J Korean Soc Spine Surg.
2011 Mar;18(1):29-33. 10.4184/jkss.2011.18.1.29.
Cervical Facet Cyst Causing Progressive Paraplegia: A Case Report and Review of Literature
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Chonnam National University Hospital, Gwangju, Korea. hyseo2001@hanmail.net
- KMID: 1448029
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4184/jkss.2011.18.1.29
Abstract
- STUDY DESIGN: A case report and literature review.
OBJECTIVES
To report a patient with a cervical facet cyst causing progressive paraplegia, and to review the clinical features, treatment and outcomes of a cervical facetal cyst. SUMMARY OF LITERATURE REVIEW: Extradural intraspinal synovial cysts of the cervical spine are quite rare. They typically occur in the cervical region at the C1-C2 junction or in the space adjacent to the facet joints in the lower cervical spine, and show similar clinical features to the intervertebral disc protrusion.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
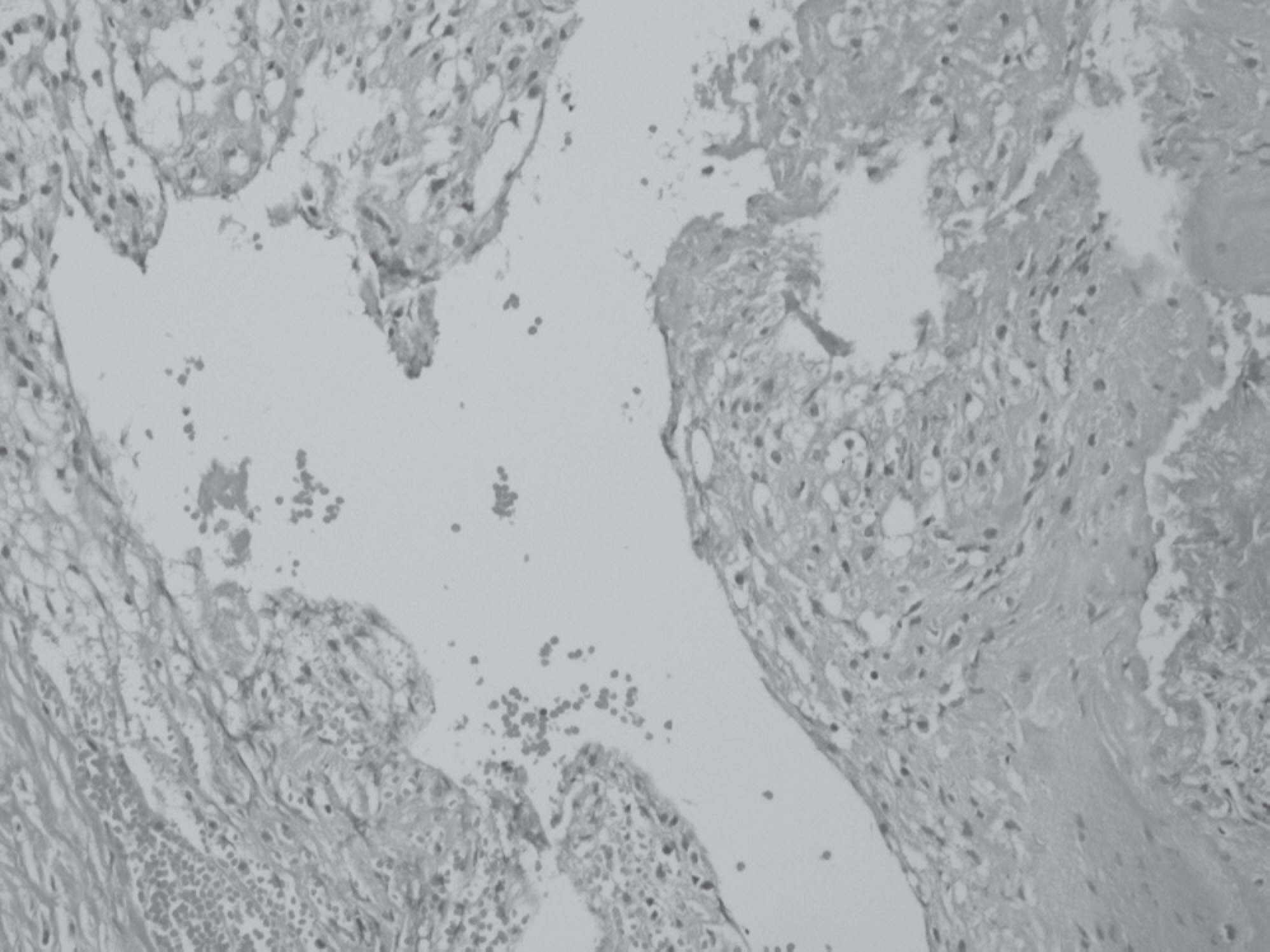
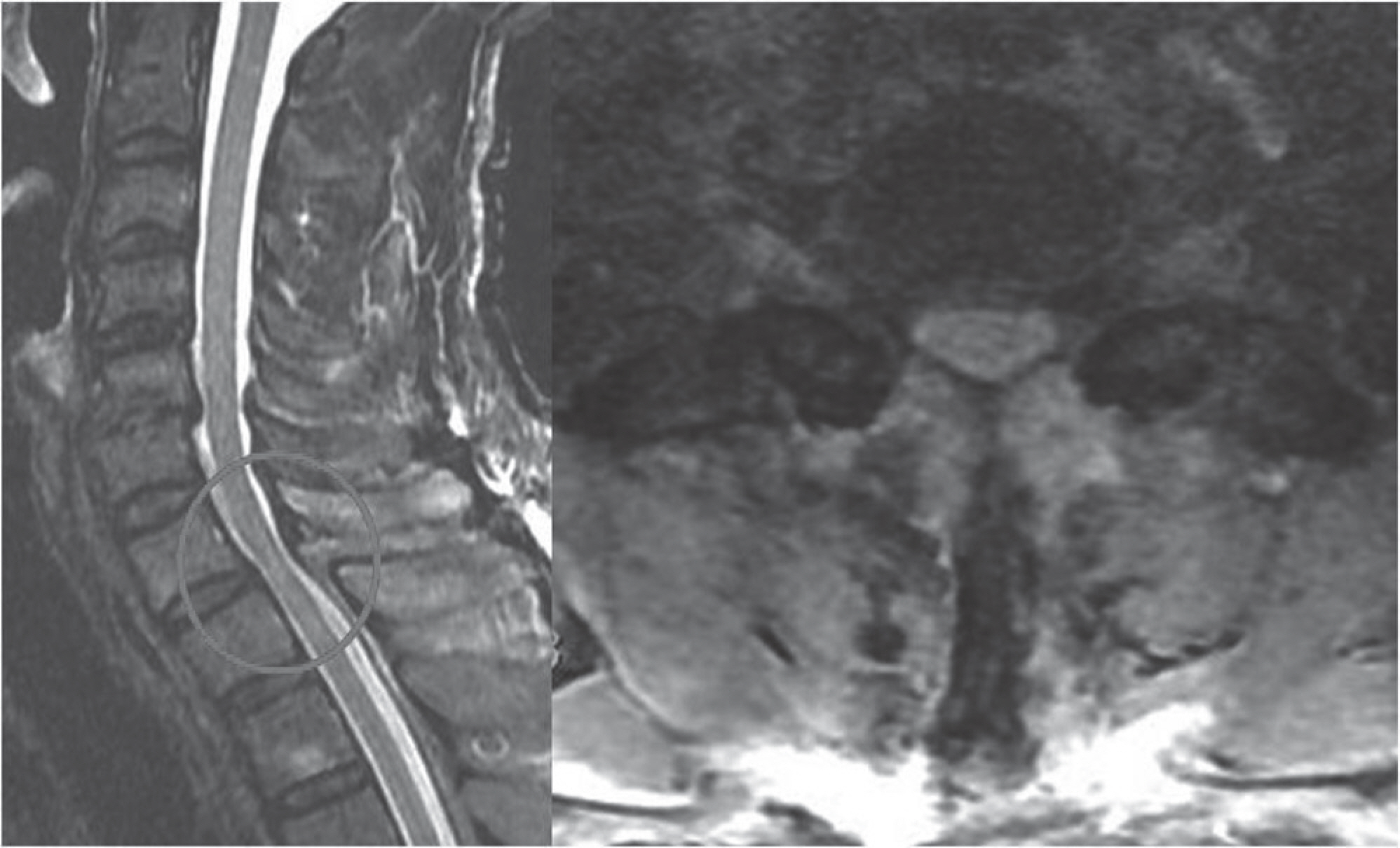
This article reports a case of a male patient, 64 years old, who presented with a 2 day history of numbness below the nipple and progressive paraplegia. A physical examination at admission revealed a wheelchair ambulatory state due to a motor deficit (motor grade good) below both hip flexors. Magnetic resonance imaging of the cervical spine showed an extradural lesion with a left lateral extension between C7 and T1, causing spinal cord compression. The patient underwent a hemi-laminectomy of C7 and complete cyst excision through the posterior approach. His motor power improved to almost normal.
