Korean J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr.
2011 Dec;14(Suppl 1):S9-S18. 10.5223/kjpgn.2011.14.Suppl1.S9.
Clinical Approach to Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders in Children: Revolve Around on Cyclic Vomiting Syndrome and Aerophagia
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatrics, Dankook University College of Medicine, Cheonan, Korea. pdlks@hanmail.net
- KMID: 1451144
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5223/kjpgn.2011.14.Suppl1.S9
Abstract
- Functional gaonic or recurrent gastrointestinal symptoms not explained by structural or biochemical abnormalities. The Rome II pediatric criteria for FGIDs were announced in 1999. The Rome III criteria, update and revise the pediatric criteria, included FGIDs criteria of infant and toddler to child and adolescent (aged 4 to 18 years). The aerophagia was classified into abdominal pain-related FGIDs in the ROME II criteria. However, cyclic vomiting syndrome and aerophagia, both were classified into vomiting and aerophagia part in the ROME III criteria. We describe the clinical features, diagnostic criteria, and treatments of cyclic vomiting syndrome and aerophaiga among pediatrstrointestinal disorders (FGIDs) are defined as a chric FGIDs
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Rasquin A, Di Lorenzo C, Forbes D, Guiraldes E, Hyams JS, Staiano A, et al. Childhood functional gastrointestinal disorders: child/adolescent. Gastroenterology. 2006. 130:1527–1537.
Article2. Apley J, Naish N. Recurrent abdominal pains: a field survey of 1,000 school children. Arch Dis Child. 1958. 33:165–170.
Article3. Kleiman RE, Goulet O, Mieli-Vergani G, Sanderson IR, Sherman PM, Shneider BL. Walker's pediatric gastrointestinal disease: physiology, diagnosis, management. 2008. 5th ed. Hamilton: BC Decker INC;712–713.4. Rasquin-Weber A, Hyman PE, Cucchiara S, Fleisher DR, Hyams JS, Milla PJ, et al. Childhood functional gastrointestinal disorders. Gut. 1999. 45:Suppl 2. ii60–ii68.
Article5. Ko JS. Update on pediatric functional upper gastrointestinal disorders. Korean J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2007. 10:Suppl 1. 29–35.6. Han JJ, Yang HR, Ko JS, Seo JK. Chronic abdominal pain-related childhood functional gastrointestinal disorders based on the Rome III criteria in Korea. Korean J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2009. 12:111–119.
Article7. Kim DS, Nho HN, Kim C, Lee HW, Yoon JH, Uhm JH. Diagnosis of functional gastrointestinal disorders with Rome III criteria in korean pediatric and adolescent patients: clinical usefulness of QPGS. Korean J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2009. 12:120–132.
Article8. Hwang JB, Jeong SH. Practical diagnostic approaches to chronic abdominal pain in children and adolescents. J Korean Med Assoc. 2009. 52:271–284.
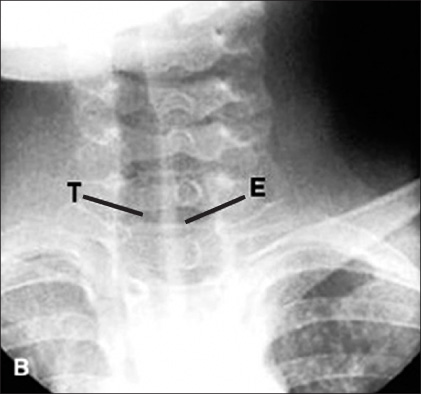
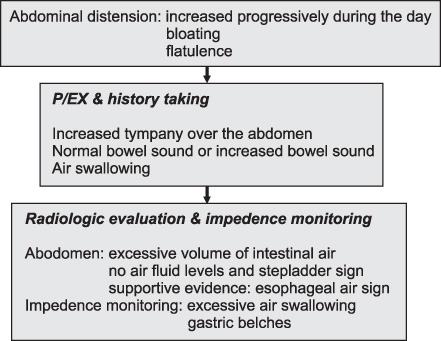
Article9. Hwang JB. Update in pathologic childhood aerophagia. Korean J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2007. 10:Suppl 2. 37–45.10. Smith SW. Aerophagy. Br Med J. 1940. 1:296–297.
Article11. Chitkara DK, Bredenoord AJ, Wang M, Rucker MJ, Talley NJ. Aerophagia in children: characterization of a functional gastrointestinal disorder. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2005. 17:518–522.
Article12. Appleby BS, Rosenberg PB. Aerophagia as the initial presenting symptom of a depressed patient. Prim Care Companion J Clin Psychiatry. 2006. 8:245–246.
