Lab Anim Res.
2012 Dec;28(4):265-271. 10.5625/lar.2012.28.4.265.
Anti-obesity effects of Rapha diet(R) preparation in mice fed a high-fat diet
- Affiliations
-
- 1College of Veterinary Medicine, Chungbuk National University, Cheongju, Korea. solar93@cbu.ac.kr
- 2Rapha Biotech Inc., Burnaby, Canada.
- KMID: 1431410
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5625/lar.2012.28.4.265
Abstract
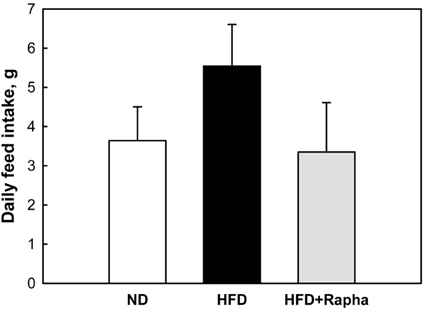
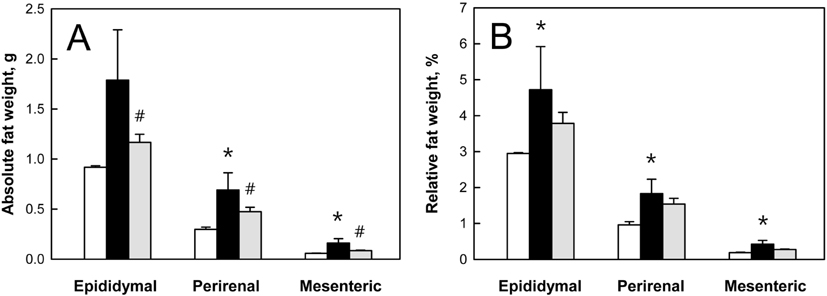
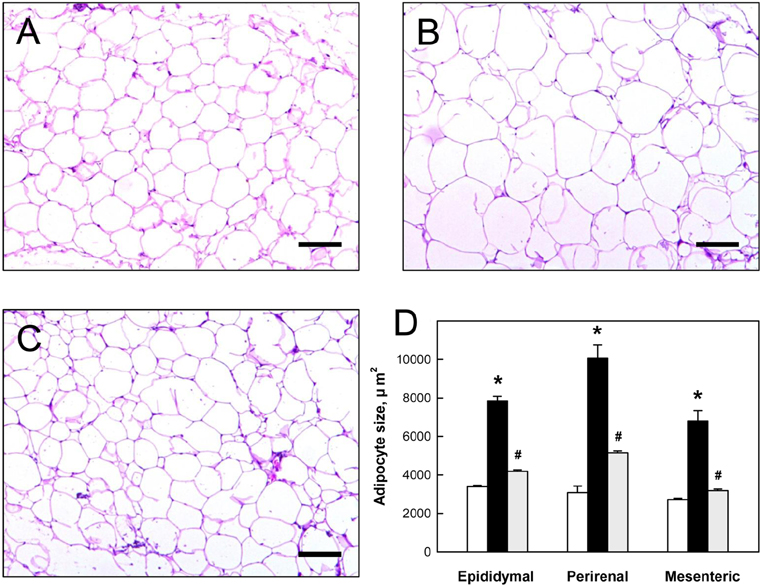
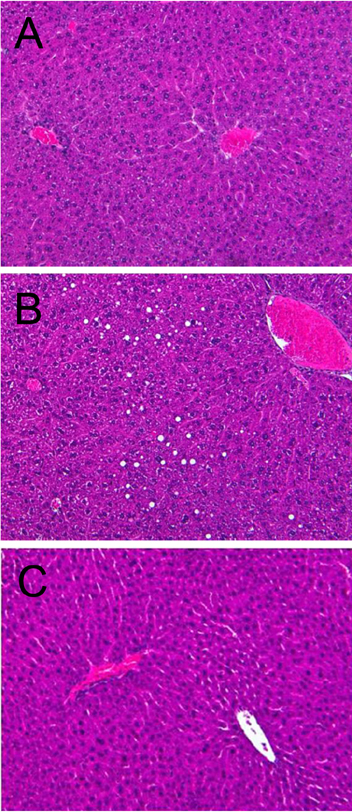
- The anti-obesity activities of Rapha diet(R) preparation containing silkworm pupa peptide, Garcinia cambogia, white bean extract, mango extract, raspberry extract, cocoa extract, and green tea extract were investigated in mice with dietary obesity. Male C57BL/6 mice were fed a high-fat diet (HFD) containing 3% Rapha diet(R) preparation for 8 weeks, and blood and tissue parameters of obesity were analyzed. The HFD markedly enhanced body weight gain by increasing the weights of epididymal, perirenal, and mesenteric adipose tissues. The increased body weight gain induced by HFD was significantly reduced by feeding Rapha diet(R) preparation, in which decreases in the weight of abdominal adipose tissue and the size of abdominal adipocytes were confirmed by microscopic examination. Long-term feeding of HFD increased blood triglycerides and cholesterol levels, leading to hepatic lipid accumulation. However, Rapha diet(R) preparation not only reversed the blood lipid levels, but also attenuated hepatic steatosis. The results indicate that Rapha diet(R) preparation could improve HFD-induced obesity by reducing both lipid accumulation and the size of adipocytes.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Anti-hyperlipidemic activity of Rhynchosia nulubilis seeds pickled with brown rice vinegar in mice fed a high-fat diet
Ki-Moon Park, Seung Ho Lee
Nutr Res Pract. 2013;7(6):453-459. doi: 10.4162/nrp.2013.7.6.453.
