J Korean Fract Soc.
2013 Jul;26(3):205-211. 10.12671/jkfs.2013.26.3.205.
Minimally Invasive Plate Osteosynthesis with Locking Compression Plate for Distal Femur Fracture
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, School of Medicine, Chosun University, Gwangju, Korea. shha@chosun.ac.kr
- KMID: 1431665
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2013.26.3.205
Abstract
- PURPOSE
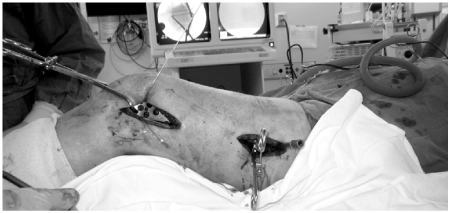
To analyze the clinical and radiologic results of minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis (MIPO) for distal femur fractures using a locking compression plate (LCP) and to evaluate its usefulness.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
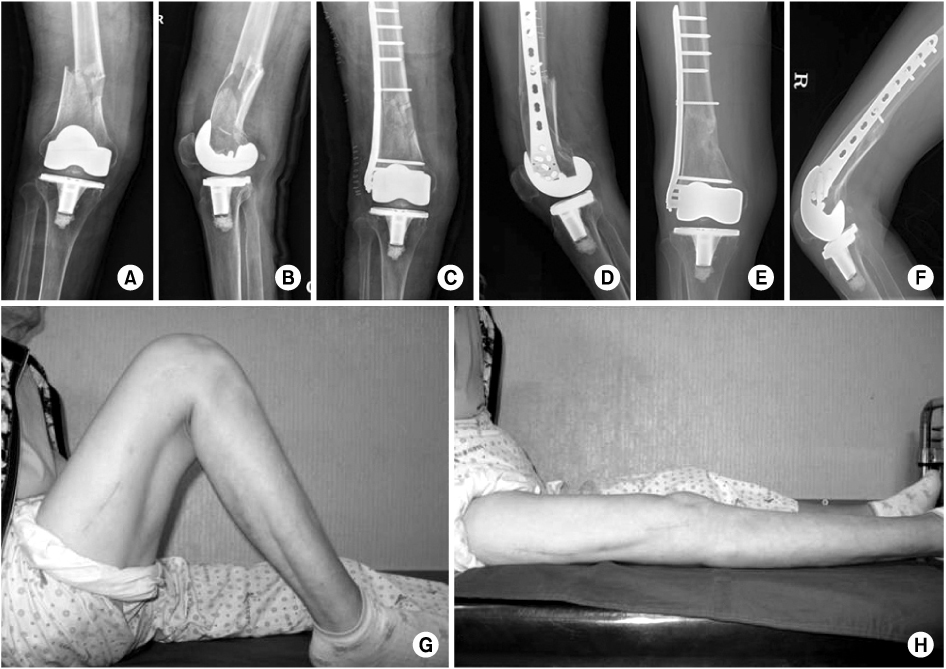
From May 2006 to April 2011, 23 patients (24 cases) with distal femur fracture were treated by MIPO with a LCP and followed-up for at least 12 months. Mean age was 61.6 years (35-80 years). Union time and post-operative alignment were measured on radiograph, and clinical function was evaluated by range of motion (ROM), Knee Society Score and complications.
RESULTS
In 22 patients (23 cases) except for 1 case, bony union was obtained after an average of 18 weeks (12-26 weeks). The mean ROM was 124 degrees (80-135 degrees). According to the Knee Society Score, there were 12 excellent, 8 good, 1 fair and 2 poor results and the mean score was 87.5 (60-98). Postoperative complications were nonunion in 1 case, ankylosis in 1 case, malunion in 2 cases and superficial wound infection in 2 cases.
CONCLUSION
The treatment of distal femoral fracture with MIPO using a LCP was considered a useful method which can result in satisfactory clinical and radiologic outcomes if there is accurate understanding about the surgical techniques and appropriate procedures involved.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Button G, Wolinsky P, Hak D. Failure of less invasive stabilization system plates in the distal femur: a report of four cases. J Orthop Trauma. 2004; 18:565–570.
Article2. Davison BL. Varus collapse of comminuted distal femur fractures after open reduction and internal fixation with a lateral condylar buttress plate. Am J Orthop (Belle Mead NJ). 2003; 32:27–30.3. Ehlinger M, Adam P, Abane L, Arlettaz Y, Bonnomet F. Minimally-invasive internal fixation of extra-articular distal femur fractures using a locking plate: tricks of the trade. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2011; 97:201–205.
