J Korean Soc Radiol.
2012 Feb;66(2):117-122. 10.3348/jksr.2012.66.2.117.
Usefulness of Apparent Diffusion Coefficient Values in the Nasopharynx and the Oropharynx: Differentiation of Benign and Malignant Lesions
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiology, Pusan National University School of Medicine, Pusan National University Hospital, Busan, Korea. hakjink@pusan.ac.kr
- 2Department of Pathology, Pusan National University School of Medicine, Pusan National University Hospital, Busan, Korea.
- KMID: 1439401
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3348/jksr.2012.66.2.117
Abstract
- PURPOSE
In several previous studies, apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) calculation was applied in the evaluation of head and neck tumors and is a promising technique for this application. As a result, we reevaluated the usefulness of ADC measurement with differentiation of benign and malignant pathology in the nasopharynx and oropharynx.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
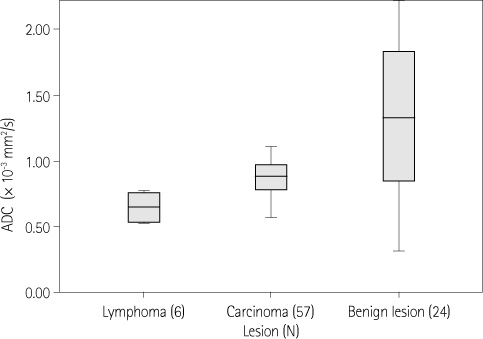
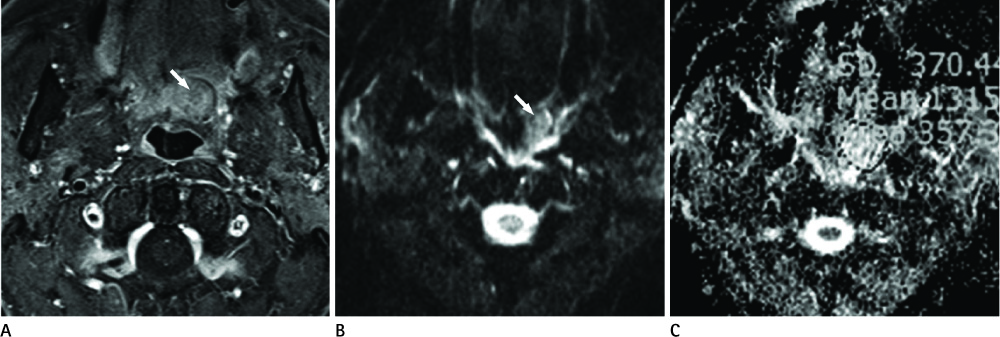
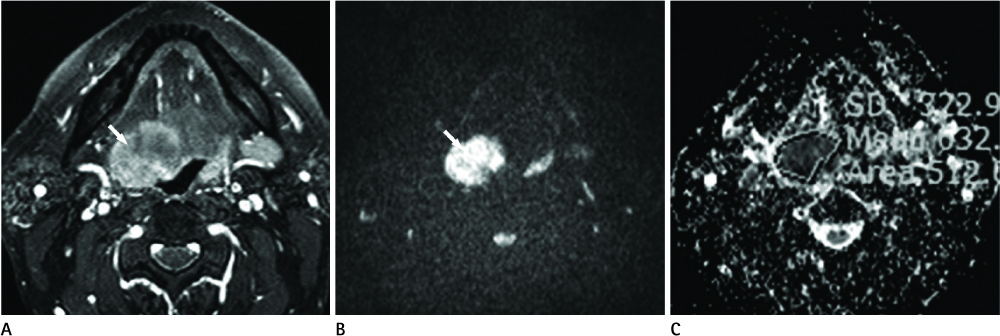
The study population consisted of 87 consecutive patients who had undergone routine nasopharyngeal and oropharyngeal MR imaging at our institution, which included diffusion weighted image and ADC map, with a clinically suspected primary tumor of nasopharynx and oropharynx. The mean ADC values in the benign and malignant groups were compared and the malignant group was divided into the lymphoma and carcinoma groups.
RESULTS
A statistically significant difference in ADC values among the benign and malignant groups using independent samples t-test with a p < 0.001. The lymphoma and carcinoma groups were compared by the Man-Whitney U test, which revealed a statistically significant difference with a p = 0.002. When an ADC of 1.1 x 10(-3) mm2/s was used to distinguish between benign and malignancy, accuracy was 85%.
