J Korean Hip Soc.
2011 Dec;23(4):318-322. 10.5371/jkhs.2011.23.4.318.
A Case Report of Unique Complications of PFNA Penetration of the Blade into the Hip Joint
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Daegu Fatima Hospital, Daegu, Korea. femur1973@hanmail.net
- KMID: 1452641
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5371/jkhs.2011.23.4.318
Abstract
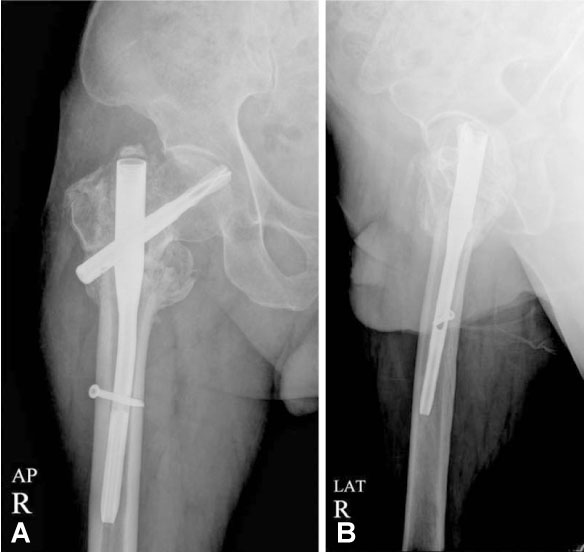
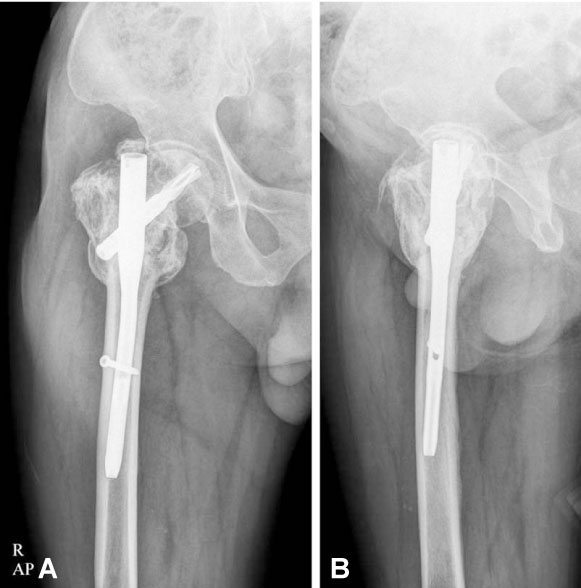
- The proximal femoral nail anti-rotation (PFNA) is a useful device to fix trochanteric fractures of the proximal femur. We report a case of postoperative penetration of the helical blade through the femoral head into the hip joint without any sign of rotational or varus instability in the fracture.
Keyword
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Excessive Sliding of the Helical Blade and the Femoral Neck Fracture after Insertion of Proximal Femoral Nail Anti-Rotation for Type A2 Intertrochanteric Fractures - A Case Report -
Bong-Ju Park, Hong-Man Cho, Ju-Han Kim, Woo-Jin Sin
J Korean Fract Soc. 2013;26(2):151-155. doi: 10.12671/jkfs.2013.26.2.151.
Reference
-
1. Halder SC. The Gamma nail for peritrochanteric fractures. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1992. 74:340–344.
Article2. Boldin C, Seibert FJ, Frankhauser F, Peicha G, Grechenig W, Szyszkowitz R. The Proximal femoral nail (PFN) - a minimal invasive treatment of unstable proximal femoral fractures: a prospective study of 55 patients with a follow-up of 15 months. Acta Orthop Scand. 2003. 74:53–58.
Article3. Chang SA, Cho YH, Byun YS, Han JH, Park JY, Lee CY. The treatment of trochanteric femoral fracture with using proximal femoral nail antirotation (PFNA). J Korean Hip Soc. 2009. 21:252–256.
Article4. Byun YS, Yoo CH, Nam JM, Cho YH, Shin DJ. Unstable trochanteric fractures of the femur treated with a condylar blade plate. J Korean Soc Fract. 2002. 15:320–327.
Article5. Sommers MB, Roth C, Hall H, et al. A laboratory model to evaluate cotout resistance of implants for pertrochanteric fracture fixation. J Orthop Trauma. 2004. 18:361–368.
Article6. Baumgaertner MR, Curtin SL, Lindskog DM, Keggi JM. The value of the tip-apex distance in predicting failure of fixation of peritrochanteric fractures of the hip. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1995. 77:1058–1064.
Article7. Garden RS. Low-angle fixation in fractures of the femoral neck. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1961. 43-B:647–663.
Article8. Cleveland M, Bosworth DM, Thompson FR, Wilson HJ Jr, Ishizuka T. A ten-year analysis of intertrochanteric fractures of the femur. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1959. 41-A:1399–1408.
Article9. Adams CI, Robinson CM, Court-Brown CM, Mcqueen MM. Prospective randomized controlled trial of an intramedullary nail versus dynamic screw and plate for intertrochanteric fractures of the femur. J Orthop Trauma. 2001. 15:394–400.
Article10. Simmermacher RK, Bosch AM, Van der Werken C. The AO/ASIF-proximal femoral nail (PFN): a new device for the treatment of unstable proximal femoral fractures. Injury. 1999. 30:327–332.
Article11. Butt MS, Krikler SJ, Nafie S, Ali MS. Comparison of dynamic hip screw and gamma nail: a prospective randomized controlled trial. Injury. 1995. 26:615–618.
Article12. Strauss E, Frank J, Lee J, Kummer FJ, Tejwani N. Helical blade versus sliding hip screw for treatment of unstable intertrochanteric hip fractures: a biomechanical evaluation. Injury. 2006. 37:984–989.
Article13. Brunner A, Jöckel JA, Babst R. The PFNA proximal femur nail in treatment of unstable proximal femur fractures--3 cases of postoperative perforation of the helical blade into the hip joint. J Orthop Trauma. 2008. 22:731–736.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Results of the Proximal Femoral Nail-Antirotation (PFNA) in Patients with an Unstable Pertrochanteric Fracture
- Results of Treating Senile Osteoporotic Peritrochanteric Fracture with Proximal Femoral Nail Antirotation (PFNA)
- Excessive Sliding of the Helical Blade and the Femoral Neck Fracture after Insertion of Proximal Femoral Nail Anti-Rotation for Type A2 Intertrochanteric Fractures - A Case Report -
- PFNA and PFN in Intertrochanteric Fractures: Comparison Study of Sliding
- The Effect of Valgus Reduction on the Position of the Blade of the Proximal Femoral Nail Antirotation in Intertrochanteric Hip Fractures