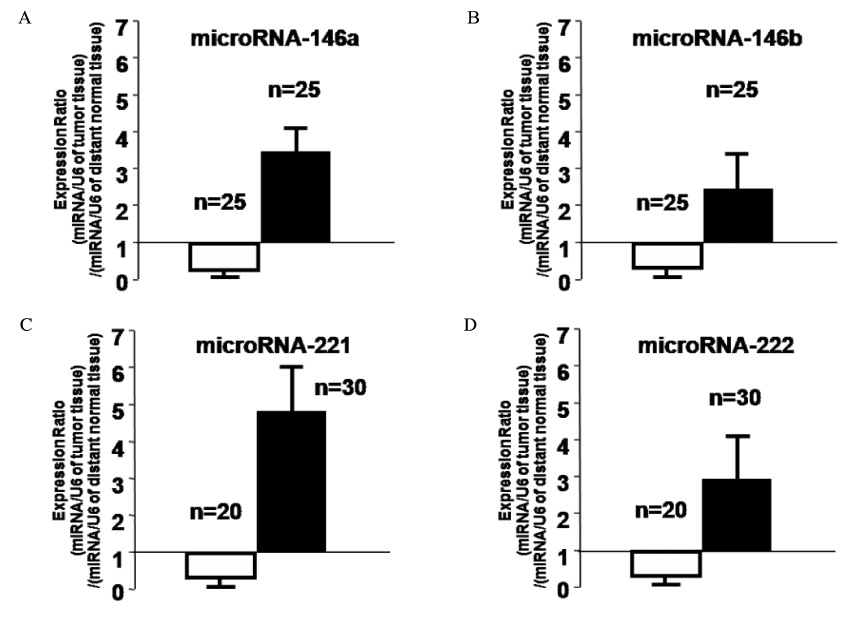
Growth stimulation with 10% FBS induced miRNA expressions in NPA cells, and transfection of RET/PTC3 and BRAFV600E also increased the expression of these miRNAs in HEK293T cells. Most (25 cases; 50%) of PTCa showed increased expression of miRNA-146a/b and 30 cases (60%) had elevated expression of miRNA-221 and miRNA-222 compared to normal thyroid samples from the contralateral lobe. However, increased miRNA expression did not correlate with clinicopathological factors.
CONCLUSION
Expression of miRNA 146a/b, 221, and 222 was increased by BRAFV600E and RET/PTC3 rearrangement and might have a role in tumorigenesis in PTCa. However, expression levels of these miRNAs did not correlate with clinicopathological parameters of patients with PTCa.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Lee RC, Feinbaum RL, Ambros V. The C. elegans heterochronic gene lin-4 encodes small RNAs with antisense complementarity to lin-14. Cell. 1993. 75:843–854.2. Wightman B, Ha I, Ruvkun G. Posttranscriptional regulation of the heterochronic gene lin-14 by lin-4 mediates temporal pattern formation in C. elegans. Cell. 1993. 75:855–862.3. Griffiths-Jones S, Grocock RJ, van Dongen S, Bateman A, Enright AJ. miRBase: microRNA sequences, targets and gene nomenclature. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006. 34:D140–D144.4. Zeng Y. Principles of micro-RNA production and maturation. Oncogene. 2006. 25:6156–6162.5. Hammond SM, Boettcher S, Caudy AA, Kobayashi R, Hannon GJ. Argonaute2, a link between genetic and biochemical analyses of RNAi. Science. 2001. 293:1146–1150.6. Cerutti H, Casas-Mollano JA. On the origin and functions of RNA-mediated silencing: from protists to man. Curr Genet. 2006. 50:81–99.7. Chen CZ. MicroRNAs as oncogenes and tumor suppressors. N Engl J Med. 2005. 353:1768–1771.8. Esquela-Kerscher A, Slack FJ. Oncomirs - microRNAs with a role in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 2006. 6:259–269.9. Lu J, Getz G, Miska EA, Alvarez-Saavedra E, Lamb J, Peck D, Sweet-Cordero A, Ebert BL, Mak RH, Ferrando AA, Downing JR, Jacks T, Horvitz HR, Golub TR. MicroRNA expression profiles classify human cancers. Nature. 2005. 435:834–838.10. Takamizawa J, Konishi H, Yanagisawa K, Tomida S, Osada H, Endoh H, Harano T, Yatabe Y, Nagino M, Nimura Y, Mitsudomi T, Takahashi T. Reduced expression of the let-7 microRNAs in human lung cancers in association with shortened postoperative survival. Cancer Res. 2004. 64:3753–3756.11. Iorio MV, Ferracin M, Liu CG, Veronese A, Spizzo R, Sabbioni S, Magri E, Pedriali M, Fabbri M, Campiglio M, Menard S, Palazzo JP, Rosenberg A, Musiani P, Volinia S, Nenci I, Calin GA, Querzoli P, Negrini M, Croce CM. MicroRNA gene expression deregulation in human breast cancer. Cancer Res. 2005. 65:7065–7070.12. Voorhoeve PM, le Sage C, Schrier M, Gillis AJ, Stoop H, Nagel R, Liu YP, van Duijse J, Drost J, Griekspoor A, Zlotorynski E, Yabuta N, De Vita G, Nojima H, Looijenga LH, Agami R. A genetic screen implicates miRNA-372 and miRNA-373 as oncogenes in testicular germ cell tumors. Cell. 2006. 124:1169–1181.13. He H, Jazdzewski K, Li W, Liyanarachchi S, Nagy R, Volinia S, Calin GA, Liu CG, Franssila K, Suster S, Kloos RT, Croce CM, de la Chapelle A. The role of microRNA genes in papillary thyroid carcinoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005. 102:19075–19080.14. Cahill S, Smyth P, Denning K, Flavin R, Li J, Potratz A, Guenther SM, Henfrey R, O'Leary JJ, Sheils O. Effect of BRAFV600E mutation on transcription and post-transcriptional regulation in a papillary thyroid carcinoma model. Mol Cancer. 2007. 6:21.15. Cahill S, Smyth P, Finn SP, Denning K, Flavin R, O'Regan EM, Li J, Potratz A, Guenther SM, Henfrey R, O'Leary JJ, Sheils O. Effect of ret/PTC 1 rearrangement on transcription and post-transcriptional regulation in a papillary thyroid carcinoma model. Mol Cancer. 2006. 