Reference
-
1. Popkin BM, Doak CM. The obesity epidemic is a worldwide phenomenon. Nutr Rev. 1998. 56:106–114.2. Sjöström LV. Mortality of severely obese subjects. Am J Clin Nutr. 1992. 55:2 Suppl. 516S–523S.3. Lavie CJ, Milani RV, Ventura HO. Obesity and cardiovascular disease; risk factor, paradox, and impact of weight loss. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2009. 53:1925–1932.4. Steppan CM, Bailey ST, Bhat S, Brown EJ, Banerjee RR, Wright CM, Patel HR, Ahima RS, Lazar MA. The hormone resistin links obesity to diabetes. Nature. 2001. 409(6818):307–312.5. Calle EE, Kaaks R. Overweight, obesity and cancer: epidemiological evidence and proposed mechanisms. Nat Rev Cancer. 2004. 4(8):579–591.6. Racette SB, Deusinger SS, Deusinger RH. Obesity: overview of prevalence, etiology, and treatment. Phys Ther. 2003. 83(3):276–288.7. Smith C, Marks A, Lieberman M. Marks' Basic Medical Biochemistry: A Clinical Approach. 2004. 2nd ed. Baltimore: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins;579–681.8. Curioni CC, Lourenço PM. Long-term weight loss after diet and exercise: a systematic review. Int J Obes (Lond). 2005. 29(10):1168–1174.9. Cooke D, Bloom S. The obesity pipeline: current strategies in the development of anti-obesity drugs. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2006. 5(11):919–931.10. Ioannides-Demos LL, Proietto J, Tonkin AM, McNeil JJ. Safety of drug therapies used for weight loss and treatment of obesity. Drug Saf. 2006. 29(4):277–302.11. Shin M, Park M, Youn M, Lee Y, Nam M, Park I, Jeong Y. Effects of silk protein hydrolysates on blood glucose and serum lipid in db/db diabetic mice. J Korean Soc Food Sci Nutr. 2006. 35:1343–1348.12. Lee Y, Park M, Choi J, Kim J, Nam M, Jeong Y. Effects of silk protein hydrolysates on blood glucose level, serum insulin and leptin secretion in OLEFT rats. J Korean Soc Food Sci Nutr. 2007. 36:703–707.13. Jung EY, Lee HS, Lee HJ, Kim JM, Lee KW, Suh HJ. Feeding silk protein hydrolysates to C57BL/KsJ-db/db mice improves blood glucose and lipid profiles. Nutr Res. 2010. 30(11):783–790.14. Kim TM, Ryu JM, Seo IK, Lee KM, Yeon S, Kang S, Hwang SY, Kim YB. Effects of red ginseng powder and silk peptide on hypercholesterolemia and atherosclerosis in rabbits. Lab Anim Res. 2008. 24:67–75.15. Lee SH, Park D, Yang G, Bae DK, Yang YH, Kim TK, Kim D, Kyung J, Yeon S, Koo KC, Lee JY, Hwang SY, Joo SS, Kim YB. Silk and silkworm pupa peptides suppress adipogenesis in preadipocytes and fat accumulation in rats fed a high-fat diet. Eur J Nutr. 2012. 51(8):1011–1019.16. Shin S, Park D, Yeon S, Jeon JH, Kim TK, Joo SS, Lim WT, Lee JY, Kim YB. Stamina-enhancing effects of silk amino acid preparations in mice. Lab Anim Res. 2009. 25:127–134.17. Shin S, Yeon S, Park D, Oh J, Kang H, Kim S, Joo SS, Lim WT, Lee JY, Choi KC, Kim KY, Kim SU, Kim JC, Kim YB. Silk amino acids improve physical stamina and male reproductive function of mice. Biol Pharm Bull. 2010. 33(2):273–278.18. Kim KY, Lee HN, Kim YJ, Park T. Garcinia cambogia extract ameliorates visceral adiposity in C57BL/6J mice fed on a high-fat diet. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 2008. 72(7):1772–1780.19. Hayamizu K, Hirakawa H, Oikawa D, Nakanishi T, Takagi T, Tachibana T, Furuse M. Effect of Garcinia cambogia extract on serum leptin and insulin in mice. Fitoterapia. 2003. 74(3):267–273.20. Jena BS, Jayaprakasha GK, Singh RP, Sakariah KK. Chemistry and biochemistry of (-)-hydroxycitric acid from Garcinia. J Agric Food Chem. 2002. 50(1):10–22.21. Fantini N, Cabras C, Lobina C, Colombo G, Gessa GL, Riva A, Donzelli F, Morazzoni P, Bombardelli E, Carai MA. Reducing effect of a Phaseolus vulgaris dry extract on food intake, body weight, and glycemia in rats. J Agric Food Chem. 2009. 57(19):9316–9323.22. Barrett ML, Udani JK. A proprietary alpha-amylase inhibitor from white bean (Phaseolus vulgaris): a review of clinical studies on weight loss and glycemic control. Nutr J. 2011. 