J Vet Sci.
2011 Dec;12(4):353-361. 10.4142/jvs.2011.12.4.353.
Genotypic characterization of Staphylococcus aureus isolated from bovines, humans, and food in Indonesia
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Clinical Pathology, Faculty of Veterinary Medicine, Gadjah Mada University, Jl. Fauna 2, Karangmalang, Yogyakarta 55281, Indonesia. isrinasalasia@yahoo.com
- 2Department of Pharmacology, Faculty of Veterinary Medicine, Gadjah Mada University, Jl. Fauna 2, Karangmalang, Yogyakarta 55281, Indonesia.
- KMID: 1365019
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4142/jvs.2011.12.4.353
Abstract
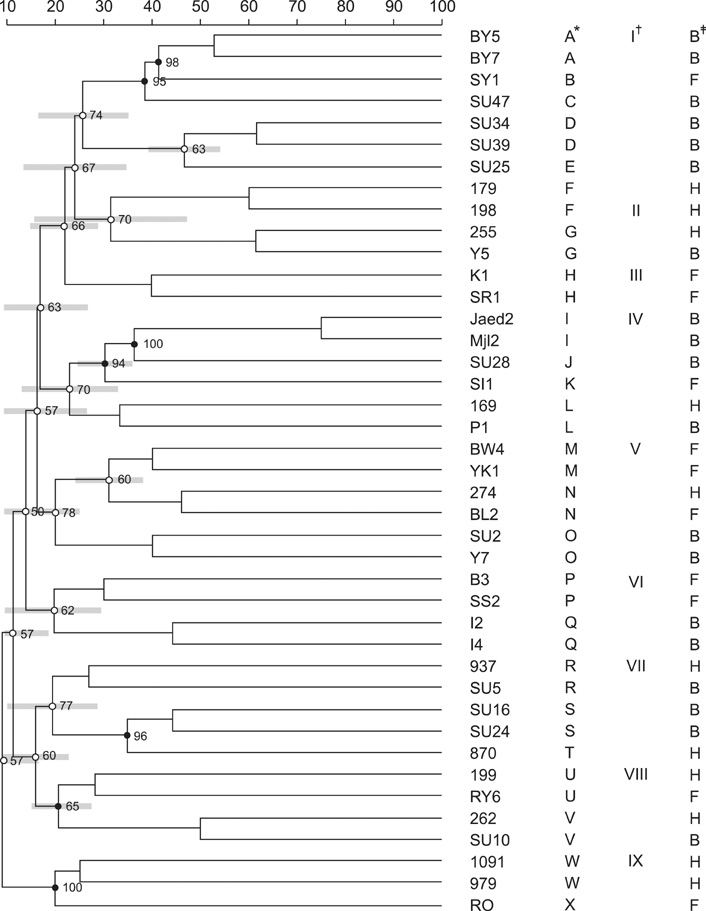
- The present study determined the genetic relationships between 41 Staphyloccocus (S.) aureus isolates from bovines, humans, and food using a single enzyme amplified fragment length polymorphism (AFLP) technique. We evaluated the prevalence of staphylococcal enterotoxin (SE) genes and other virulence gene determinants by PCR. The identification of S. aureus was based on culturing and biochemical tests, and by amplifying a specific section of the 23S rRNA gene. PCR amplification of the SE genes (sea, seb, sec, see, seg, seh, and sei) singly or in combination was observed. Most isolates of bovine origin harbored hla (84%) and cap5 (74%), while most isolates from humans harbored hla (73%), cap8 (91%), and fnbA (100%). Strains from food sources were positive for hla (100%), cap5 (100%), and cap8 (64%) unlike isolates from humans or bovines. A single enzyme AFLP analysis revealed a correlation between AFLP clusters of some strains and the source of the isolates The genotypic results of the present study might help to better understand the distribution of prevalent S. aureus clones among humans, bovines, and food and will help control S. aureus infections in Indonesia.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Amplified Fragment Length Polymorphism Analysis
Animals
Bacterial Proteins/genetics/metabolism
Cattle
Female
*Food Microbiology
Gene Expression Regulation, Bacterial
Humans
Indonesia/epidemiology
Mastitis, Bovine/epidemiology/microbiology
Phylogeny
Staphylococcal Infections/epidemiology/microbiology/*veterinary
Staphylococcus aureus/*genetics
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Profile of Antimicrobial Resistance of Staphylococcus aureus and Molecular Epidemiologic Characterization of Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) Isolated from Hands of People Using Multitude Facilities
Tae Sun Kim, Min Ji Kim, Sun Hee Kim, Hye-young Kee, Jin-jong Seo, Eun-Sun Kim, Yong-Un Moon, Puil Youl Ryu, Dong-Ryong Ha
Infect Chemother. 2012;44(4):289-298. doi: 10.3947/ic.2012.44.4.289.
