J Korean Med Sci.
2013 Feb;28(2):295-299. 10.3346/jkms.2013.28.2.295.
Attenuation of Spinal Cord Injury-Induced Astroglial and Microglial Activation by Repetitive Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation in Rats
- Affiliations
-
- 1Clinical Trial Center for Medical Devices of Yeungnam University Hospital, Daegu, Korea. spineahn@ynu.ac.kr
- 2Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, School of Medicine, Yeungnam University, Daegu, Korea.
- 3Department of Anatomy and Cell Biology, School of Medicine, Hanyang University, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 1429206
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2013.28.2.295
Abstract
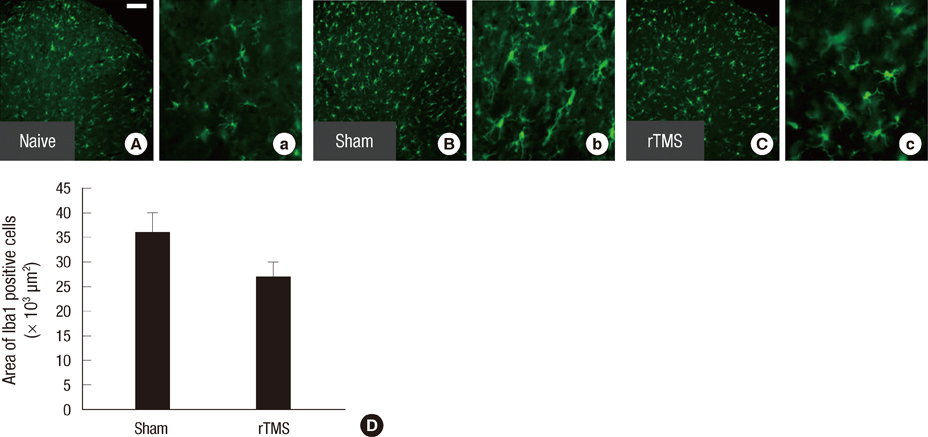
- Spinal cord injury (SCI) causes not only loss of sensory and motor function below the level of injury but also chronic pain, which is difficult and challenging of the treatment. Repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation (rTMS) to the motor cortex, of non-invasive therapeutic methods, has the motor and sensory consequences and modulates pain in SCI-patients. In the present study, we studied the effectiveness of rTMS and the relationship between the modulation of pain and the changes of neuroglial expression in the spinal cord using a rat SCI-induced pain model. Elevated expressions of Iba1 and GFAP, specific microglial and astrocyte markers, was respectively observed in dorsal and ventral horns at the L4 and L5 levels in SCI rats. But in SCI rats treated with 25 Hz rTMS for 8 weeks, these expressions were significantly reduced by about 30%. Our finding suggests that this attenuation of activation by rTMS is related to pain modulation after SCI. Therefore, rTMS might provide an alternative means of attenuating neuropathic pain below the level of SCI.
MeSH Terms
-
Animals
Astrocytes/*cytology
Calcium-Binding Proteins/metabolism
Disease Models, Animal
Immunohistochemistry
Male
Microfilament Proteins/metabolism
Microglia/*cytology
Nerve Tissue Proteins/metabolism
Neuralgia/etiology
Rats
Rats, Sprague-Dawley
Spinal Cord Injuries/complications/pathology/*therapy
*Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation
Calcium-Binding Proteins
Microfilament Proteins
Nerve Tissue Proteins
Figure
Reference
-
1. Hulsebosch CE. From discovery to clinical trials: treatment strategies for central neuropathic pain after spinal cord injury. Curr Pharm Des. 2005. 11:1411–1420.2. Nakae A, Nakai K, Yano K, Hosokawa K, Shibata M, Mashimo T. The animal model of spinal cord injury as an experimental pain model. J Biomed Biotechnol. 2011. 2011:939023.3. Willis A, Mihalevich M, Neff RA, Mendelowitz D. Three types of postsynaptic glutamatergic receptors are activated in DMNX neurons upon stimulation of NTS. Am J Physiol. 1996. 271:R1614–R1619.4. Salter MW. Cellular neuroplasticity mechanisms mediating pain persistence. J Orofac Pain. 2004. 18:318–324.5. Wasner G, Lee BB, Engel S, McLachlan E. Residual spinothalamic tract pathways predict development of central pain after spinal cord injury. Brain. 2008. 131:2387–2400.6. Hains BC, Waxman SG. Activated microglia contribute to the maintenance of chronic pain after spinal cord injury. J Neurosci. 2006. 26:4308–4317.7. Colburn RW, Rickman AJ, DeLeo JA. The effect of site and type of nerve injury on spinal glial activation and neuropathic pain behavior. Exp Neurol. 1999. 157:289–304.8. Kim SJ, Park SM, Cho YW, Jung YJ, Lee DG, Jang SH, Park HW, Hwang SJ, Ahn SH. Changes in expression of mRNA for interleukin-8 and effects of interleukin-8 receptor inhibitor in the spinal dorsal horn in a rat model of lumbar disc herniation. Spine. 2011. 36:2139–2146.9. Lindia JA, McGowan E, Jochnowitz N, Abbadie C. Induction of CX3CL1 expression in astrocytes and CX3CR1 in microglia in the spinal cord of a rat model of neuropathic pain. J Pain. 2005. 6:434–438.10. Park HW, Ahn SH, Kim SJ, Seo JM, Cho YW, Jang SH, Hwang SJ, Kwak SY. Changes in spinal cord expression of fractalkine and its receptor in a rat model of disc herniation by autologous nucleus pulposus. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2011. 36:E753–E760.11. Sweitzer SM, Colburn RW, Rutkowski M, DeLeo JA. Acute peripheral inflammation induces moderate glial activation and spinal IL-1beta expression that correlates with pain behavior in the rat. Brain Res. 1999. 829:209–221.12. Grunhaus L, Dannon PN, Schreiber S, Dolberg OH, Amiaz R, Ziv R, Lefkifker E. Repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation is as effective as electroconvulsive therapy in the treatment of nondelusional major depressive disorder: an open study. Biol Psychiatry. 2000. 47:314–324.13. Kim YH, You SH, Ko MH, Park JW, Lee KH, Jang SH, Yoo WK, Hallett M. Repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation-induced corticomotor excitability and associated motor skill acquisition in chronic stroke. Stroke. 