J Bacteriol Virol.
2011 Sep;41(3):147-156. 10.4167/jbv.2011.41.3.147.
Change of Vibrio vulnificus Metalloprotease VvpE Production by Temperature and Salinity
- Affiliations
-
- 1Research Center for Resistant Cells, Chosun University Medical School, Gwangju, Korea. shsin@chosun.ac.kr
- 2Department of Microbiology, Chosun University Medical School, Gwangju, Korea.
- KMID: 1449889
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4167/jbv.2011.41.3.147
Abstract
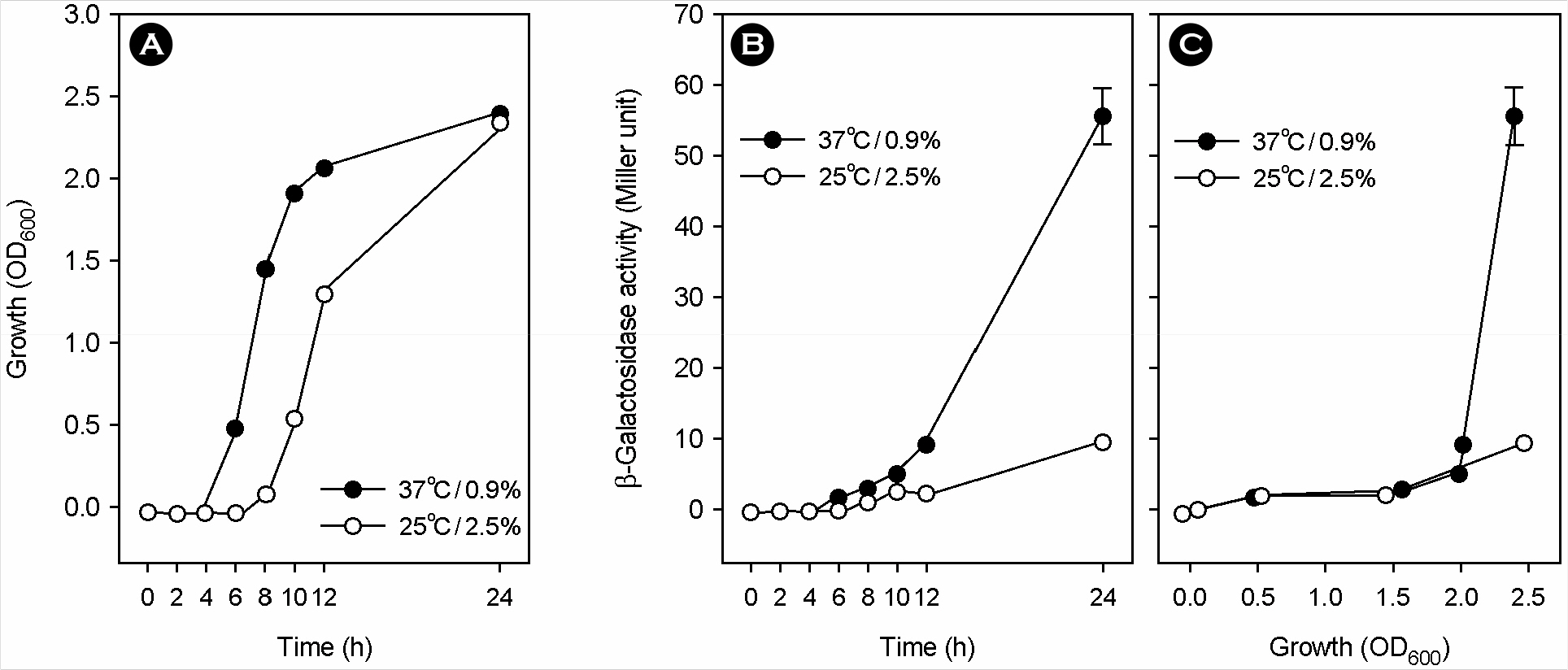
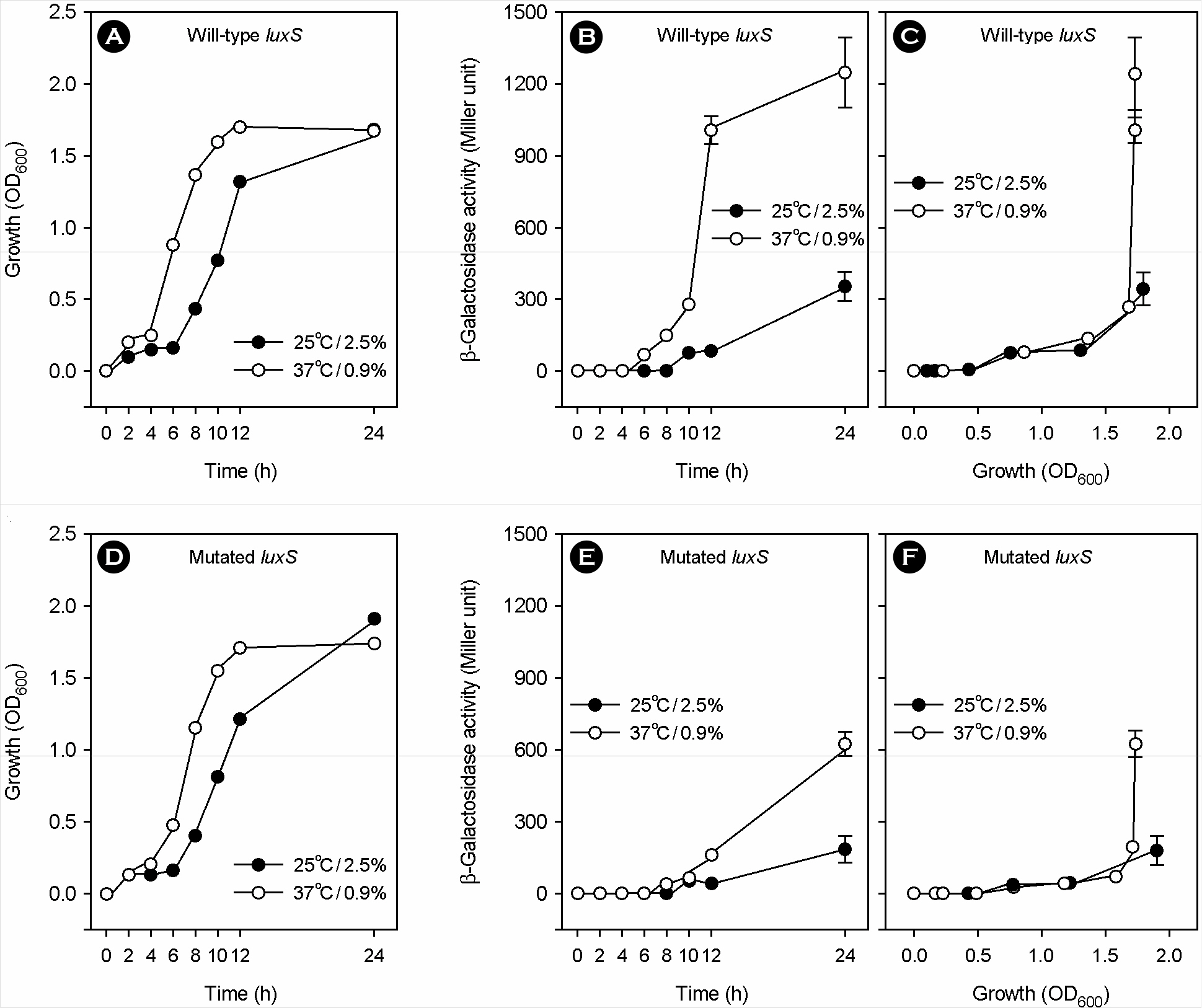
- Vibrio vulnificus, a gram-negative halophilic marine bacterium and opportunistic pathogen, must withstand various environmental changes, especially the simultaneous change of temperature and salinity (SCTS) from 25degrees C/2.5% to 37degrees C/0.9% upon entering the human body. Previous studies have suggested that temperature and salinity may affect the production of metalloprotease VvpE via the LuxS-mediated autoinducer-2 quorum sensing system (AI-2-QSS). However, this hypothesis remains to be verified through coherent experiments. In this study, SCTS stimulated V. vulnificus growth with no increase in total growth levels. The SCTS-mediated prolongation of the stationary growth phase resulted in a significant increase in growth phase-dependent luxS and vvpE transcriptions; however, SCTS did not affect luxS or vvpE transcription levels during the exponential growth phase. SCTS also advanced extracellular VvpE production, which was consistent with vvpE transcription and V. vulnificus growth. SCTS-mediated modulation of vvpE expression was slightly attenuated but still observed in the background of a luxS mutation which seriously repressed vvpE expression. These results indicate that SCTS stimulates luxS and vvpE expression by stimulating V. vulnificus growth; however, the LuxS-mediated AI-2-QSS plays only a minor role, if any, in the SCTS-mediated modulation of vvpE expression.
