Yonsei Med J.
2012 Nov;53(6):1159-1164. 10.3349/ymj.2012.53.6.1159.
Xanthogranulomatous Pyelonephritis in Korean Children
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Urology, Pusan National University School of Medicine, Research Institute for Convergence of Biomedical Science and Technology, Pusan National University Yangsan Hospital, Yangsan, Korea. toughkil76@naver.com
- KMID: 1414259
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2012.53.6.1159
Abstract
- PURPOSE
Xanthogranulomatous pyelonephritis (XGP) is rare among children. In most cases, XGP is diffusely or focally enlarged, mimicking the neoplastic process. The aim of this study was to examine clinical characteristics and outcomes of Korean children with XGP.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Fourteen children (9 boys, 5 girls) with XGP were reviewed retrospectively. The cohort included 2 children managed at our institution and 12 children reported in the Korean literature. The patients' records were reviewed with respect to age at diagnosis, clinical presentation, management method, and other characteristic features.
RESULTS
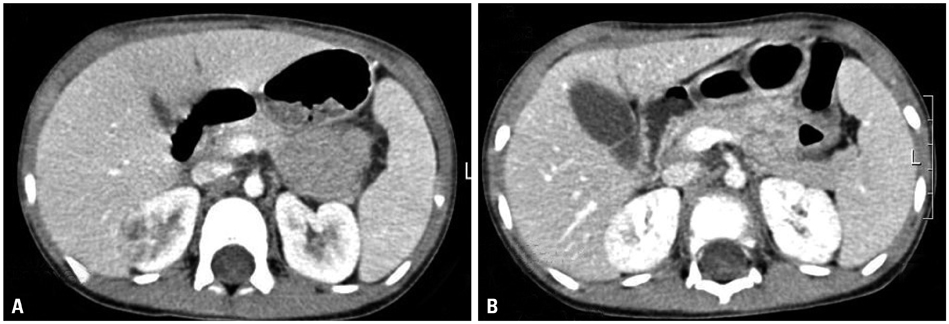
The mean age was 79.4+/-66.5 months (range 1-168 months). Common clinical presentations included fever (85.7%), abdominal pain (57.1%), and palpable mass (28.6%). Laboratory abnormalities included leukocytosis (57.1%), anemia (57.1%), and pyuria (57.1%). The types of XGP that were diagnosed based on preoperative radiologic studies included the focal form in 9 children and the diffuse form in 5. Thirteen children underwent nephrectomy, and 1 child received conservative medical therapy.
CONCLUSION
The possibility of XGP should be considered if a child is diagnosed with a renal mass, especially if it is a small renal mass associated with fever, leukocytosis, or stone. Nephrectomy is the treatment of choice for the diffuse form, whereas partial nephrectomy or conservative medical therapy may be indicated to manage focal XGP.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Hammadeh MY, Nicholls G, Calder CJ, Buick RG, Gornall P, Corkery JJ. Xanthogranulomatous pyelonephritis in childhood: pre-operative diagnosis is possible. Br J Urol. 1994. 73:83–86.
Article2. Parsons MA, Harris SC, Longstaff AJ, Grainger RG. Xanthogranulomatous pyelonephritis: a pathological, clinical and aetiological analysis of 87 cases. Diagn Histopathol. 1983. 6:203–219.3. Hendrickson RJ, Lutfiyya WL, Karrer FM, Furness PD 3rd, Mengshol S, Bensard DD. Xanthogranulomatous pyelonephritis. J Pediatr Surg. 2006. 41:e15–e17.
