Minimally Invasive Osteosynthesis with Locking Compression Plate for Distal Tibia Fractures
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Chonnam National University Medical School and Hospital, Gwangju, Korea. kbleeos@chonnam.ac.kr
- KMID: 1449414
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2011.24.1.33
Abstract
- PURPOSE
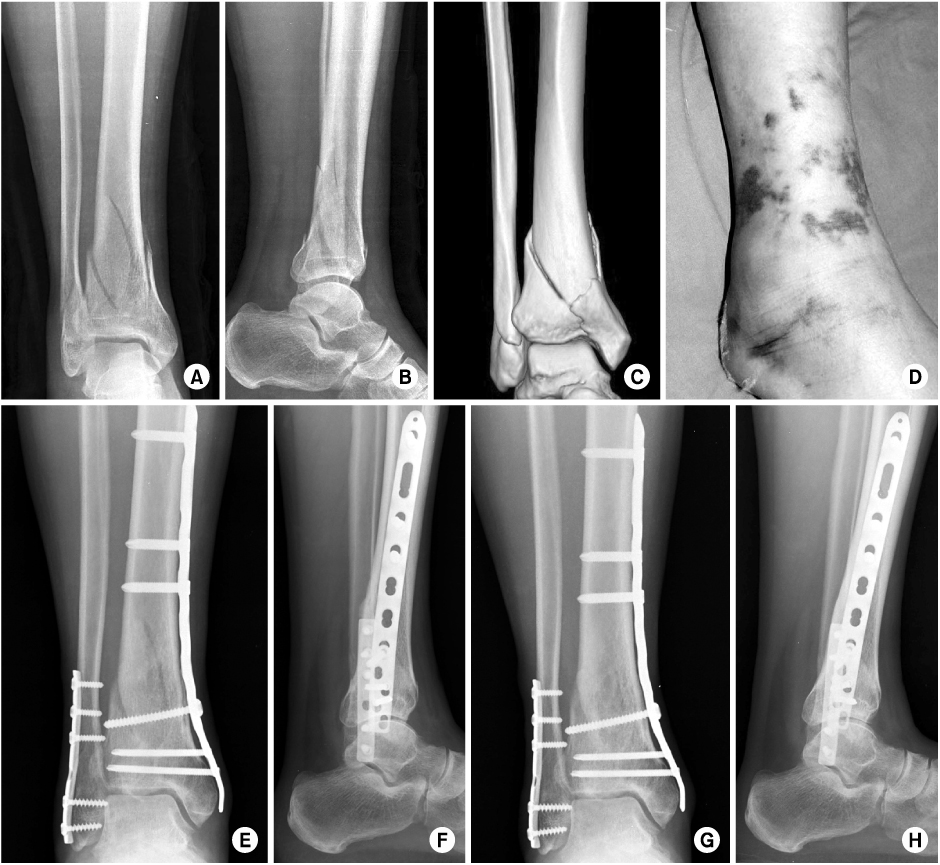
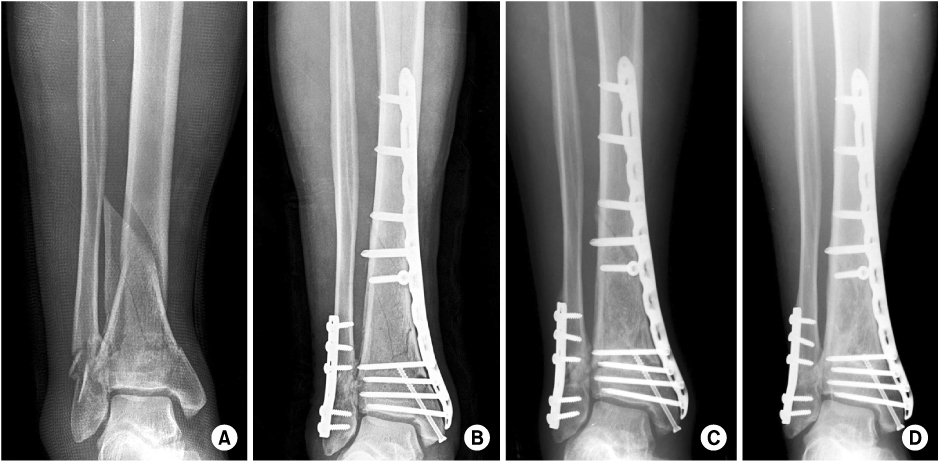
To evaluate the outcome of minimally invasive osteosynthesis using locking compression plate for distal tibia fractures.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Forty five patients (45 cases) who underwent minimally invasive osteosynthesis using locking compression plate for distal tibia fractures between January 2006 and June 2008, were followed for more than one year. The average duration of the follow-up was 30.5 months (12~54 months). The fracture types were as followed: 26 cases (58%) of extraarticular fractures, 19 cases (42%) of intraarticular fractures, and 16 cases (36%) of open fractures.
