Ann Lab Med.
2012 Jul;32(4):283-288. 10.3343/alm.2012.32.4.283.
Role of Plasma Exchange in ABO-incompatible Kidney Transplantation
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Laboratory Medicine, Yonsei University Health System, Seoul, Korea. hyunok1019@yuhs.ac
- 2Department of Surgery, Yonsei University Health System, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 1380088
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3343/alm.2012.32.4.283
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
In the past, ABO incompatibility was an absolute contraindication for solid organ transplantation. However, multiple recent trials have suggested strategies for overcoming the reactions between graft antigens and recipient antibodies that cause graft rejection. In this study, we determined the usefulness of plasma exchange (PE) for removing anti-A/B antibodies that cause hyperacute/acute humoral graft rejection in patients undergoing ABO-incompatible kidney transplantation.
METHODS
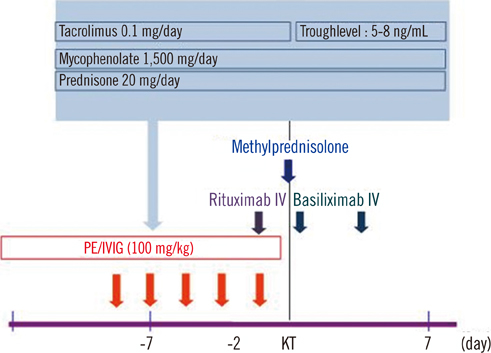
In our study, 12 patients underwent ABO-incompatible kidney transplantation. All recipients received pre-transplantation conditioning by PE or intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG) administration. After pre-transplantation conditioning, anti-A/B antibody titers were evaluated, and transplantation was performed when the titer was below 1:8. To assess the transplantation outcome, anti-A/B antibody titers, creatinine level, estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR), and proteinuria levels were measured.
RESULTS
Anti-A/B antibody titers were below 1:8 in all patients at the time of transplantation. eGFR measured on post-transplant day 14 showed that 10 patients had immediate recovery of graft function, while 2 patients had slow recovery of graft function. Short-term outcomes of ABO-incompatible kidney transplantation (measured as creatinine levels) after reducing anti-A/B antibody titers were similar to those of ABO-compatible kidney transplantation. After transplantation, the anti-A/B antibody titers were below 1:8 in 7 patients, but the remaining 5 patients required post-transplantation PE and IVIG treatment to prevent antigen-antibody reactions.
CONCLUSIONS
With the increasing demand for kidney donations, interest in overcoming the ABO incompatibility barrier has increased. PE may be an important breakthrough in increasing the availability of kidneys for transplantation.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
ABO Blood-Group System/*immunology
Adult
*Blood Group Incompatibility/immunology
Creatinine/blood
Female
Glomerular Filtration Rate
Graft Rejection/therapy
Humans
Immunoglobulins, Intravenous/therapeutic use
Isoantibodies/immunology/physiology
Kidney Transplantation/*immunology
Male
Middle Aged
*Plasma Exchange
Proteinuria
Transplantation Conditioning
Transplantation Immunology
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
The Effect of Bortezomib on Antibody-Mediated Rejection after Kidney Transplantation
Juhan Lee, Beom Seok Kim, Yongjung Park, Jae Geun Lee, Beom Jin Lim, Hyeon Joo Jeong, Yu Seun Kim, Kyu Ha Huh
Yonsei Med J. 2015;56(6):1638-1642. doi: 10.3349/ymj.2015.56.6.1638.Therapeutic Plasma Exchange Using the Spectra Optia Cell Separator Compared With the COBE Spectra
Do-kyun Kim, Sinyoung Kim, Seok Hoon Jeong, Hyun Ok Kim, Hyung Jik Kim
Ann Lab Med. 2015;35(5):506-509. doi: 10.3343/alm.2015.35.5.506.
Reference
-
1. KONOS 2009 annual report. Korean Network for Organ Sharing. 2010.2. Szczepiorkowski ZM, Winters JL, Bandarenko N, Kim HC, Linenberger ML, Marques MB, et al. Guidelines on the use of therapeutic apheresis in clinical practice-evidence-based approach from the Apheresis Applications Committee of the American Society for Apheresis. J Clin Apher. 2010. 25:83–177.
