Ann Lab Med.
2012 May;32(3):234-237. 10.3343/alm.2012.32.3.234.
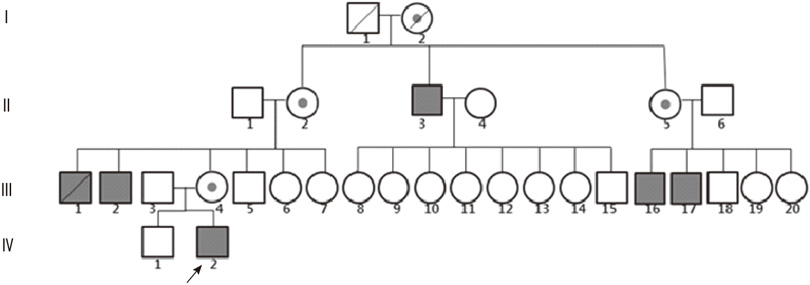
X-Linked Spondyloepiphyseal Dysplasia Tarda: Identification of a TRAPPC2 Mutation in a Korean Pedigree
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Laboratory Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. chez@catholic.ac.kr
- 2Department of Orthopedic Surgery, The Catholic University of Korea College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 1381692
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3343/alm.2012.32.3.234
Abstract
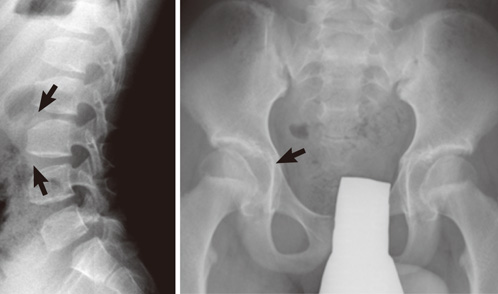
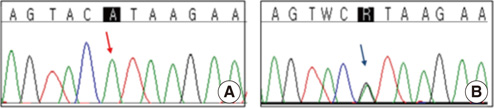
- Spondyloepiphyseal dysplasia (SED) comprises a heterogeneous group of skeletal dysplasias that primarily affect the epiphyses and vertebral bodies. Patients affected by SED usually exhibit short stature and experience early development of degenerative osteoarthritis. SED is subdivided into congenita and tarda forms according to the age at onset and clinical severity, and further subdivided into genetically different forms according to the mode of inheritance and the gene involved. We report a 14-yr-old Korean male who presented with a disproportionately short stature and a short trunk. A pedigree analysis of 3 generations with 6 affected persons revealed an X-linked recessive mode of inheritance. Mutation analysis of the TRAPPC2 (previously called SEDL) gene, the only gene associated with X-linked spondyloepiphyseal dysplasia tarda (X-linked SEDT; MIM 313400), was performed, and a splice-donor site mutation in intron 3 of the TRAPPC2 gene (c.93+5G>A) was identified in the proband and in his unaffected mother (a heterozygote). This mutation is one of the 2 most frequent mutations reported in the medical literature, and is known to result in exon 3 skipping. This is the first report of a genetically confirmed X-linked SEDT case in Korea and highlights the importance of recognizing the mode of inheritance in the diagnosis of X-linked SEDT.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Three Cases of Spondyloepiphyseal Dysplasia Tarda in One Korean Family
Sang Wan Chung, Eun Ha Kang, Yun Jong Lee, You-Jung Ha, Yeong Wook Song
Yonsei Med J. 2016;57(5):1290-1293. doi: 10.3349/ymj.2016.57.5.1290.
Reference
-
1. Fiedler J, Le Merrer M, Mortier G, Heuertz S, Faivre L, Brenner RE. X-linked spondyloepiphyseal dysplasia tarda: Novel and recurrent mutations in 13 European families. Hum Mutat. 2004. 24:103.
Article2. Gedeon AK, Tiller GE, Le Merrer M, Heuertz S, Tranebjaerg L, Chitayat D, et al. The molecular basis of X-linked spondyloepiphyseal dysplasia tarda. Am J Hum Genet. 2001. 68:1386–1397.
Article3. Gedeon AK, Colley A, Jamieson R, Thompson EM, Rogers J, Sillence D, et al. Identification of the gene (SEDL) causing X-linked spondyloepiphyseal dysplasia tarda. Nat Genet. 1999. 22:400–404.
Article4. Wynne-Davies R, Gormley J. The prevalence of skeletal dysplasias. An estimate of their minimum frequency and the number of patients requiring orthopaedic care. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1985. 67:133–137.
Article5. Langer LO Jr. Spondyloepiphysial dysplasia tarda. Hereditary chondrodysplasia with characteristic vertebral configuration in the adult. Radiology. 1964. 82:833–839.6. Szpiro-Tapia S, Sefiani A, Guilloud-Bataille M, Heuertz S, Le Marec B, Frézal J, et al. Spondyloepiphyseal dysplasia tarda: linkage with genetic markers from the distal short arm of the X chromosome. Hum Genet. 1988. 81:61–63.
Article7. Xia XY, Cui YX, Zhou YC, Zhou X, Shi YC, Wei L, et al. A novel insertion mutation in the SEDL gene results in X-linked spondyloepiphyseal dysplasia tarda in a large Chinese pedigree. Clin Chim Acta. 2009. 410:39–42.
Article8. Gécz J, Hillman MA, Gedeon AK, Cox TC, Baker E, Mulley JC. Gene structure and expression study of the SEDL gene for spondyloepiphyseal dysplasia tarda. Genomics. 2000. 69:242–251.
Article9. Tiller GE, Hannig VL, Dozier D, Carrel L, Trevarthen KC, Wilcox WR, et al. A recurrent RNA-splicing mutation in the SEDL gene causes X-linked spondyloepiphyseal dysplasia tarda. Am J Hum Genet. 2001. 68:1398–1407.
Article10. MacKenzie JJ, Fitzpatrick J, Babyn P, Ferrero GB, Ballabio A, Billingsley G, et al. X linked spondyloepiphyseal dysplasia: a clinical, radiological, and molecular study of a large kindred. J Med Genet. 1996. 33:823–828.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case with Spondyloepiphyseal Dysplasia Tarda with TRAPPC2 Mutation
- Three Cases of Spondyloepiphyseal Dysplasia Tarda in One Korean Family
- A Case of Spondyloepiphyseal Dysplasia Tarda (SEDT) Misdiagnosed as Ankylosing Spondylitis
- Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis and Thoracic Myelopathy in Spondyloepiphyseal Dysplasia Congenita: A Case Report
- A Case of Spondyloepiphyseal Dysplasia Congenita