Korean J Gastroenterol.
2011 Mar;57(3):166-172. 10.4166/kjg.2011.57.3.166.
The Seroprevalence Rate, Vaccination Rate and Seroconversion Rate of Hepatitis A in Central Region of Korea
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Dankook University College of Medicine, Cheonan, Korea. sm1213@paran.com
- 2Department of Pediatrics, Dankook University College of Medicine, Cheonan, Korea.
- 3Department of Nuclear Medicine, Dankook University College of Medicine, Cheonan, Korea.
- KMID: 1128355
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4166/kjg.2011.57.3.166
Abstract
- BACKGROUND/AIMS
Acute hepatitis A (HAV) is markedly increasing recently on. Some patients with acute hepatitis A show severe clinical course. The seroprevalence rate of IgG anti-HAV has been changing with the regions and the times. Vaccination and seroconversion rate of HAV are not well known. In this study, we aimed to study the difference of seroprevalence rate of IgG anti-HAV according to various clinical factors and to know the vaccination rate and seroconversion rate below 10 years old in the central region of South Korea including Cheonan city.
METHODS
Seven hundred seventy two subjects were included in the study from January to September 2009. We analyzed seroprevalence rate of IgG anti-HAV according to sex, age, region, and other viral markers. We interviewed the history of vaccination(1st, 2nd) and analyzed seroconversion rate according to vaccination time below 10 years old.
RESULTS
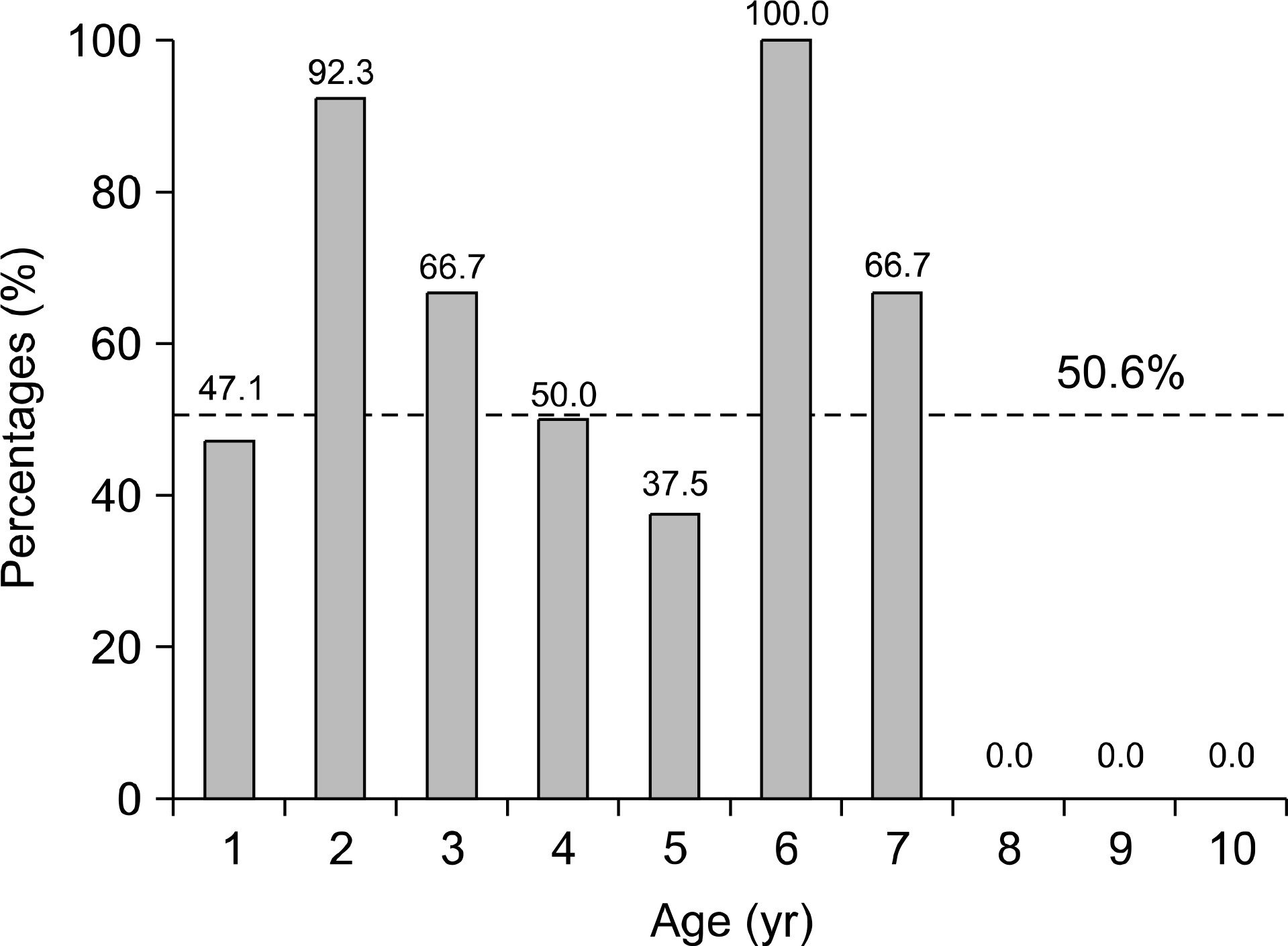
The total seroprevalence rate of IgG anti-HAV was 65.3%. The seroprevalence rate of IgG anti-HAV rate in 2nd, 3rd, and 4th decade was very low (1.9%, 18.8%, 44.8%). The vaccination rate of children was about 50%. The seroconversion rate after 1st, and 2nd vaccination were 85%, 96%.