Article3. Starzl TE, Marchioro TL, Talmage DW, Waddell WR. Splenectomy and thymectomy in human renal homotransplantation. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1963. 113:929–932.
Article4. Ishida H, Koyama I, Sawada T, Utsumi K, Murakami T, Sannomiya A, et al. Anti-AB titer changes in patients with ABO incompatibility after living related kidney transplantations: survey of 101 cases to determine whether splenectomies are necessary for successful transplantation. Transplantation. 2000. 70:681–685.5. Huh KH, Kim MS, Kim YS, Kim HJ, Kim HJ, Kim HO, et al. Options for successful renal transplantation in recipients with incompatible living donors: Severance Hospital experience. Clin Transpl. 2010. 323–326.6. Roback JD, editor. Technical manual. 2011. 17th ed. Bethesda: American Association of Blood Banks;907–911.7. Levey AS, Coresh J, Greene T, Marsh J, Stevens LA, Kusek JW, et al. Expressing the Modification of Diet in Renal Disease Study equation for estimating glomerular filtration rate with standardized serum creatinine values. Clin Chem. 2007. 53:766–772.
Article8. Kim SI, Rha KH, Lee JH, Kim HJ, Kwon K, Kim YS, et al. Favorable outcomes among recipients of living-donor nephrectomy using video-assisted minilaparotomy. Transplantation. 2004. 77:1725–1728.
Article9. Hur M, Moon HW, Kwon SW. Ortiz J, Andre J, editors. ABO-incompatible kidney transplantation. Understanding the complexities of kidney transplantation. 2011. InTech;332–348.
Article10. Kong JM, Lee DR, Jeong JH, Choi JH, Lee JO, Lee WR, et al. ABO blood group incompatible living donor kidney transplantation without splenectomy. J Korean Soc Transplant. 2009. 23:71–76.11. Moon HW, Yun YM, Hur M, Park JH, Lee HW, Chang SH, et al. An experience of ABO-incompatible kidney transplantation using plasmapheresis and anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody. Korean J Lab Med. 2009. 29:585–588.
Article12. Hellegering J, Visser J, Kloke HJ, D'Ancona FC, Hoitsma AJ, van der Vliet JA, et al. Poor early graft function impairs long-term outcome in living donor kidney transplantation. World J Urol. 2012. [Epub ahead of print].
Article13. Fidler ME, Gloor JM, Lager DJ, Larson TS, Griffin MD, Textor SC, et al. Histologic findings of antibody-mediated rejection in ABO blood-group-incompatible living-donor kidney transplantation. Am J Transplant. 2004. 4:101–107.
Article14. Gloor JM, Lager DJ, Fidler ME, Grande JP, Moore SB, Winters JL, et al. A Comparison of splenectomy versus intensive posttransplant antidonor blood group antibody monitoring without splenectomy in ABO-incompatible kidney transplantation. Transplantation. 2005. 80:1572–1577.
Article15. Toki D, Ishida H, Setoguchi K, Shimizu T, Omoto K, Shirakawa H, et al. Acute antibody-mediated rejection in living ABO-incompatible kidney transplantation: long-term impact and risk factors. Am J Transplant. 2009. 9:567–577.
Article16. Derksen R, Schuurman H, Meyling F, Struyvenberg A, Kater L. The efficacy of plasma exchange in the removal of plasma components. J Lab Clin Med. 1984. 104:346–354.17. Winters JL, Gloor JM, Pineda AA, Stegall MD, Moore SB. Plasma exchange conditioning for ABO-incompatible renal transplantation. J Clin Apher. 2004. 19:79–85.
Article18. Madore F, Lazarus JM, Brady HR. Therapeutic plasma exchange in renal diseases. J Am Soc Nephrol. 1996. 7:367–386.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- ABO-Incompatible Kidney Transplantation
- Initial ABO Antibody Titer as a Variable for Estimating Number of Therapeutic Plasma Exchange prior to ABO Incompatible Kidney Transplantation
- Analysis of the Results of ABO-Incompatible Kidney Transplantation: In Comparison with ABO-Compatible Kidney Transplantation
- Case of ABO-Incompatible Living Donor Kidney Transplantation without Blood Products in a Jehovah's Witness
- Successful Pediatric ABO-Incompatible Kidney Transplantation without Pretransplant Plasmapheresis: Report of a Case