Lab Anim Res.
2010 Mar;26(1):109-115. 10.5625/lar.2010.26.1.109.
Isolation of Early Neurogenesis Genes with Xenopus cDNA Microarray
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Biochemistry, College of Medicine, Hallym University, Chuncheon, Korea. jbkim@hallym.ac.kr
- 2Department of Anatomy, School of Medicine, Kyungpook National University, Daegu, Korea.
- 3Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 1458948
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5625/lar.2010.26.1.109
Abstract
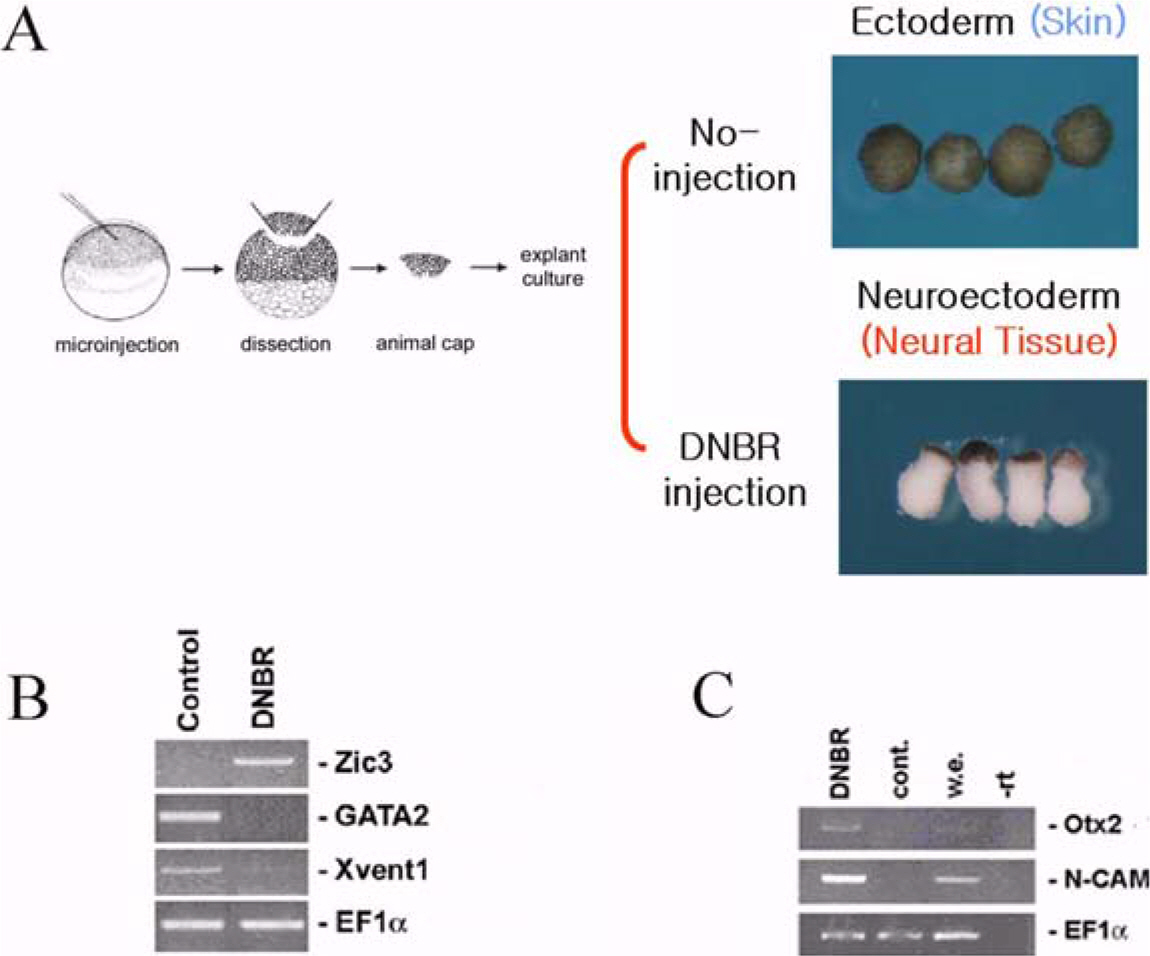
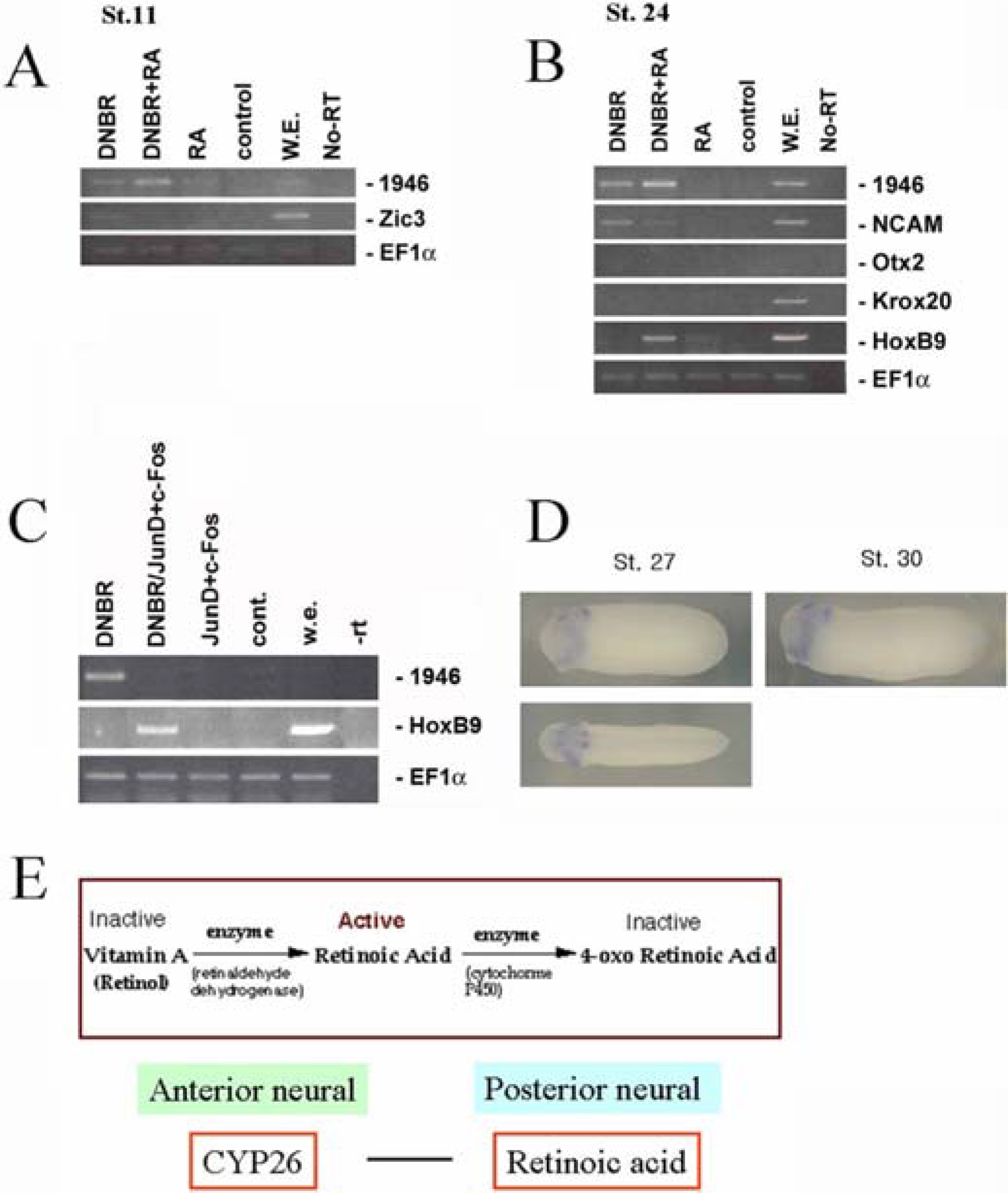
- Neurogenesis is the process that develops neuroectoderm from ectoderm. Bone morphogenetic protein (BMP) inhibition in ectodermal cells is necessary and sufficient for neurogenesis in Xenopus embryos. To isolate genes involved in early neurogenesis, Xenous Affymetrix gene chips representing 14,400 genes were analyzed in early stage of neuroectodermal cells that were produced by inhibition of BMP signaling with overexpression of a dominant-negative receptor. We identified 265 candidate genes including 107 ESTs which were newly expressed during the early neurogenesis by blocking BMP signaling. The candidates of 10 ESTs were selected and examined for upregulation in neuroectoderm. Five EST genes were confirmed to be upregulated in neuroectoderm and examined for time-dependent expression patterns in intact embryos. Two EST genes were cloned and identified as a homology of CYP26c (Xl.1946.1.A1_at) and Kielin containing VWC domain (Xl.15853.1.A1_at). One of them, CYP26c, was further characterized for its transcriptional regulation and role of anterior-posterior patterning during neurogenesis. Taken together, we analyzed and characterized genes expressed in early neurogenesis. The results suggest that neurogenesis by inhibition of BMP provides useful system to isolate genes involved in early events of neurogenesis during early vertebrate embryogenesis.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
Abreu J.G.., Ketpura N.I.., Reversade B.., De Robertis E.M.2002. Connective-tissue growth factor (CTGF) modulates cell signalling by BMP and TGF-β. Nat. Cell. Biol. 4(8):599–604.