RESULTS
The patient showed good recovery of myelopathy, and he was able to walk with a cane 3 months after surgery. A 1 year follow-up did not reveal any recurrence or new neurological conditions.
CONCLUSION
Cervical facet cysts are rare lesions that are occasionally signaled by progressive paraplegia but can be treated successfully by a surgical excision.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Acute Myelopathy Caused by a Cervical Synovial Cyst
Dong Shin Kim, Jin Seo Yang, Yong Jun Cho, Suk Hyung Kang
J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2014;56(1):55-57. doi: 10.3340/jkns.2014.56.1.55.
Reference
-
1. Holtzman RN, Dubin R, Yang WC, Rorat E, Liu HM, Leeds NE. Bilateral symptomatic intraspinal T12-L1 synovial cysts. Surg Neurol. 1987; 28:225–30.2. Shima Y, Rothman SL, Yasura K, Takahashi S. Degenerative intraspinal cyst of the cervical spine: case report and literature review. Spine. 2002; 27:E18–22.3. Costa F, Menghetti C, Cardia A, Fornari M, Ortolina A. Cervical synovial cyst: case report and review of lilterature. Eur Spine J. 2010; 19(Suppl 2):S100–2.4. Finkelstein SD, Sayegh R, Watson P, Knuckey N. Juxtafacet cysts. Report of two cases and review of clinocopathologic features. Spine. 1993; 18:779–82.5. Freidberg SR, Fellows T, Thomas CB, Mancall AC. Experience with symptomatic spinal epidural cysts. Neurosurgery. 1994; 34:989–93.
Article6. Bydon A, Xu R, Parker SL, McGirt MJ, Bydon M, Gokaslan ZL, Witham TF. Recurrent back and leg pain and cyst reformation after surgical resection of spinal synovial cysts: systematic review of reported postoperative outcomes. Spine J. 2010; 10:820–6.7. Kao CC, Winkler SS, Turner JH. Synovial cyst of spinal facet: Case report. J Neurosurg. 1974; 41:372–6.8. Jabre A, Shahbabian S, Keller JT. Synovial cyst of the cervical spine. Neurosurgery. 1987; 20:316–8.
Article9. Stoodley MA, Jones NR, Scott G. Cervical and thoracic juxtafacet cysts causing neurologic deficits. Spine. 2000; 25:970–3.
Article10. Colen CB, Rengachary S. Spontaneous resolution of a cervical synovial cyst. Case illustration. J Neurosurg Spine. 2006; 4:186.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Hemorrhagic Facet Cyst in the Lumbar Spine Causing Contralateral Leg Symptoms: A Case Report
- A Case of Cervical Synovial Cyst Causing Myelopathy
- Paraplegia due to Spinal Epidermoid Cyst Rupture at Asthma Attack
- Synovial Cyst in the Cervical Region Causing Severe Myelopathy
- Ganglion Cyst of the Dorsal Aspect of the Lumbar Facet Joint: a case report