Clin Orthop Surg.
2012 Sep;4(3):242-245. 10.4055/cios.2012.4.3.242.
Modified Mason-Allen Suture Bridge Technique: A New Suture Bridge Technique with Improved Tissue Holding by the Modified Mason-Allen Stitch
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Hanyang University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 2Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Kyung Hee University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. shoulderrhee@hanmail.net
- KMID: 1392988
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4055/cios.2012.4.3.242
Abstract
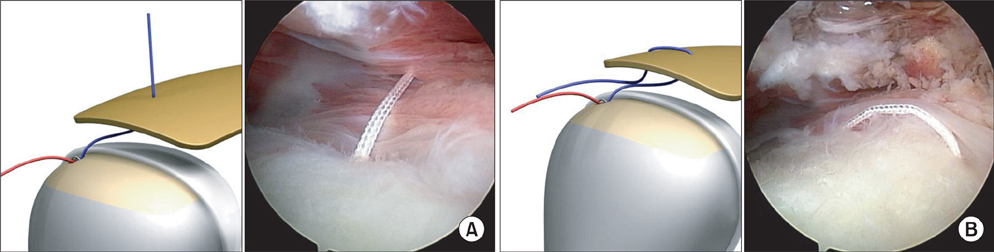
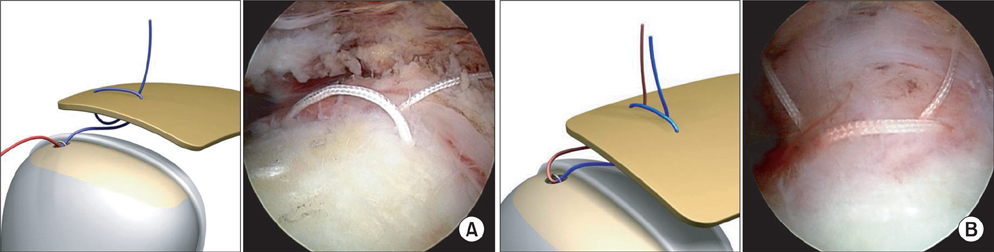
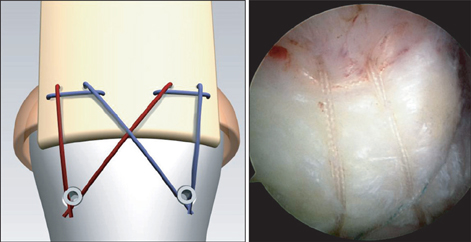
- We present a new method of suture bridge technique for medial row fixation using a modified Mason-Allen stitch instead of a horizontal mattress. Medial row configuration of the technique is composed of the simple stitch limb and the modified Mason-Allen stitch limb. The limbs are passed through the tendon by a shuttle relay. The simple stitch limb passes the cuff once and the modified Mason-Allen stitch limb passes three times which creates a rip stop that prevents tendon pull-out. In addition, the Mason-Allen suture bridge configuration is basically a knotless technique which has an advantage of reducing a possibility of strangulation of the rotator cuff tendon, impingement or irritation that may be caused by knot.
Keyword
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
A Modified Mac Suture Bridge Technique: Clinical and Radiological Outcomes of the Treatment of Rotator Cuff Tear with Poor Tissue Quality
Sang Jin Cheon, Hyo Yeol Lee, Sung Jin Ahn
J Korean Orthop Assoc. 2017;52(5):392-402. doi: 10.4055/jkoa.2017.52.5.392.
Reference
-
1. Accousti KJ, Flatow EL. Technical pearls on how to maximize healing of the rotator cuff. Instr Course Lect. 2007. 56:3–12.2. Toussaint B, Schnaser E, Lafosse L, Bahurel J, Gobezie R. A new approach to improving the tissue grip of the medial-row repair in the suture-bridge technique: the "modified lasso-loop stitch". Arthroscopy. 2009. 25(6):691–695.
Article3. Demirhan M, Atalar AC, Kilicoglu O. Primary fixation strength of rotator cuff repair techniques: a comparative study. Arthroscopy. 2003. 19(6):572–576.
Article4. Gerber C, Schneeberger AG, Beck M, Schlegel U. Mechanical strength of repairs of the rotator cuff. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1994. 76(3):371–380.
Article5. Rhee YG, Vishvanathan T, Thailoo BK, Rojpornpradit T, Lim CT. The '3 sister portals' for arthroscopic repair of massive rotator cuff tears. Tech Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2007. 8(2):53–57.
Article6. Ma CB, MacGillivray JD, Clabeaux J, Lee S, Otis JC. Biomechanical evaluation of arthroscopic rotator cuff stitches. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2004. 86(6):1211–1216.
Article7. Park MC, Elattrache NS, Ahmad CS, Tibone JE. "Transosseous-equivalent" rotator cuff repair technique. Arthroscopy. 2006. 22(12):1360.e1–1360.e5.
Article8. Park MC, Tibone JE, ElAttrache NS, Ahmad CS, Jun BJ, Lee TQ. Part II: Biomechanical assessment for a footprint-restoring transosseous-equivalent rotator cuff repair technique compared with a double-row repair technique. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2007. 16(4):469–476.
Article9. Cummins CA, Murrell GA. Mode of failure for rotator cuff repair with suture anchors identified at revision surgery. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2003. 12(2):128–133.
Article10. Barmakian JT, Lin H, Green SM, Posner MA, Casar RS. Comparison of a suture technique with the modified Kessler method: resistance to gap formation. J Hand Surg Am. 1994. 19(5):777–781.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Is the UU Stitch Really Alternative to Modified MA (Mason-Allen) Stitch for Rotator Cuff Repair?: Biomechanical Comparative Study of UU to Modified MA Stitch
- Biomechanical Comparison of the Modified ML (Mattress Locking) Suture and the Modified MA (Mason-Allen) Suture in Rotator Cuff Repairs
- Short-Term Results of a Modified Kidner Procedure Using a Suture Bridge Technique for Symptomatic Type II Accessory Navicular
- Arthroscopic Rotator Cuff Repair: Double Rows & Suture Bridge Technique
- A Modified Mac Suture Bridge Technique: Clinical and Radiological Outcomes of the Treatment of Rotator Cuff Tear with Poor Tissue Quality