Electrolyte Blood Press.
2009 Jun;7(1):1-4. 10.5049/EBP.2009.7.1.1.
Ubiquitination of Aquaporin: in the kidney
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Biochemistry and Cell Biology, School of Medicine, Kyungpook National University, Daegu, Korea. thkwon@knu.ac.kr
- KMID: 1464781
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5049/EBP.2009.7.1.1
Abstract
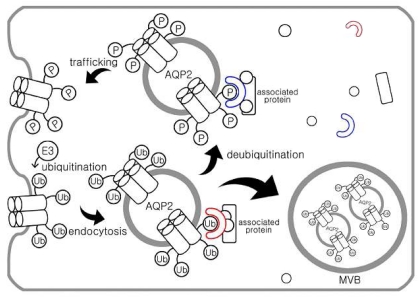
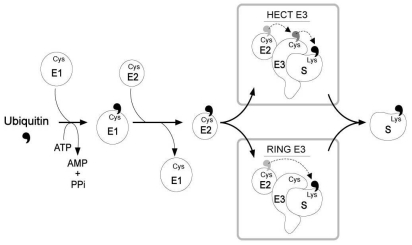
- Ubiquitination is known to be important for endocytosis and lysosomal degradation of aquaporin-2 (AQP2). Ubiquitin (Ub) is covalently attached to the lysine residue of the substrate proteins and activation and attachment of Ub to a target protein is mediated by the action of three enzymes (i.e., E1, E2, and E3). In particular, E3 Ub-protein ligases are known to have substrate specificity. This minireview will discuss the ubiquitination of AQP2 and identification of potential E3 Ub-protein ligases for 1-deamino-8-D-arginine vasopressin (dDAVP)-dependent AQP2 regulation.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Knepper M, Burg M. Organization of nephron function. Am J Physiol. 1983; 244:F579–F589. PMID: 6305206.
Article2. Knepper MA, Nielsen S, Chou CL, DiGiovanni SR. Mechanism of vasopressin action in the renal collecting duct. Semin Nephrol. 1994; 14:302–321. PMID: 7938946.3. Nielsen S, Frokiaer J, Marples D, Kwon TH, Agre P, Knepper MA. Aquaporins in the kidney: from molecules to medicine. Physiol Rev. 2002; 82:205–244. PMID: 11773613.4. Nielsen S, Chou CL, Marples D, Christensen EI, Kishore BK, Knepper MA. Vasopressin increases water permeability of kidney collecting duct by inducing translocation of aquaporin-CD water channels to plasma membrane. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1995; 92:1013–1017. PMID: 7532304.
Article5. Terris J, Ecelbarger CA, Nielsen S, Knepper MA. Long-term regulation of four renal aquaporins in rats. Am J Physiol. 1996; 271:F414–F422. PMID: 8770174.
Article6. Kwon TH, Nielsen J, Moller HB, Fenton RA, Nielsen S, Frokiaer J. Aquaporins in the kidney. Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2009; 95–132. PMID: 19096774.
Article7. Nejsum LN, Zelenina M, Aperia A, Frokiaer J, Nielsen S. Bidirectional regulation of AQP2 trafficking and recycling: involvement of AQP2-S256 phosphorylation. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2005; 288:F930–F938. PMID: 15625084.
Article8. Zelenina M, Christensen BM, Palmer J, Nairn AC, Nielsen S, Aperia A. Prostaglandin E(2) interaction with AVP: effects on AQP2 phosphorylation and distribution. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2000; 278:F388–F394. PMID: 10710543.9. van Balkom BW, Savelkoul PJ, Markovich D, Hofman E, Nielsen S, van der Sluijs P, et al. The role of putative phosphorylation sites in the targeting and shuttling of the aquaporin-2 water channel. J Biol Chem. 2002; 277:41473–41479. PMID: 12194985.
Article10. Kamsteeg EJ, Hendriks G, Boone M, Konings IB, Oorschot V, van der Sluijs P, et al. Short-chain ubiquitination mediates the regulated endocytosis of the aquaporin-2 water channel. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2006; 103:18344–18349. PMID: 17101973.
Article11. Hershko A, Ciechanover A, Varshavsky A. Basic Medical Research Award. The ubiquitin system. Nat Med. 2000; 6:1073–1081. PMID: 11017125.12. Hershko A. Ubiquitin: roles in protein modification and breakdown. Cell. 1983; 34:11–12. PMID: 6309404.
Article13. Hershko A, Heller H, Elias S, Ciechanover A. Components of ubiquitin-protein ligase system. Resolution, affinity purification, and role in protein breakdown. J Biol Chem. 1983; 258:8206–8214. PMID: 6305978.
Article14. Hochstrasser M. Lingering mysteries of ubiquitin-chain assembly. Cell. 2006; 124:27–34. PMID: 16413479.
Article15. Wilkinson KD. The discovery of ubiquitin-dependent proteolysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2005; 102:15280–15282. PMID: 16230621.
Article16. Wilkinson KD, Ventii KH, Friedrich KL, Mullally JE. The ubiquitin signal: assembly, recognition and termination. Symposium on ubiquitin and signaling. EMBO Rep. 2005; 6:815–820. PMID: 16113643.17. Staub O, Dho S, Henry P, Correa J, Ishikawa T, McGlade J, et al. WW domains of Nedd4 bind to the proline-rich PY motifs in the epithelial Na+ channel deleted in Liddle's syndrome. EMBO J. 1996; 15:2371–2380. PMID: 8665844.
Article18. Abriel H, Loffing J, Rebhun JF, Pratt JH, Schild L, Horisberger JD, et al. Defective regulation of the epithelial Na+ channel by Nedd4 in Liddle's syndrome. J Clin Invest. 1999; 103:667–673. PMID: 10074483.19. Malik B, Price SR, Mitch WE, Yue Q, Eaton DC. Regulation of epithelial sodium channels by the ubiquitin-proteasome proteolytic pathway. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2006; 290:F1285–F1294. PMID: 16682484.
Article20. Lee YJ, Choi HJ, Lim JS, Earm JH, Lee BH, Kim IS, et al. A novel method of ligand peptidomics to identify peptide ligands binding to AQP2-expressing plasma membranes and intracellular vesicles of rat kidney. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2008; 295:F300–F309. PMID: 18480184.
Article21. van Balkom BW, Boone M, Hendriks G, Kamsteeg EJ, Robben JH, Stronks HC, et al. LIP5 interacts with aquaporin 2 and facilitates its lysosomal degradation. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2009; 20:990–1001. PMID: 19357255.
Article22. Uawithya P, Pisitkun T, Ruttenberg BE, Knepper MA. Transcriptional profiling of native inner medullary collecting duct cells from rat kidney. Physiol Genomics. 2008; 32:229–253. PMID: 17956998.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Regulation of aquaporin-2 in the kidney : A molecular mechanism of body-water homeostasis
- Altered Renal Expression of Aquaporin-2 Water Channels in Two-Kidney, One Clip Hypertension in Rats
- Role of Nitric Oxide in the Regulation of Aquaporin-2 Water Channels in Rat Kidney
- Altered Regulation of Aquaporin-2 Water Channels in the Kidney Following Acute Blood Volume Depletion in Rats
- Vasopressin and Vasopressin Receptor Antagonists