CONCLUSION
ADC values were useful for distinguishing between benign and malignancy in the nasopharynx and oropharynx.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Stejskal EO, Tanner JE. Use of spin echo in pulsed magnetic field gradient to study anisotropic restricted diffusion and flow. J Chem Phys. 1965; 43:3579–3603.2. Pattany PM, Puckett WR, Klose KJ, Quencer RM, Bunge RP, Kasuboski L, et al. High-resolution diffusion-weighted MR of fresh and fixed cat spinal cords: evaluation of diffusion coefficients and anisotropy. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 1997; 18:1049–1056.3. Moseley ME, Cohen Y, Kucharczyk J, Mintorovitch J, Asgari HS, Wendland MF, et al. Diffusion-weighted MR imaging of anisotropic water diffusion in cat central nervous system. Radiology. 1990; 176:439–445.4. Chenevert TL, Brunberg JA, Pipe JG. Anisotropic diffusion in human white matter: demonstration with MR techniques in vivo. Radiology. 1990; 177:401–405.5. Turner R, Le Bihan D, Maier J, Vavrek R, Hedges LK, Pekar J. Echo-planar imaging of intravoxel incoherent motion. Radiology. 1990; 177:407–414.6. Bammer R. Basic principles of diffusion-weighted imaging. Eur J Radiol. 2003; 45:169–184.7. Wang J, Takashima S, Takayama F, Kawakami S, Saito A, Matsushita T, et al. Head and neck lesions: characterization with diffusion-weighted echo-planar MR imaging. Radiology. 2001; 220:621–630.8. Srinivasan A, Dvorak R, Perni K, Rohrer S, Mukherji SK. Differentiation of benign and malignant pathology in the head and neck using 3T apparent diffusion coefficient values: early experience. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2008; 29:40–44.9. Maeda M, Kato H, Sakuma H, Maier SE, Takeda K. Usefulness of the apparent diffusion coefficient in line scan diffusion-weighted imaging for distinguishing between squamous cell carcinomas and malignant lymphomas of the head and neck. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2005; 26:1186–1192.10. Guo AC, Cummings TJ, Dash RC, Provenzale JM. Lymphomas and high-grade astrocytomas: comparison of water diffusibility and histologic characteristics. Radiology. 2002; 224:177–183.11. Sasaki M, Eida S, Sumi M, Nakamura T. Apparent diffusion coefficient mapping for sinonasal diseases: differentiation of benign and malignant lesions. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2011; 32:1100–1106.12. Sumi M, Sakihama N, Sumi T, Morikawa M, Uetani M, Kabasawa H, et al. Discrimination of metastatic cervical lymph nodes with diffusion-weighted MR imaging in patients with head and neck cancer. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2003; 24:1627–1634.13. Habermann CR, Arndt C, Graessner J, Diestel L, Petersen KU, Reitmeier F, et al. Diffusion-weighted echo-planar MR imaging of primary parotid gland tumors: is a prediction of different histologic subtypes possible? AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2009; 30:591–596.14. Eida S, Sumi M, Sakihama N, Takahashi H, Nakamura T. Apparent diffusion coefficient mapping of salivary gland tumors: prediction of the benignancy and malignancy. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2007; 28:116–121.15. Ries T, Arndt C, Regier M, Graessner J, Cramer MC, Reitmeier F, et al. Value of apparent diffusion coefficient calculation before and after gustatory stimulation in the diagnosis of acute or chronic parotitis. Eur Radiol. 2008; 18:2251–2257.16. White ML, Zhang Y, Robinson RA. Evaluating tumors and tumorlike lesions of the nasal cavity, the paranasal sinuses, and the adjacent skull base with diffusion-weighted MRI. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 2006; 30:490–495.17. Kubota R, Yamada S, Kubota K, Ishiwata K, Tamahashi N, Ido T. Intratumoral distribution of fluorine-18-fluorodeoxyglucose in vivo: high accumulation in macrophages and granulation tissues studied by microautoradiography. J Nucl Med. 1992; 33:1972–1980.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Usefulness of Diffusion-Weighted MR Imaging for Breast Lesions: Comparing the Apparent Diffusion Coefficient (ADC) Values and the Pathologic Results
- Reversal of a Large Ischemic Lesion with Low Apparent Diffusion Coefficient Value by Rapid Spontaneous Recanalization
- Usefulness of Apparent Diffusion Coefficient in Ovarian Cystic Tumors Using Diffusion-Weighted Magnetic Resonance Imaging
- Usefulness of Apparent Diffusion Coefficient in Ovarian Cystic Tumors Using Diffusion-Weighted Magnetic Resonance Imaging
- Comparison of Monoexponential, Biexponential, Stretched-Exponential, and Kurtosis Models of Diffusion-Weighted Imaging in Differentiation of Renal Solid Masses