Reference
-
1. Akineden Ö, Annemüller C, Hassan AA, Lämmler C, Wolter W, Zschöck M. Toxin genes and other characteristics of Staphylococcus aureus isolates from milk of cows with mastitis. Clin Diagn Lab Immunol. 2001. 8:959–964.
Article2. Annemüller C, Lämmler C, Zschöck M. Genotyping of Staphylococcus aureus isolated from bovine mastitis. Vet Microbiol. 1999. 69:217–224.3. Baba T, Takeuchi F, Kuroda M, Yuzawa H, Aoki K, Oguchi A, Nagai Y, Iwama N, Asano K, Naimi T, Kuroda H, Cui L, Yamamoto K, Hiramatsu K. Genome and virulence determinants of high virulence community-acquired MRSA. Lancet. 2002. 359:1819–1827.
Article4. Boerema JA, Clemens R, Brightwell G. Evaluation of molecular methods to determine enterotoxigenic status and molecular genotype of bovine, ovine, human and food isolates of Staphylococcus aureus. Int J Food Microbiol. 2006. 107:192–201.
Article5. Booth MC, Pence LM, Mahasreshti P, Callegan MC, Gilmore MS. Clonal associations among Staphylococcus aureus isolates from various sites of infection. Infect Immun. 2001. 69:345–352.
Article6. Brakstad OG, Aasbakk K, Maeland JA. Detection of Staphylococcus aureus by polymerase chain reaction amplification of the nuc gene. J Clin Microbiol. 1992. 30:1654–1660.
Article7. Brückler J, Schwarz S, Untermann F. Blobel H, Schlieβer T, editors. Staphylokokken-Infektionen und Enterotoxine band. II/I. Handbuch der bakteriellen Infektionen bei Tieren, 2. Auflage. 1994. Stuttgart: Gustav Fischer Verlag Jena.8. Ferens WA, Davis WC, Hamilton MJ, Park YH, Deobald CF, Fox L, Bohach G. Activation of bovine lymphocyte subpopulations by Staphylococcal enterotoxin C. Infect Immun. 1998. 66:573–580.
Article9. Griffiths AJF, Wessler SR, Lewontin RC, Gelbart WM, Suzuki DT, Miller JH. An Introduction to Genetic Analysis. 2004. 8th ed. New York: Freeman WH;782.10. Hayakawa Y, Hayashi M, Shimano T, Komae H, Takeuchi K, Endau M, Igarashi H, Hashimoto N, Takeuchi S. Production of exfoliative toxin A by Staphylococcus aureus isolated from mastitic cow's milk and farm bulk milk. J Vet Med Sci. 1998. 60:1281–1283.
Article11. Hookey JV, Richardson JF, Cookson BD. Molecular typing of Staphylococcus aureus based on PCR restriction fragment length polymorphism and DNA sequence analysis of the coagulase gene. J Clin Microbiol. 1998. 36:1083–1089.
Article12. Jarraud S, Cozon G, Vandenesch F, Bes M, Etienne J, Lina G. Involvement of enterotoxins G and I in staphylococcal toxic shock syndrome and staphylococcal scarlet fever. J Clin Microbiol. 1999. 37:2446–2449.
Article13. Johnson WM, Tyler SD, Ewan EP, Ashton FE, Pollard DR, Rozee KR. Detection of genes for enterotoxins, exfoliative toxins, and toxic shock syndrome toxin 1 in Staphylococcus aureus by the polymerase chain reaction. J Clin Microbiol. 1991. 29:426–430.
Article14. Jönsson K, Signäs C, Müller HP, Lindberg M. Two different genes encode fibronectin binding proteins in Staphylococcus aureus. The complete nucleotide sequence and characterization of the second gene. Eur J Biochem. 1991. 202:1041–1048.