Article13. Frye RE, Hait EJ. Air swallowing caused recurrent ileus in Tourette's syndrome. Pediatrics. 2006. 117:e1249–e1252.
Article14. Hwang JB, Choi WJ, Kim JS, Lee SY, Jung CH, Lee YH, et al. Clinical features of pathologic childhood aerophagia: early recognition and essential diagnostic criteria. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2005. 41:612–616.
Article15. Bredenoord AJ, Weusten BL, Sifrim D, Timmer R, Smout AJ. Aerophagia, gastric, and supragastric belching: a study using intraluminal electrical impedance monitoring. Gut. 2004. 53:1561–1565.
Article16. Hemmink GJ, Weusten BL, Bredenoord AJ, Timmer R, Smout AJ. Aerophagia: excessive air swallowing demonstrated by esophageal impedance monitoring. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2009. 7:1127–1129.
Article17. Bredenoord AJ. Excessive belching and aerophagia: two different disorders. Dis Esophagus. 2010. 23:347–352.
Article18. Basaran UN, Inan M, Aksu B, Ceylan T. Colon perforation due to pathologic aerophagia in an intellectually disabled child. J Paediatr Child Health. 2007. 43:710–712.
Article19. Wyllie R, Hyams J, Kay M. Pediatric gastrointestinal and liver disease. 2011. 4th ed. Philadelphia: Saunders;101–104.20. Fitzpatrick E, Bourke B, Drumm B, Rowland M. The incidence of cyclic vomiting syndrome in children: population-based study. Am J Gastroenterol. 2008. 103:991–995. quiz 6.
Article21. Gee S. On fitful or recurrent vomiting. St Bart Hosp Rep. 1882. 18.22. Li BU, Lefevre F, Chelimsky GG, Boles RG, Nelson SP, Lewis DW, et al. North American Society for Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology, and Nutrition consensus statement on the diagnosis and management of cyclic vomiting syndrome. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2008. 47:379–393.
Article23. The International Classification of Headache Disorders: 2nd edition. Cephalalgia. 2004. 24:Suppl 1. 9–160.24. Park JY, Nam SO, Eun SH, You SJ, Kang HC, Eun BL, et al. Multicenter clinical study of childhood periodic syndromes that are common precursors to migraine using new criteria of the International Classification of Headache Disorders (ICHD-II). Korean J Pediatr. 2009. 52:557–566.
Article25. Cheon JM, Um MR, Lee MH, Beck NS. Clinical evaluation of cyclic vomiting syndrome. J Korean Pediatr Soc. 2000. 43:1223–1231.26. Yang HR, Ko JS, Seo JK. A study on the disease course and prognosis of cyclic vomiting syndrome. J Korean Pediatr Soc. 2001. 44:1141–1156.27. Yang HR. Recent concepts on cyclic vomiting syndrome in children. J Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2010. 16:139–147.
Article28. Pareek N, Fleisher DR, Abell T. Cyclic vomiting syndrome: what a gastroenterologist needs to know. Am J Gastroenterol. 2007. 102:2832–2840.
Article29. Bae SH. Cyclic vomiting syndrome. Korean J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2007. 10:Suppl 2. 25–30.30. Zaki EA, Freilinger T, Klopstock T, Baldwin EE, Heisner KR, Adams K, et al. Two common mitochondrial DNA polymorphisms are highly associated with migraine headache and cyclic vomiting syndrome. Cephalalgia. 2009. 29:719–728.
Article31. Boles RG, Zaki EA, Lavenbarg T, Hejazi R, Foran P, Freeborn J, et al. Are pediatric and adult-onset cyclic vomiting syndrome (CVS) biologically different conditions? Relationship of adult-onset CVS with the migraine and pediatric CVS-associated common mtDNA polymorphisms 16519T and 3010A. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2009. 21:936–972.
Article32. Park MR, Seo JK, Ko JS, Chang JY, Yang HR. Acute intermittent porphyria presented with recurrent abdominal pain and hypertension. Korean J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2011. 14:81–85.
Article33. Sim YJ, Kim Jm, Kwon S, Choe BH. Clinical experience with amitriptyline for management of children with cyclic vomiting syndrome. Korean J Pediatr. 2009. 52:538–543.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Recent Concepts on Cyclic Vomiting Syndrome in Children
- Cyclic Vomiting Syndrome Developed after Stroke
- Practical Diagnostic Approaches to Chronic Abdominal Pain in Children and Adolescents
- New approach to chronic recurrent abdominal pain in children
- The New Rome IV Criteria for Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders in Infants and Toddlers