Article4. Ehlinger M, Adam P, Arlettaz Y, et al. Minimally-invasive fixation of distal extra-articular femur fractures with locking plates: limitations and failures. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2011; 97:668–674.
Article5. Frigg R, Appenzeller A, Christensen R, Frenk A, Gilbert S, Schavan R. The development of the distal femur Less Invasive Stabilization System (LISS). Injury. 2001; 32:Suppl 3. SC24–SC31.
Article6. Giles JB, DeLee JC, Heckman JD, Keever JE. Supracondylar-intercondylar fractures of the femur treated with a supracondylar plate and lag screw. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1982; 64:864–870.
Article7. Han SB, Choi IC, Lee SH, Suh DH, Cho HJ. Minimal invasive plate osteosynthesis for distal femoral fracture. J Korean Fract Soc. 2006; 19:11–16.
Article8. Janzing HM, Stockman B, Van Damme G, Rommens P, Broos PL. The retrograde intramedullary nail: prospective experience in patients older than sixty-five years. J Orthop Trauma. 1998; 12:330–333.
Article9. Kregor PJ, Stannard JA, Zlowodzki M, Cole PA. Treatment of distal femur fractures using the less invasive stabilization system: surgical experience and early clinical results in 103 fractures. J Orthop Trauma. 2004; 18:509–520.
Article10. Kregor PJ, Stannard J, Zlowodzki M, Cole PA, Alonso J. Distal femoral fracture fixation utilizing the Less Invasive Stabilization System (L.I.S.S.): the technique and early results. Injury. 2001; 32:Suppl 3. SC32–SC47.
Article11. Krettek C, Müller M, Miclau T. Evolution of minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis (MIPO) in the femur. Injury. 2001; 32:Suppl 3. SC14–SC23.
Article12. Krettek C, Schandelmaier P, Miclau T, Bertram R, Holmes W, Tscherne H. Transarticular joint reconstruction and indirect plate osteosynthesis for complex distal supracondylar femoral fractures. Injury. 1997; 28:Suppl 1. A31–A41.
Article13. Mize RD. Surgical management of complex fractures of the distal femur. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1989; (240):77–86.
Article14. Park KC, Chung KS, Moon JK. Treatment of distal femur fracture with minimally invasive locking compression plate osteosynthesis. J Korean Fract Soc. 2012; 25:13–19.
Article15. Perren SM. Evolution of the internal fixation of long bone fractures. The scientific basis of biological internal fixation: choosing a new balance between stability and biology. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2002; 84:1093–1110.16. Schatzker J. Fractures of the distal femur revisited. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1998; (347):43–56.
Article17. Schatzker J, Home G, Waddell J. The Toronto experience with the supracondylar fracture of the femur, 1966-72. Injury. 1974; 6:113–128.
Article18. Schütz M, Müller M, Krettek C, et al. Minimally invasive fracture stabilization of distal femoral fractures with the LISS: a prospective multicenter study. Results of a clinical study with special emphasis on difficult cases. Injury. 2001; 32:Suppl 3. SC48–SC54.
Article19. Siliski JM, Mahring M, Hofer HP. Supracondylar-intercondylar fractures of the femur. Treatment by internal fixation. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1989; 71:95–104.
Article20. Wagner M. General principles for the clinical use of the LCP. Injury. 2003; 34:Suppl 2. B31–B42.
Article21. Zlowodzki M, Bhandari M, Marek DJ, Cole PA, Kregor PJ. Operative treatment of acute distal femur fractures: systematic review of 2 comparative studies and 45 case series (1989 to 2005). J Orthop Trauma. 2006; 20:366–371.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Comparison of Results of Minimally Invasive Plate Osteosynthesis according to Types of Locking Plate in Distal Femoral Fractures
- Treatment of Distal Femur Fracture with Minimally Invasive Locking Compression Plate Osteosynthesis
- Clinical Outcomes of Locking Compression Plate Fixation through Minimally Invasive Percutaneous Plate Osteosynthesis in the Treatment of Distal Tibia Fracture
- Analysis of the Result Treated with Locking Compression Plate-Distal Tibia and Zimmer Periarticular Locking Plate in Distal Tibia Fracture
- Minimally Invasive Osteosynthesis with Locking Compression Plate for Distal Tibia Fractures