Keyword
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
SmcR, the Quorum-sensing Master Regulator, Is Partially Involved in Temperature/Salinity-mediated Changes in Metalloprotease vvpE Expression in Vibrio vulnificus
Choon-Mee Kim, Sung-Heui Shin
J Bacteriol Virol. 2012;42(1):29-39. doi: 10.4167/jbv.2012.42.1.29.
Reference
-
1). Jones MK., Oliver JD. Vibrio vulnificus: disease and pathogenesis. Infect Immun. 2009. 77:1723–33.2). Carnes EC., Lopez DM., Donegan NP., Cheung A., Gresham H., Timmins GS, et al. Confinement-induced quorum sensing of individual Staphylococcus aureus bacteria. Nat Chem Biol. 2010. 6:41–5.3). McDougald D., Rice SA., Kjelleberg S. SmcR-dependent regulation of adaptive phenotypes in Vibrio vulnificus. J Bacteriol. 2001. 183:758–62.4). Jones MK., Warner E., Oliver JD. Survival of and in situ gene expression by Vibrio vulnificus at varying salinities in estuarine environments. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2008. 74:182–7.5). Shao CP., Hor LI. Metalloprotease is not essential for Vibrio vulnificus virulence in mice. Infect Immun. 2000. 68:3569–73.6). Jeong HS., Lee MH., Lee KH., Park SJ., Choi SH. SmcR and cyclic AMP receptor protein coactivate Vibrio vulnificus vvpE encoding elastase through the RpoS-dependent promoter in a synergistic manner. J Biol Chem. 2003. 278:45072–81.7). Park J., Ryu SY., Kim CM., Shin SH. Two forms of Vibrio vulnificus metalloprotease VvpE are secreted via the type II general secretion system. J Microbiol. 2008. 46:338–43.8). Shao CP., Hor LI. Regulation of metalloprotease gene expression in Vibrio vulnificus by a Vibrio harveyi LuxR homologue. J Bacteriol. 2001. 183:1369–75.9). Kawase T., Miyoshi S., Sultan Z., Shinoda S. Regulation system for protease production in Vibrio vulnificus. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2004. 240:55–9.10). Vandeville A., Winzer K., Heurlier K., Tang CM., Hardie KR. Making sense of metabolism: autoinducer-2, LuxS and pathogenic bacteria. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2005. 3:383–96.
Article11). Kim HS., Shin SH., Park HR., Lee SE., Kim CM., Kim SY, et al. Effects of salinity, temperature, and glucose on the production of Vibrio vulnificus hemolysin. J Bacteriol Virol. 2002. 32:355–65.12). Reddy GP., Hayat U., Abeygunawardana C., Fox C., Wright AC., Raneval DR Jr, et al. Purification and determination of the structure of capsular polysaccharide of Vibrio vulnificus M06-24. J Bacteriol. 1992. 174:2620–30.13). Kim SY., Lee SE., Kim YR., Kim CM., Rhy PY., Choy HE, et al. Regulation of Vibrio vulnificus virulence by LuxS quorum-sensing system. Mol Microbiol. 2003. 48:1647–64.14). Miller VL., Mekalanos JJ. A novel suicide vector and its use in construction of insertion mutations: Osmoregulation of outer membrane proteins and virulence determinants in Vibrio cholerae requires toxR. J Bacteriol. 1988. 170:2575–83.15). McGee K., Hörstedt P., Milton DL. Identification and characterization of additional flagellin genes from Vibrio anguillarum. J Bacteriol. 1996. 178:5188–98.16). Farinha MA., Kropinski AM. Construction of broad-host-range plasmid vectors for easy visible selection and analysis of promoters. J Bacteriol. 1990. 172:3496–9.