Article4. Ahn SY, Kim CC, Cho JH. A case of xanthogranulomatous pyelonephritis in child. Korean J Urol. 1977. 18:541–544.5. Jung GW, Jeong MK, Yoon JB. Xanthogranulomatous pyelonephritis in childhood: a case report. Korean J Urol. 1986. 27:911–914.6. Jeong KS, Kim DS, Cho JH. A cases of xanthogranulomatous pyelonephritis in children. Korean J Urol. 1994. 35:82–85.7. Chung HS, Hwang JC, Suh HJ, Jung SY, Baek YK. Bilateral xanthogranulomatous pyelonephritis in a child. Korean J Urol. 1996. 37:98–100.8. Yim SB, Kwon CK, Lee JH, Shin JS, Yim JS, Hwang MH, et al. A case of xanthogranulomatous pyelonephritis in children. Korean J Urol. 1997. 38:1117–1120.9. Choi SH, Lee JH, Cho SR. Xanthogranulomatous pyelonephritis in a child. Korean J Urol. 2005. 46:1231–1234.10. Lee HN, Kim KH, Ryu IW, Han MC, Chung WS. Xanthogranulomatous pyelonephritis in an infant. Korean J Urol. 2006. 47:1367–1370.
Article11. Samuel M, Duffy P, Capps S, Mouriquand P, Williams D, Ransley P. Xanthogranulomatous pyelonephritis in childhood. J Pediatr Surg. 2001. 36:598–601.
Article12. Sugie S, Tanaka T, Nishikawa A, Yoshimi N, Kato K, Mori H, et al. Fine-needle aspiration cytology of xanthogranulomatous pyelonephritis. Urology. 1991. 37:376–379.
Article13. Petronic V, Buturovic J, Isvaneski M. Xanthogranulomatous pyelonephritis. Br J Urol. 1989. 64:336–338.
Article14. Tolia BM, Iloreta A, Freed SZ, Fruchtman B, Bennett B, Newman HR. Xanthogranulomatous pyelonephritis: detailed analysis of 29 cases and a brief discussion of atypical presentations. J Urol. 1981. 126:437–442.
Article15. Anhalt MA, Cawood CD, Scott R Jr. Xanthogranulomatous pyelonephritis: a comprehensive review with report of 4 additional cases. J Urol. 1971. 105:10–17.
Article16. Kural AR, Akaydin A, Oner A, Ozbay G, Solok V, Oruc N, et al. Xanthogranulomatous pyelonephritis in children and adults. Br J Urol. 1987. 59:383–385.
Article17. Levy M, Baumal R, Eddy AA. Xanthogranulomatous pyelonephritis in children. Etiology, pathogenesis, clinical and radiologic features, and management. Clin Pediatr (Phila). 1994. 33:360–366.18. Zugor V, Schott GE, Labanaris AP. Xanthogranulomatous pyelonephritis in childhood: a critical analysis of 10 cases and of the literature. Urology. 2007. 70:157–160.
Article19. Hartman DS, Davis CJ Jr, Goldman SM, Isbister SS, Sanders RC. Xanthogranulomatous pyelonephritis: sonographic--pathologic correlation of 16 cases. J Ultrasound Med. 1984. 3:481–488.
Article20. Tiu CM, Chou YH, Chiou HJ, Lo CB, Yang JY, Chen KK, et al. Sonographic features of xanthogranulomatous pyelonephritis. J Clin Ultrasound. 2001. 29:279–285.
Article21. Kim JC. US and CT findings of xanthogranulomatous pyelonephritis. Clin Imaging. 2001. 25:118–121.
Article22. Kenny PJ. Pollack HM, McClennan BL, Dyer R, editors. Xanthogranulomatous pyelonephritis. Clinical Urography. 2000. Vol. 1:2nd ed. Philadelphia: WB Saunders;952–962.23. Marteinsson VT, Due J, Aagenaes I. Focal xanthogranulomatous pyelonephritis presenting as renal tumour in children. Case report with a review of the literature. Scand J Urol Nephrol. 1996. 30:235–239.24. Rasoulpour M, Banco L, Mackay IM, Hight DW, Berman MM. Treatment of focal xanthogranulomatous pyelonephritis with antibiotics. J Pediatr. 1984. 105:423–425.
Article25. Ho CI, Wen YK, Chen ML. Xanthogranulomatous pyelonephritis successfully treated with antibiotics only. J Chin Med Assoc. 2008. 71:643–645.
Article