10:24.23. Masibo M, He Q. Major mango polyphenols and their potential significance to human health. Compr Rev Food Sci Food Saf. 2008. 7:309–319.24. Lucas EA, Li W, Peterson SK, Brown A, Kuvibidila S, Perkins-Veazie P, Clarke SL, Smith BJ. Mango modulates body fat and plasma glucose and lipids in mice fed a high-fat diet. Br J Nutr. 2011. 106(10):1495–1505.25. Morimoto C, Satoh Y, Hara M, Inoue S, Tsujita T, Okuda H. Anti-obese action of raspberry ketone. Life Sci. 2005. 77(2):194–204.26. Park KS. Raspberry ketone increases both lipolysis and fatty acid oxidation in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Planta Med. 2010. 76(15):1654–1658.27. Suh JH, Romain C, González-Barrio R, Cristol JP, Teissèdre PL, Crozier A, Rouanet JM. Raspberry juice consumption, oxidative stress and reduction of atherosclerosis risk factors in hypercholesterolemic golden Syrian hamsters. Food Funct. 2011. 2(7):400–405.28. Matsui N, Ito R, Nishimura E, Yoshikawa M, Kato M, Kamei M, Shibata H, Matsumoto I, Abe K, Hashizume S. Ingested cocoa can prevent high-fat diet-induced obesity by regulating the expression of genes for fatty acid metabolism. Nutrition. 2005. 21(5):594–601.29. Murase T, Nagasawa A, Suzuki J, Hase T, Tokimitsu I. Beneficial effects of tea catechins on diet-induced obesity: stimulation of lipid catabolism in the liver. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord. 2002. 26(11):1459–1464.30. Wolfram S, Wang Y, Thielecke F. Anti-obesity effects of green tea: from bedside to bench. Mol Nutr Food Res. 2006. 50(2):176–187.31. Ashida H, Furuyashiki T, Nagayasu H, Bessho H, Sakakibara H, Hashimoto T, Kanazawa K. Anti-obesity actions of green tea: possible involvements in modulation of the glucose uptake system and suppression of the adipogenesis-related transcription factors. BioFactors. 2004. 22(1-4):135–140.32. Fajas L, Auboeuf D, Raspé E, Schoonjans K, Lefebvre AM, Saladin R, Najib J, Laville M, Fruchart JC, Deeb S, Vidal-Puig A, Flier J, Briggs MR, Staels B, Vidal H, Auwerx J. The organization, promoter analysis, and expression of the human PPARgamma gene. J Biol Chem. 1997. 272(30):18779–18789.33. Li J, Yu X, Pan W, Unger RH. Gene expression profile of rat adipose tissue at the onset of high-fat-diet obesity. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2002. 282(6):E1334–E1341.34. Wahli W, Braissant O, Desvercne B. Peroxisome proliferator activated receptors: transcriptional regulators of adipogenesis, lipid metabolism and more.... Chem Biol. 1995. 2(5):261–266.35. Schoonjans K, Staels B, Auwerx J. The peroxisome proliferator activated receptors (PPARS) and their effects on lipid metabolism and adipocyte differentiation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1996. 1302(2):93–109.36. Mandrup S, Lane MD. Regulating adipogenesis. J Biol Chem. 1997. 272(9):5367–5370.37. Preuss HG, Bagchi D, Bagchi M, Rao CV, Dey DK, Satyanarayana S. Effects of a natural extract of (-)-hydroxycitric acid (HCA-SX) and a combination of HCA-SX plus niacin-bound chromium and Gymnema sylvestre extract on weight loss. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2004. 6(3):171–180.38. Hasani-Ranjbar S, Nayebi N, Larijani B, Abdollahi M. A systematic review of the efficacy and safety of herbal medicines used in the treatment of obesity. World J Gastroenterol. 2009. 15(25):3073–3085.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Anti-obesity and LDL-cholesterol lowering effects of silkworm hemolymph in C57BL/6N mice fed high fat diet
- Anti-inflammatory and anti-diabetic effects of brown seaweeds in high-fat diet-induced obese mice
- The effects of Momordica charantia on obesity and lipid profiles of mice fed a high-fat diet
- Expression of eotaxin in 3T3-L1 adipocytes and the effects of weight loss in high-fat diet induced obese mice
- Effects of Intermittent Fasting on Splenic Galectin-3 Protein Expression in High-fat Diet-fed Mice