5:70.16. Jung HS, Kim DW, Jo YS, Chung HK, Song JH, Park JS, Park KC, Park SH, Hwang JH, Jo KW, Shong M. Regulation of protein kinase B tyrosine phosphorylation by thyroid-specific oncogenic RET/PTC kinases. Mol Endocrinol. 2005. 19:2748–2759.17. Kim DW, Chung HK, Park KC, Hwang JH, Jo YS, Chung J, Kalvakolanu DV, Resta N, Shong M. Tumor suppressor LKB1 inhibits activation of signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3) by thyroid oncogenic tyrosine kinase rearranged in transformation (RET)/papillary thyroid carcinoma (PTC). Mol Endocrinol. 2007. 21:3039–3049.18. Wan PT, Garnett MJ, Roe SM, Lee S, Niculescu-Duvaz D, Good VM, Jones CM, Marshall CJ, Springer CJ, Barford D, Marais R. Mechanism of activation of the RAF-ERK signaling pathway by oncogenic mutations of B-RAF. Cell. 2004. 116:855–867.19. Jo YS, Huang S, Kim YJ, Lee IS, Kim SS, Kim JR, Oh T, Moon Y, An S, Ro HK, Kim JM, Shong M. Diagnostic value of pyrosequencing for the BRAF (V600E) mutation in ultrasound-guided fine-needle aspiration biopsy samples of thyroid incidentalomas. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 2009. 70:139–144.20. Xing M. BRAF mutation in papillary thyroid cancer: pathogenic role, molecular bases, and clinical implications. Endocr Rev. 2007. 28:742–762.21. Nikiforova MN, Nikiforov YE. Molecular genetics of thyroid cancer: implications for diagnosis, treatment and prognosis. Expert Rev Mol Diagn. 2008. 8:83–95.22. Chung KW, Yang SK, Lee GK, Kim EY, Kwon S, Lee SH, Park do J, Lee HS, Cho BY, Lee ES, Kim SW. Detection of BRAFV600E mutation on fine needle aspiration specimens of thyroid nodule refines cyto-pathology diagnosis, especially in BRAF600E mutation-prevalent area. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 2006. 65:660–666.23. Karube Y, Tanaka H, Osada H, Tomida S, Tatematsu Y, Yanagisawa K, Yatabe Y, Takamizawa J, Miyoshi S, Mitsudomi T, Takahashi T. Reduced expression of Dicer associated with poor prognosis in lung cancer patients. Cancer Sci. 2005. 96:111–115.24. Pallante P, Visone R, Ferracin M, Ferraro A, Berlingieri MT, Troncone G, Chiappetta G, Liu CG, Santoro M, Negrini M, Croce CM, Fusco A. MicroRNA deregulation in human thyroid papillary carcinomas. Endocr Relat Cancer. 2006. 13:497–508.25. Visone R, Russo L, Pallante P, De Martino I, Ferraro A, Leone V, Borbone E, Petrocca F, Alder H, Croce CM, Fusco A. MicroRNAs (miR)-221 and miR-222, both overexpressed in human thyroid papillary carcinomas, regulate p27Kip1 protein levels and cell cycle. Endocr Relat Cancer. 2007. 14:791–798.26. Cuellar TL, McManus MT. MicroRNAs and endocrine biology. J Endocrinol. 2005. 187:327–332.27. Dalmay T, Edwards DR. MicroRNAs and the hallmarks of cancer. Oncogene. 2006. 25:6170–6175.28. Johnson SM, Grosshans H, Shingara J, Byrom M, Jarvis R, Cheng A, Labourier E, Reinert KL, Brown D, Slack FJ. RAS is regulated by the let-7 microRNA family. Cell. 2005. 120:635–647.29. O'Donnell KA, Wentzel EA, Zeller KI, Dang CV, Mendell JT. c-Myc-regulated microRNAs modulate E2F1 expression. Nature. 2005. 435:839–843.30. Taganov KD, Boldin MP, Chang KJ, Baltimore D. NF-kappaB-dependent induction of microRNA miR-146, an inhibitor targeted to signaling proteins of innate immune responses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006. 103:12481–12486.31. Jazdzewski K, Murray EL, Franssila K, Jarzab B, Schoenberg DR, de la Chapelle A. Common SNP in pre-miR-146a decreases mature miR expression and predisposes to papillary thyroid carcinoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008. 105:7269–7274.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Expression of miRNA 146a/b, 221 and 222 in Thyroid Cancer
- Gastric Carcinogenesis in the miR-222/221 Transgenic Mouse Model
- Genistein Improves the Major Depression through Suppressing the Expression of miR-221/222 by Targeting Connexin 43
- MicroRNAs and periodontal disease: a qualitative systematic review of human studies
- MicroRNA expression profiling of diagnostic needle aspirates from surgical pancreatic cancer specimens