2006. 37:1471–1476.14. Lomarev MP, Kim DY, Richardson SP, Voller B, Hallett M. Safety study of high-frequency transcranial magnetic stimulation in patients with chronic stroke. Clin Neurophysiol. 2007. 118:2072–2075.15. Pridmore S, Oberoi G. Transcranial magnetic stimulation applications and potential use in chronic pain: studies in waiting. J Neurol Sci. 2000. 182:1–4.16. Pridmore S, Oberoi G, Marcolin M, George M. Transcranial magnetic stimulation and chronic pain: current status. Australas Psychiatry. 2005. 13:258–265.17. Saitoh Y, Hirayama A, Kishima H, Shimokawa T, Oshino S, Hirata M, Tani N, Kato A, Yoshimine T. Reduction of intractable deafferentation pain due to spinal cord or peripheral lesion by high-frequency repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation of the primary motor cortex. J Neurosurg. 2007. 107:555–559.18. Defrin R, Grunhaus L, Zamir D, Zeilig G. The effect of a series of repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulations of the motor cortex on central pain after spinal cord injury. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2007. 88:1574–1580.19. Bae YK, Kim SJ, Seo JM, Cho YW, Ahn SH, Kang IS, Park HW, Hwang S. Effects of continuous repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation on pain response in spinal cord injured rat. J Korean Acad Rehabil Med. 2010. 34:259–264.20. Gwak YS, Hulsebosch CE. Remote astrocytic and microglial activation modulates neuronal hyperexcitability and below-level neuropathic pain after spinal injury in rat. Neuroscience. 2009. 161:895–903.21. Gruner JA. A monitored contusion model of spinal cord injury in the rat. J Neurotrauma. 1992. 9:123–128.22. Anderson AJ, Robert S, Huang W, Young W, Cotman CW. Activation of complement pathways after contusion-induced spinal cord injury. J Neurotrauma. 2004. 21:1831–1846.23. Basso DM, Beattie MS, Bresnahan JC. A sensitive and reliable locomotor rating scale for open field testing in rats. J Neurotrauma. 1995. 12:1–21.24. Canovero S, Barbara MM, Zollino G. Canovero S, editor. Noninvasive stimulation for choronic pain. Textbook of therapeutic cortical stimulation. 2009. NY: Nova Science Publishers Inc.;113–179.25. Johnson S, Summers J, Pridmore S. Changes to somatosensory detection and pain thresholds following high frequency repetitive TMS of the motor cortex in individuals suffering from chronic pain. Pain. 2006. 123:187–192.26. Canavero S, Bonicalzi V, Dotta M, Vighetti S, Asteggiano G, Cocito D. Transcranial magnetic cortical stimulation relieves central pain. Stereotact Funct Neurosurg. 2002. 78:192–196.27. Ben-Shachar D, Gazawi H, Riboyad-Levin J, Klein E. Chronic repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation alters beta-adrenergic and 5-HT2 receptor characteristics in rat brain. Brain Res. 1999. 816:78–83.28. Wang HY, Crupi D, Liu J, Stucky A, Cruciata G, Di Rocco A, Friedman E, Quartarone A, Ghilardi MF. Repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation enhances BDNF-TrkB signaling in both brain and lymphocyte. J Neurosci. 2011. 31:11044–11054.29. Leo RJ, Latif T. Repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation (rTMS) in experimentally induced and chronic neuropathic pain: a review. J Pain. 2007. 8:453–459.30. Lefaucheur JP, Drouot X, Menard-Lefaucheur I, Keravel Y, Nguyen JP. Motor cortex rTMS restores defective intracortical inhibition in chronic neuropathic pain. Neurology. 2006. 67:1568–1574.31. Lefaucheur JP, Hatem S, Nineb A, Menard-Lefaucheur I, Wendling S, Keravel Y, Nguyen JP. Somatotopic organization of the analgesic effects of motor cortex rTMS in neuropathic pain. Neurology. 2006. 67:1998–2004.32. Pleger B, Janssen F, Schwenkreis P, Volker B, Maier C, Tegenthoff M. Repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation of the motor cortex attenuates pain perception in complex regional pain syndrome type I. Neurosci Lett. 2004. 356:87–90.33. Yoon YW, Dong H, Arends JJ, Jacquin MF. Mechanical and cold allodynia in a rat spinal cord contusion model. Somatosens Mot Res. 2004. 21:25–31.34. Choi Y, Yoon YW, Na HS, Kim SH, Chung JM. Behavioral signs of ongoing pain and cold allodynia in a rat model of neuropathic pain. Pain. 1994. 59:369–376.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Effects of Continuous Repetitive Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation on Pain Response in Spinal Cord Injured Rat
- Effects of Functional Magnetic Stimulation on the Functional Recovery in a Rat Model of Spinal Cord Injury
- Repetitive Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation for Limb-Kinetic Apraxia in Parkinson's Disease
- Safety Review for Clinical Application of Repetitive Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation
- Application of Non-invasive Brain Stimulation on Dysphagia after Stroke