J Korean Surg Soc.
2009 Apr;76(4):270-272. 10.4174/jkss.2009.76.4.270.
Ileal Perforation Caused by Ingestion of Multiple Magnets
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Surgery, Kyung Hee University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. drchoi@khu.ac.kr
- KMID: 1465068
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4174/jkss.2009.76.4.270
Abstract
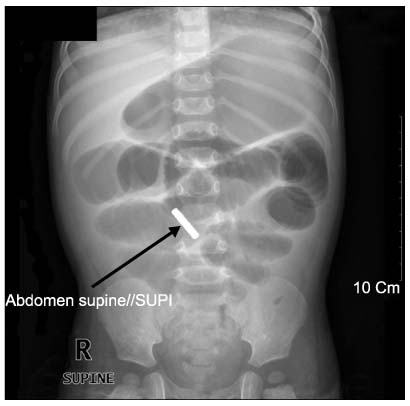
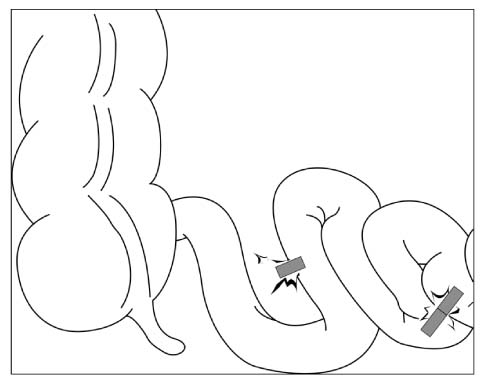
- Ingestion of foreign bodies is a common clinical problem encountered in early childhood. But ingestion of multiple magnets can cause serious lethal complications. Magnets located within another bowel loop may attract each other across the intestinal walls, resulting pressure necrosis, bowel perforation, fistula formation, intestinal obstruction, and death. Clinicians who care for children should be aware of this unexpected risk of magnetic ingestion. We report a case of ileal perforation caused by ingestion of multiple magnets in a child.
Keyword
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
A Case of Magnet Ingestion in a Child with Autism: Gastro-Colonoscopic Removal without Surgical Complication
Joo Whee Kim, Mi Sun Lim, Soon Chul Kim, Eun Hye Lee, Jae Sung Ko, Jeong Kee Seo
Korean J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2011;14(3):299-304. doi: 10.5223/kjpgn.2011.14.3.299.
Reference
-
1. Schwartz GF, Polsky HS. Ingested foreign bodies of the gastrointestinal tract. Am Surg. 1976. 42:236–238.2. Alzahem AM, Soundappan SS, Jefferies H, Cass DT. Ingested magnets and gastrointestinal complications. J Paediatr Child Health. 2007. 43:497–498.3. Cauchi JA, Shawis RN. Multiple magnet ingestion and gastrointestinal morbidity. Arch Dis Child. 2002. 87:539–540.4. Lee SK, Beck NS, Kim HH. Mischievous magnets: unexpected health hazard in children. J Pediatr Surg. 1996. 31:1694–1695.5. Hachimi-Idrissi S, Corne L, Vandenplas Y. Management of ingested foreign bodies in childhood: our experience and review of the literature. Eur J Emerg Med. 1998. 5:319–323.6. Hernandez Anselmi E, Gutierrez San Roman C, Barrios Fontoba JE, Ayuso Gonzalez L, Valdes Dieguez E, Lluna Gonzalez J, et al. Intestinal perforation caused by magnetic toys. J Pediatr Surg. 2007. 42:E13–E16.7. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Gastrointestinal injuries from magnet ingestion in children--United States, 2003-2006. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2006. 55:1296–1300.8. Kircher MF, Milla S, Callahan MJ. Ingestion of magnetic foreign bodies causing multiple bowel perforations. Pediatr Radiol. 2007. 37:933–936.9. Dutta S, Barzin A. Multiple magnet ingestion as a source of severe gastrointestinal complications requiring surgical intervention. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med. 2008. 162:123–125.10. Butterworth J, Feltis B. Toy magnet ingestion in children: revising the algorithm. J Pediatr Surg. 2007. 42:e3–e5.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Gastrointestinal Perforation Caused by Neodymium Magnet Toys: A Dangerous Foreign Body with SuperStrength
- Small Bowel Complication Due to Magnetic Foreign Body Ingestion in Childhood
- A Case of Ingesting Multiple Magnets Removed by Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection
- Underestimated risks of rare-earth magnet ingestion in children: when does it need surgery?
- A Case of Gastro-colic Fistula with Peritonitis Due to Ingested Magnets