Korean J Gastroenterol.
2012 Apr;59(4):282-288. 10.4166/kjg.2012.59.4.282.
Comparison of Treatments in Patients with Inoperable Stage IV Advanced Esophageal Cancer
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Kosin University College of Medicine, Busan, Korea. mipark@ns.kosinmed.or.kr
- 2Department of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery, Kosin University College of Medicine, Busan, Korea.
- 3Department of Therapeutic Radiology, Kosin University College of Medicine, Busan, Korea.
- KMID: 1364831
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4166/kjg.2012.59.4.282
Abstract
- BACKGROUND/AIMS
The aim of this study was to compare palliative treatments such as chemotherapy, chemoradiotherapy or radiotherapy with best supportive care in patients with inoperable advanced esophageal cancer.
METHODS
A total of 67 patients with inoperable advanced esophageal cancer visiting Kosin University Gospel Hospital between January 2000 and July 2010 were included in a retrospective analysis. Patients were categorized as having palliative treatment or best supportive care to compare their prognosis.
RESULTS
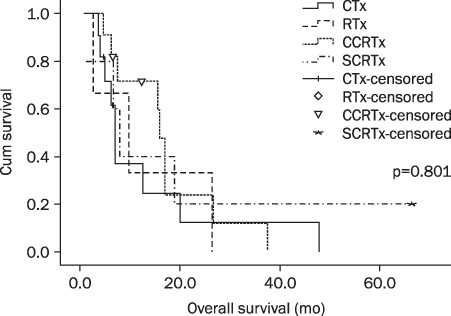
The median survival was 6.4 months in 67 patients. There was significant difference in median survival between the palliative and best supportive treatment (9.8 months vs. 4.5 months, p=0.01). The patients who underwent palliative treatment had superior 1-year and 3-year overall survival rate than those with best supportive treatment (27%, 10% vs. 5%, 5%, respectively). The 1-year and 3-year overall survival rate of palliative treatment was 18% (1-year overall survival rate) in chemotherapy, 33% (1-year overall survival rate) in radiotherapy, 45% and 9% in concurrent chemoradiotherapy, and 20% and 20% in sequential chemoradiotherapy, respectively.
CONCLUSIONS
These results may suggest that palliative treatments are more effective than best supportive care. Further prospective studies are still needed to elucidate beneficial effect of palliative treatments on inoperable advanced esophageal cancer.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Annual report on the cause of death statistics, 2009 [Internet]. 2010. cited 2010 December 29. Daejeon: Korea National Statistical Office;Available from: http://kosis.kr.2. Anderson SE, Minsky BD, Bains M, Kelsen DP, Ilson DH. Combined modality therapy in esophageal cancer: the memorial experience. Semin Surg Oncol. 2003. 21:228–232.3. O'Rourke I, Tait N, Bull C, Gebski V, Holland M, Johnson DC. Oesophageal cancer: outcome of modern surgical management. Aust N Z J Surg. 1995. 65:11–16.4. Esophageal Cancer Version 2. NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology, 2011 [Internet]. 2011. cited 2011 Jan 12. Fort Washington: National Comprehensive Cancer Network;Available from: http://www.nccn.org.5. Schmid EU, Alberts AS, Greeff F, et al. The value of radiotherapy or chemotherapy after intubation for advanced esophageal carcinoma--a prospective randomized trial. Radiother Oncol. 1993. 28:27–30.6. Greene FL, Page DL, Fleming ID, et al. AJCC cancer staging manual. 2002. 6th ed. New York: Springer-Verlag;91–98.7. WHO handbook for reporting results of cancer treatment. No. 48. 1979. Geneva: World Health Organization Offset Publication;22–26.8. National Cancer Institute. Cancer therapy evaluation program. Common toxicity criteria manual: common toxicity criteria. version 2.0. 1999. Bethesda: National Cancer Institute.9. Herskovic A, Martz K, al-Sarraf M, et al. Combined chemotherapy and radiotherapy compared with radiotherapy alone in patients with cancer of the esophagus. N Engl J Med. 1992. 326:1593–1598.10. Smith TJ, Ryan LM, Douglass HO Jr, et al. Combined chemoradiotherapy vs. radiotherapy alone for early stage squamous cell carcinoma of the esophagus: a study of the Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1998. 42:269–276.11. Ohtsu A, Boku N, Muro K, et al. Definitive chemoradiotherapy for T4 and/or M1 lymph node squamous cell carcinoma of the esophagus. J Clin Oncol. 1999. 17:2915–2921.12. Ishida K, Ando N, Yamamoto S, Ide H, Shinoda M. Phase II study of cisplatin and 5-fluorouracil with concurrent radiotherapy in advanced squamous cell carcinoma of the esophagus: a Japan Esophageal Oncology Group (JEOG)/Japan Clinical Oncology Group trial (JCOG9516). Jpn J Clin Oncol. 2004. 34:615–619.13. Natsugoe S, Ikeda M, Baba M, et al. Kyushu Study Group for Adjuvant Therapy of Esophageal Cancer. Long-term survivors of advanced esophageal cancer without surgical treatment: a multicenter questionnaire survey in Kyushu, Japan. Dis Esophagus. 2003. 16:239–242.14. Higuchi K, Koizumi W, Tanabe S, et al. A phase I trial of definitive chemoradiotherapy with docetaxel, cisplatin, and 5-fluorouracil (DCF-R) for advanced esophageal carcinoma: Kitasato digestive disease & oncology group trial (KDOG 0501). Radiother Oncol. 2008. 87:398–404.15. Bidoli P, Bajetta E, Stani SC, et al. Ten-year survival with chemotherapy and radiotherapy in patients with squamous cell carcinoma of the esophagus. Cancer. 2002. 94:352–361.16. Ku GY, Ilson DH. Preoperative therapy in esophageal cancer. Clin Adv Hematol Oncol. 2008. 6:371–379.17. Thomson IG, Smithers BM, Gotley DC, et al. Thoracoscopic-assisted esophagectomy for esophageal cancer: analysis of patterns and prognostic factors for recurrence. Ann Surg. 2010. 252:281–291.18. Crosby TD, Brewster AE, Borley A, et al. Definitive chemoradiation in patients with inoperable oesophageal carcinoma. Br J Cancer. 2004. 90:70–75.19. Aoyama N, Koizumi H, Minamide J, Yoneyama K, Isono K. Prognosis of patients with advanced carcinoma of the esophagus with complete response to chemotherapy and/or radiation therapy: a questionnaire survey in Japan. Int J Clin Oncol. 2001. 6:132–137.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Treatment of Esophageal Cancer
- Curative Radiotherapy of Supraglottic Cancer
- Clinical Factors to Predict the Response to Concurrent Chemoradiotherapy and Survival in Esophageal Cancer Patients
- Long-Term Survival in Stage IV Esophageal Adenocarcinoma with Chemoradiation and Serial Endoscopic Cryoablation
- Two Cases of Histopathologically Advanced (Stage IV)Early Gastric Cancer