ArticleAbu-Abed S.., Dolle P.., Metzger D.., Beckett B.., Chambon P.., Petkovich M.2001. The retinoic acid-metabolizing enzyme, CYP26A1, is essential for normal hindbrain patterning, vertebral identity, and development of posterior structures. Genes Dev. 15(2):226–240.
ArticleAriizumi T.., Takahashi S.., Chan T.C.., Ito Y.., Michiue T.., Asashima M.2009. Isolation and differentiation of Xenopus animal cap cells. Curr. Protoc. Stem Cell Biol. (Gregory, R., Elefanty, A., Yamashita, Y., Patient, R., Schlaeger, T. and Snyder, E. eds), 9: 1D.5.1-1D.5.31. John Wiley and Sons., New York.Cha S.W.., Hwang Y.S.., Chae J.P.., Lee S.Y.., Lee H.S.., Daar I.., Park M.J.., Kim J.2004. Inhibition of FGF signaling causes expansion of the endoderm in Xenopus. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 315(1):100–106.
ArticleCornish E.J.., Hassan S.M.., Martin J.D.., Li S.., Merzdorf C.S.2009. A microarray screen for direct targets of Zic1 identifies an aquaporin gene, aqp-3b, expressed in the neural folds. Dev. Dyn. 238(5):1179–1194.Curran T.., Gordon M.B.., Rubino K.L.., Sambucetti L.C.1987. Isolation and characterization of the c-fos(rat) cDNA and analysis of post-translational modification in vitro. Oncogene. 2(1):79–84.Feledy J.A.., Beanan M.J.., Sandoval J.J.., Goodrich J.S.., Lim J.H.., Matsuo-Takasaki M.., Sato S.M.., Sargent T.D.1999. Inhibitory patterning of the anterior neural plate in Xenopus by homeodomain factors Dlx3 and Msx1. Dev. Biol. 212(2):455–464.
ArticleGarcia Abreu J.., Coffinier C.., Larrain J.., Oelgeschlager M.., De Robertis E.M.2002. ).Chordin-like CR domains and the regulation of evolutionarily conserved extracellular signaling systems. Gene. 287(1-2):39–47.
ArticleHarland R.M.1991. In situ hybridization: an improved whole-mount method for Xenopus embryos. Methods Cell. Biol. 36:685–695.Hawley S.H.., Wunnenberg-Stapleton K.., Hashimoto C.., Laurent M.N.., Watabe T.., Blumberg B.W.., Cho K.W.1995. Disruption of BMP signals in embryonic Xenopus ectoderm leads to direct neural induction. Genes Dev. 9(23):2923–2935.
ArticleHemmati-Brivanlou A.., Kelly O.G.., Melton D.A.1994. Follistatin, an antagonist of activin, is expressed in the Spemann organizer and displays direct neuralizing activity. Cell. 77(2):283–295.
ArticleHemmati-Brivanlou A.., Melton D.1997. Vertebrate neural induction. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 20:43–60.
ArticleHollemann T.., Chen Y.., Grunz H.., Pieler T.1998. Regionalized metabolic activity establishes boundaries of retinoic acid signalling. EMBO J. 17(24):7361–7372.
ArticleKarsten S.L.., Kudo L. C.., Geschwind D. H.2008. Gene expression analysis of neural cells and tissues using DNA microarrays. Curr. Protoc. Neurosci. (Crawley, J.N., Gerfen, C., Rogawski, M., Sibley, D., Skolnick, P. and Wray, S. eds), 45: 4.28.1-4.28.38, John Wiley and Sons., New York.Kudoh T.., Wilson S.W.., Dawid I.B.2002. Distinct roles for Fgf, Wnt and retinoic acid in posteriorizing the neural ectoderm. Development. 129(18):4335–4346.
ArticleLamb T.M.., Knecht A.K.., Smith W.C.., Stachel S.E.., Economides A.N.., Stahl N.., Yancopolous G. D.., Harland R.M.1993. Neural induction by the secreted polypeptide noggin. Science. 262(5134):713–718.