RESULTS
All patients achieved bone union at average of 21weeks (12~36 weeks). The average American Orthopedic Foot & Ankle Society ankle-hindfoot scales was 84.6 points (65~100 points) and range of ankle motion averaged at 46.5 degrees (20~60 degrees). Complications included 6 cases of superficial infection, 3 cases of malalignment and 5 cases of skin irritation by plate. There were no cases of deep infection, skin necrosis, shortening and metal breakage.
CONCLUSION
Minimally invasive osteosynthesis using locking compression plate for distal tibia fractures is considered to be an effective method with high healing rate, rapid functional recovery and low complication rate due to minimal disruption of bone and soft tissue biology and improved fixation strength.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 4 articles
-
Comparison of the Results between Intramedullary Nailing and Plate Fixation for Distal Tibia Fractures
JungHan Kim, Heui-Chul Gwak, Chang-Rack Lee, Yang-Hwan Jung
J Korean Foot Ankle Soc. 2015;19(3):86-90. doi: 10.14193/jkfas.2015.19.3.86.Comparative Analysis of Minimally Invasive Plate Osteosynthesis and Intramedullary Nailing in the Treatment of the Distal Tibia Fractures
Ho-Min Lee, Young-Sung Kim, Jong-Pil Kim, Phil-Hyun Chung, Suk Kang, Kaung Suk Jo
J Korean Fract Soc. 2018;31(3):94-101. doi: 10.12671/jkfs.2018.31.3.94.Anterolateral Minimally Invasive Plate Osteosynthesis of Distal Tibial Fractures Using an Anterolateral Locking Plate
Dongwhan Suh, Hwan Hee Lee, Young Hoon Han, Jae Jung Jeong
J Korean Foot Ankle Soc. 2020;24(1):19-24. doi: 10.14193/jkfas.2020.24.1.19.Minimally Invasive Plate Osteosynthesis for Fractures of Distal Tibia
Tae Hun Kim, So Hak Chung
Kosin Med J. 2014;29(1):23-29. doi: 10.7180/kmj.2014.29.1.23.
Reference
-
1. Ahmad MA, Sivaraman A, Zia A, Rai A, Patel AD. Percutaneous locking plates for fractures of the distal tibia: our experience and a review of the literature. J Trauma. 2010. 4.2. Anderson LD, Hutchins WC, Wright PE, Disney JM. Fractures of the tibia and fibula treated by casts and transfixing pins. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1974. 105:179–191.
Article3. Baumgaertel F, Buhl M, Rahn BA. Fracture healing in biological plate osteosynthesis. Injury. 1998. 29:Suppl 3. C3–C6.
Article4. Chung ST, Kim HS, Cha SD, et al. Treatment of distal tibia fracture using MIPPO technique with locking compression plate: comparative study of the intraarticular fracture and extraarticular fracture. J Korean Foot Ankle Soc. 2009. 13:162–168.5. Claes L, Heitemeyer U, Krischak G, Braun H, Hierholzer G. Fixation technique influences osteogenesis of comminuted fractures. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1999. 365:221–229.
Article6. Collinge C, Protzman R. Outcomes of minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis for metaphyseal distal tibia fractures. J Orthop Trauma. 2010. 24:24–29.
Article7. Collinge C, Sanders R, DiPasquale T. Treatment of complex tibial periarticular fractures using percutaneous techniques. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2000. 375:69–77.
Article8. Dillin L, Slabaugh P. Delayed wound healing, infection, and nonunion following open reduction and internal fixation of tibial plafond fractures. J Trauma. 1986. 26:1116–1119.
Article9. Edge AJ, Denham RA. External fixation for complicated tibial fractures. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1981. 63:92–97.
Article10. Foux A, Yeadon AJ, Uhthoff HK. Improved fracture healing with less rigid plates. A biomechanical study in dogs. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1997. 339:232–245.
Article11. Fracture and dislocation compendium. Orthopaedic trauma association committee for coding and classification. J Orthop Trauma. 1996. 10:Suppl 1. v–ix. 1–154.12. Francois J, Vandeputte G, Verheyden F, Nelen G. Percutaneous plate fixation of fractures of the distal tibia. Acta Orthop Belg. 2004. 70:148–154.13. Frigg R. Locking Compression Plate (LCP). An osteosynthesis plate based on the dynamic compression plate and the point contact fixator (PC-Fix). Injury. 2001. 32:Suppl 2. 63–66.