Article15. Kuroda M, Ohta T, Uchiyama I, Baba T, Yuzawa H, Kobayashi I, Cui L, Oguchi A, Aoki K, Nagai Y, Kian J, Ito T, Kanamori M, Matsumaru H, Maruyama A, Murakami H, Hosoyama A, Mizutani-Ui Y, Takahashi NK, Sawano T, Inoue R, Kaito C, Sekimizu K, Hirakawa H, Kuhara S, Goto S, Yabuzaki J, Kanehisa M, Yamashita A, Oshima K, Furuya K, Yoshino C, Shiba T, Hattori M, Ogasawara N, Hayashi H, Hiramatsu K. Whole genome sequencing of meticillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Lancet. 2001. 357:1225–1240.16. Monday SR, Bohach GA. Use of multiplex PCR to detect classical and newly described pyrogenic toxin genes in staphylococcal isolates. J Clin Microbiol. 1999. 37:3411–3414.
Article17. Moore PCL, Lindsay JA. Genetic variation among hospital isolates of methicillin-sensitive Staphylococcus aureus: evidence for horizontal transfer of virulence genes. J Clin Microbiol. 2001. 39:2760–2767.
Article18. Nilsson H, Björk P, Dohlsten M, Antonsson P. Staphylococcal enterotoxin H displays unique MHC class II-binding properties. J Immunol. 1999. 163:6686–6693.19. Nishi J, Yoshinaga M, Miyanohara H, Kawahara M, Kawabata M, Motoya T, Owaki T, Oiso S, Kawakami M, Kamewari S, Koyama Y, Wakimoto N, Tokuda K, Manago K, Maruyama I. An epidemiologic survey of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus by combined use of mec-HVR genotyping and toxin genotyping in a university hospital in Japan. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol. 2002. 23:506–510.
Article20. Sandel MK, McKillip JL. Virulence and recovery of Staphylococcus aureus relevant to the food industry using improvements on traditional approaches. Food Control. 2004. 15:5–10.
Article21. Sheagren JN. Staphylococcus aureus: the persistent pathogen. N Engl J Med. 1984. 310:1368–1373.22. Soell M, Diab M, Haan-Archipoff G, Beretz A, Herbelin C, Poutrel B, Klein JP. Capsular polysaccharide types 5 and 8 of Staphylococcus aureus bind specifically to human epithelial (KB) cells, endothelial cells, and monocytes and induce release of cytokines. Infect Immun. 1995. 63:1380–1386.
Article23. Stephan R, Annemüller C, Hassan AA, Lämmler C. Characterization of enterotoxigenic Staphylococcus aureus strains isolated from bovine mastitis in north-east Switzerland. Vet Microbiol. 2001. 78:373–382.
Article24. Stewart CM. Hocking AD, editor. Staphylococcus aureus and Staphylococcal Enterotoxins. Foodborne Microorganisms of Public Health Importance. 2003. 6th ed. Sydney: The Food Microbiology Group of the Australian Institute of Food Science and Technology Inc.;359–379.25. Straub JA, Hertel C, Hammes WP. A 23S rDNA-targeted polymerase chain reaction-based system for detection of Staphylococcus aureus in meat starter cultures and dairy products. J Food Prot. 1999. 62:1150–1156.
Article26. Tsen HY, Chen TR. Use of the polymerase chain reaction for specific detection of type A, D and E enterotoxigenic Staphylococcus aureus in foods. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 1992. 37:685–690.27. Zhang S, Iandolo JJ, Stewart GC. The enterotoxin D plasmid of Staphylococcus aureus encodes a second enterotoxin determinant (sej). FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1998. 168:227–233.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Comparative studies on pheno- and genotypic properties of Staphylococcus aureus isolated from bovine subclinical mastitis in central Java in Indonesia and Hesse in Germany
- Detection of Multidrug Resistant Patterns and Associated - genes of Methicillin Resistant Staphylococcus aureus ( MRSA ) Isolated from Clinical Specimens
- A case of multiple furunculosis caused by methicillin-resistant staphylococcs aureus
- Comparison of pathogens and antimicrobial susceptibility of Staphylococcus aureus isolated from conventional and robotic milking herds
- Microbiological and genotypic factors affecting mortality in methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus bacteremia