ArticleMunoz-Sanjuan I.., Brivanlou A.H.2002a. Neural induction, the default model and embryonic stem cells. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 3(4):271–280.Munoz-Sanjuan I.., Bell E.., Altmann C.R.., Vonica A.., Brivanlou A.H.2002b. Gene profiling during neural induction in Xenopus laevis: regulation of BMP signaling by post-transcriptional mechanisms and TAB3, a novel TAK1-binding protein. Development. 129(23):5529–5540.Nakata K.., Nagai T.., Aruga J.., Mikoshiba K.1998. ).Xenopus Zic family and its role in neural and neural crest development. Mech. Dev. 75(1-2):43–51.Nieuwkoop P.D.., Faber J.1975. Normal Table of Xenopus Laevis (Daudin). North-Holland, Amsterdam.Ohuchi H.., Tomonari S.., Itoh H.., Mikawa T.., Noji S.1999. ).Identification of chick rax/rx genes with overlapping patterns of expression during early eye and brain development. Mech. Dev. 85(1-2):193–195.Piccolo S.., Sasai Y.., Lu B.., De Robertis E.M.1996. Dorsoventral patterning in Xenopus: inhibition of ventral signals by direct binding of chordin to BMP-4. Cell. 86(4):589–598.
ArticleRauscher F.J.., 3rd, Voulalas P.J.., Franza B.R. Jr.., Curran T.1988. ).Fos and Jun bind cooperatively to the AP-1 site: reconstitution in vitro. Genes. Dev. 2(12B):1687–1699.
ArticleSakai Y.., Meno C.., Fujii H.., Nishino J.., Shiratori H.., Saijoh Y.., Rossant J.., Hamada H.2001. The retinoic acid-inactivating enzyme CYP26 is essential for establishing an uneven distribution of retinoic acid along the anterio-posterior axis within the mouse embryo. Genes Dev. 15(2):213–225.
ArticleSasai Y.., Lu B.., Steinbeisser H.., Geissert D.., Gont L.K.., De Robertis E.M.1994. Xenopus chordin: a novel dorsalizing factor activated by organizer-specific homeobox genes. Cell. 79(5):779–790.
ArticleSasai Y.., Lu B.., Steinbeisser H.., De Robertis E.M.1995. Regulation of neural induction by the Chd and Bmp-4 antagonistic patterning signals in Xenopus. Nature. 376(6538):333–336.
ArticleShin Y.., Kitayama A.., Koide T.., Peiffer D.A.., Mochii M.., Liao A.., Ueno N.., Cho K.W.2005. Identification of neural genes using Xenopus DNA microarrays. Dev. Dyn. 232(2):432–444.Sive H.L.., Grainger R.M.., Harland R.M.2000. Early Development of Xenopus Laevis: A Laboratory Manual. Cold Spring Harbor press, Cold Spring Harbor.White J.A.., Guo Y.D.., Baetz K.., Beckett-Jones B.., Bonasoro J.., Hsu K.E.., Dilworth F.J.., Jones G.., Petkovich M.1996. Identification of the retinoic acid-inducible all-trans-retinoic acid 4-hydroxylase. J. Biol. Chem. 271(47):29922–29927.
ArticleWilson P.A.., Hemmati-Brivanlou A.1995. Induction of epidermis and inhibition of neural fate by BMP-4. Nature. 376(6538):331–333.
ArticleXu R.H.., Kim J.., Taira M.., Zhan S.., Sredni D.., Kung H.F.1995. A dominant negative bone morphogenetic protein 4 receptor causes neuralization in Xenopus ectoderm. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 212(1):212–219.
ArticleZaraiskii A.G.2007. Neural induction: new achievements and perspectives. Mol. Biol. (Mosk). 41(2):200–215.Zhang J.L.., Huang Y.., Qiu L.Y.., Nickel J.., Sebald W.2007. von Willebrand factor type C domain-containing proteins regulate bone morphogenetic protein signaling through different recognition mechanisms. J. Biol. Chem. 282(27):20002–20014.
ArticleZimmerman L.B.., De Jesus-Escobar J.M.., Harland R.M.1996. The Spemann organizer signal noggin binds and inactivates bone morphogenetic protein 4. Cell. 86(4):599–606.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- xCITED2 Induces Neural Genes in Animal Cap Explants of Xenopus Embryos
- Analysis of gene expression in placenta of severe preeclampsia
- Microarray Gene Expression Analysis
- Early Experience with a cDNA Microarray in Colorectal Cancer
- Profile of Gene Expression Changes During Doxorubicin Induced Apoptosis of Saos-2