Article17). Miller JH. A short course in bacterial genetics. Cold Spring Harbor, New York, Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press. 1992.18). Kim CM., Park RY., Chun HJ., Kim SY., Rhee JH., Shin SH. Vibrio vulnificus metalloprotease VvpE is essentially required for swarming. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2007. 269:170–9.19). Lee SE., Kim SY., Kim CM., Kim MK., Kim YR., Jeong K, et al. The pyrH gene of Vibrio vulnificus is an essential in vivo survival factor. Infect Immun. 2007. 75:2795–801.20). Lee SH., Hava DL., Waldor MK., Camilli A. Regulation and temporal expression patterns of Vibrio cholerae virulence genes during infection. Cell. 1999. 99:625–34.21). Heithoff DM., Conner CP., Mahan MJ. Dissecting the biology of a pathogen during infection. Trends Microbiol. 1997. 5:509–13.
Article22). Xavier KB., Bassler BL. Regulation of uptake and processing of the quorum-sensing autoinducer AI-2 in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 2005. 187:238–48.23). Tian Y., Wang Q., Liu Q., Ma Y., Cao X., Zhang Y. Role of RpoS in stress survival, synthesis of extracellular autoinducer 2, and virulence in Vibrio alginolyticus. Arch Microbiol. 2008. 190:585–94.24). Turovskiy Y., Chikindas ML. Autoinducer-2 bioassay is a qualitative, not quantitative method influenced by glucose. J Microbiol Methods. 2006. 66:497–503.
Article25). Roh JB., Lee MA., Lee HJ., Kim SM., Cho Y., Kim YJ, et al. Transcriptional regulatory cascade for elastase production in Vibrio vulnificus: LuxO activates luxT expression and LuxT represses smcR expression. J Biol Chem. 2006. 281:34775–84.26). Kim CM., Kang SM., Jeon HJ., Shin SH. Production of Vibrio vulnificus metalloprotease VvpE begins during the early growth phase: usefulness of gelatin-zymography. J Microbiol Methods. 2007. 70:96–102.27). Kim CM., Shin SH. Regulation of the Vibrio vulnificus vvpE expression by cyclic AMP-receptor protein and quorum sensing regulator SmcR. Microb Pathog. 2010. 49:348–53.28). Fraser GM., Hughes C. Swarming motility. Curr Opin Microbiol. 1999. 2:630–5.
Article29). Walker KE., Moghaddame-Jafari S., Lockatell CV., Johnson D., Belas R. ZapA, the IgA-degrading metallo-protease of Proteus mirabilis, is a virulence factor expressed specifically in swarmer cells. Mol Microbiol. 1999. 32:825–36.30). Oh MH., Lee SM., Lee DH., Choi SH. Regulation of the Vibrio vulnificus hupA gene by temperature alteration and cyclic AMP receptor protein and evaluation of its role in virulence. Infect Immun. 2009. 77:1208–15.31). Kim CM., Park RY., Park JH., Sun HY., Bai YH., Ryu PY, et al. Vibrio vulnificus vulnibactin, but not metalloprotease VvpE, is essentially required for iron-uptake from human holotransferrin. Biol Pharm Bull. 2006. 29:911–8.32). Kim CM., Chung YY., Shin SH. Iron differentially regulates gene expression and extracellular secretion of Vibrio vulnificus cytolysin-hemolysin. J Infect Dis. 2009. 200:582–9.33). Choi MH., Park RY., Sun HY., Kim CM., Bai YH., Lee SE, et al. Suppression and inactivation of Vibrio vulnificus hemolysin in cirrhotic ascites, a human ex vivo experimental system. FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol. 2006. 47:226–32.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- SmcR, the Quorum-sensing Master Regulator, Is Partially Involved in Temperature/Salinity-mediated Changes in Metalloprotease vvpE Expression in Vibrio vulnificus
- Effect of Salinity, Temperature, and Glucose on the Production of Vibrio vulnificus Hemolysin
- Production of and sensitivity to bacteriocin, "vulnificin" of vibrio vulnificus
- Isolation of Vibrio vulnificus from Seawater and Emerging Vibrio vulnificus Septicemia on Jeju Island
- Effects of Environmental Sea Water Factors on the Isolation of Vibrio vulnificus in the Western Coastal Area of Korea