Article14. Gerber C, Mast JW, Ganz R. Biological internal fixation of fractures. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 1990. 109:295–303.
Article15. Hasenboehler E, Rikli D, Babst R. Locking compression plate with minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis in diaphyseal and distal tibial fracture: a retrospective study of 32 patients. Injury. 2007. 38:365–370.
Article16. Hazarika S, Chakravarthy J, Cooper J. Minimally invasive locking plate osteosynthesis for fractures of the distal tibia--results in 20 patients. Injury. 2006. 37:877–887.
Article17. Helfet DL, Shonnard PY, Levine D, Borrelli J Jr. Minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis of distal fractures of the tibia. Injury. 1997. 28:Suppl 1. A42–A47.
Article18. Karlström G, Olerud S. Fractures of the tibial shaft; a critical evaluation of treatment alternatives. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1974. 105:82–115.19. Khoury A, Liebergall M, London E, Mosheiff R. Percutaneous plating of distal tibial fractures. Foot Ankle Int. 2002. 23:818–824.
Article20. Kim YM, Yang JH, Kim DK. Minimally invasive percutaneous plate osteosynthesis using periarticular plate for distal tibial fractures. J Korean Fract Soc. 2007. 20:315–322.
Article21. Kitaoka HB, Alexander IJ, Adelaar RS, Nunley JA, Myerson MS, Sanders M. Clinical rating systems for the ankle-hindfoot, midfoot, hallux, and lesser toes. Foot Ankle Int. 1994. 15:349–353.
Article22. Krackhardt T, Dilger J, Flesch I, Höntzsch D, Eingartner C, Weise K. Fractures of the distal tibia treated with closed reduction and minimally invasive plating. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2005. 125:87–94.
Article23. Lau TW, Leung F, Chan CF, Chow SP. Wound complication of minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis in distal tibia fractures. Int Orthop. 2008. 32:697–703.
Article24. Lee KB. Distal tibia fracture: plate osteosynthesis. J Korean Fract Soc. 2009. 22:306–313.
Article25. Maffulli N, Toms AD, McMurtie A, Oliva F. Percutaneous plating of distal tibial fractures. Int Orthop. 2004. 28:159–162.
Article26. Park KC, Park YS. Minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis for distal tibial metaphyseal fracture. J Korean Fract Soc. 2005. 18:264–268.
Article27. Park SK, Oh CW, Oh JK, et al. Staged minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis of distal tibial fractures. J Korean Fract Soc. 2010. 23:289–295.
Article28. Redfern DJ, Syed SU, Davies SJ. Fractures of the distal tibia: minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis. Injury. 2004. 35:615–620.
Article29. Ronga M, Longo UG, Maffulli N. Minimally invasive locked plating of distal tibia fractures is safe and effective. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2010. 468:975–982.
Article30. Ronga M, Shanmugam C, Longo UG, Oliva F, Maffulli N. Minimally invasive osteosynthesis of distal tibial fractures using locking plates. Orthop Clin North Am. 2009. 40:499–504.
Article31. Shon OJ, Kim DS. Minimally invasive percutaneous plate osteosynthesis using a lateral plate in distal tibial fracture. J Korean Fract Soc. 2010. 23:42–49.
Article32. Teeny SM, Wiss DA. Open reduction and internal fixation of tibial plafond fractures Variables contributing to poor results and complications. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1993. 292:108–117.33. Trafton PG. Closed unstable fractures of the tibia. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1988. 230:58–67.
Article34. Trueta J. Nonunion of fractures. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1965. 43:23–35.
Article35. Urist MR, Mazet R Jr, McLean FC. The pathogenesis and treatment of delayed union and non-union; a survey of eighty-five ununited fractures of the shaft of the tibia and one hundred control cases with similar injuries. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1954. 36:931–968.36. Watson J. Fractures and joint injuries. 1976. 5th ed. Churchill Livingstone;20–27.37. Wilber MC, Evans EB. Fractures of the femoral shaft treated surgically. J Bone Joint Surg AM. 1978. 60:489–491.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Analysis of the Result Treated with Locking Compression Plate-Distal Tibia and Zimmer Periarticular Locking Plate in Distal Tibia Fracture
- Clinical Outcomes of Locking Compression Plate Fixation through Minimally Invasive Percutaneous Plate Osteosynthesis in the Treatment of Distal Tibia Fracture
- Comparison of Results of Minimally Invasive Plate Osteosynthesis according to Types of Locking Plate in Distal Femoral Fractures
- Treatment of Distal Femur Fracture with Minimally Invasive Locking Compression Plate Osteosynthesis
- Minimally Invasive Percutaneous Plate Stabilization Using a Medial Locking Plate for Proximal Tibial Fractures: Technical Note