CONCLUSIONS
Catch-up vaccination for teenagers and young adults is needed. Immunizing children with HAV vaccine as a routine schedule should be considered.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
Adolescents' and Parental Knowledge, Health Beliefs Toward Hepatitis A Vaccination
Seo Hee Yoon, Hyo Yeon Lee, Han Wool Kim, Kyoung Ae Kong, Kyung-Hyo Kim
Korean J Pediatr Infect Dis. 2013;20(3):147-160. doi: 10.14776/kjpid.2013.20.3.147.Seroprevalence of Anti-hepatitis B Virus, Anti-hepatitis A Virus, and Anti-varicella Zoster Virus Antibodies in Nursing Students from 2009 to 2013
Park Jin-Hee, Shon Joung-A
Korean J Nosocomial Infect Control. 2013;21(1):31-36. doi: 10.14192/kjnlc.2016.21.1.31.
Reference
-
References
1. Feinstone SM, Kapikian AZ, Purceli RH. Hepatitis A: detection by immune electron microscopy of a viruslike antigen associated with acute illness. Science. 1973; 182:1026–1028.
Article2. Hadler SC, Webster HM, Erben JJ, Swanson JE, Maynard JE. Hepatitis A in day-care centers. A community-wide assessment. N Engl J Med. 1980; 302:1222–1227.3. Lee CH, Chung KW, Moon YM, Yoo JY, Sub DJ, Lee SG. An outbreak of hepatitis A in Korean young adults in 1998 [abstract]. Korean J Gastroenterol. 1998; 32(Suppl 1):105A.4. André F, Van Damme P, Safary A, Banatvala J. Inactivated hepatitis A vaccine: immunogenicity, efficacy, safety and review of official recommendations for use. Expert Rev Vaccines. 2002; 1:9–23.
Article5. Jilg W, Bittner R, Bock HL, et al. Vaccination against hepatitis A: comparison of different short-term immunization schedules. Vaccine. 1992; 10(Suppl 1):S126–S128.
Article6. Van Damme P, Matheï C, Thoelen S, Meheus A, Safary A, André FE. Single dose inactivated hepatitis A vaccine: rationale and clinical assessment of the safety and immunogenicity. J Med Virol. 1994; 44:435–441.
Article7. DeFraites RF, Feighner BH, Binn LN, et al. Immunization of US sol-diers with a two-dose primary series of inactivated hepatitis A vaccine: early immune response, persistence of antibody, and response to a third dose at 1 year. J Infect Dis. 1995; 171(Suppl 1):S61–S69.
Article8. Müller R, Chriske H, Deinhardt F, et al. Hepatitis A vaccination: schedule for accelerated immunization. Vaccine. 1992; 10(Suppl 1):S124–S125.
Article9. Just M, Berger R. Reactogenicity and immunogenicity of inactivated hepatitis A vaccines. Vaccine. 1992; 10(Suppl 1):S110–S113.
Article10. Victor J, Knudsen JD, Nielsen LP, et al. Hepatitis A vaccine. A new convenient single-dose schedule with booster when long-term immunization is warranted. Vaccine. 1994; 12:1327–1329.
Article11. Hadler SC. Global impact of hepatitis A virus infection; changing patterns. Hollinger FB, Lemon SM, Margolis HS, editors. Viral hepatitis and liver diseases. Baltimore: Williams & Wilkins;1991. p. 14–20.12. Koff RS. Hepatitis A. Lancet. 1998; 351:1643–1649.
Article13. Weitz M, Siegl G. Variation among hepatitis A virus strains. I. Genomic variation detected by T1 oligonucleotide mapping. Virus Res. 1985; 4:53–67.
Article14. Sjogren MH. Hepatitis A. Feldman M, Friledman LS, Brandt LJ, editors. Sleigenger & Fordtran's gastrointestinal and liver disease. Vol 2. 8th ed.Philadelphia: Saunders;2006. p. 1639–1646.
Article15. Shapiro CN, Coleman PJ, McQuillan GM, Alter MJ, Margolis HS. Epidemiology of hepatitis A: seroepidemiology and risk groups in the USA. Vaccine. 1992; 10(Suppl 1):S59–S62.
Article16. Bell PB. Global epidemiology of hepatitis A: Implications for control strategies. 10th International Symposium on Viral Hepatitis and Liver Disease. 2000 Apr. 9–13;Atlanta, USA.2002.17. Nelson KE. Global changes in the epidemiology of hepatitis A virus infections. Clin Infect Dis. 2006; 42:1151–1152.
Article18. Hong WS, Kim CY. Seroepidemiology of type A and type B hepatitis in Seoul area. Korean J Intern Med. 1982; 25:19–26.19. Kim TW, Lee KJ. Antibody to hepatitis A antigen in children and adolescent in Korea. J Korean Pediatr Soc. 1982; 25:36–40.20. Lim DS, Cho KH, Kim HC. Seroepidemiological study on anti-HAV antibody in Cheon-Buk Province in 1989. Korean J Intern Med. 1992; 43:57–65.21. Sohn YM, Rho HO, Park MS, et al. The changing epidemiology of hepatitis A in children and the consideration of active immunization in Korea. Yonsei Med J. 2000; 41:34–39.
Article22. Yang DW, Lee YA, Shim JY, et al. A seroepidemiologic study on hepatitis A in Seoul, Korea. J Korean Pediatr Soc. 1999; 42:180–185.23. Song YB, Lee JH, Choi MS, et al. The age-specific seroprevalence of hepatitis A virus antibody in Korea. Korean J Hepatol. 2007; 13:27–33.24. Pramoolsinsap C. Acute hepatitis A and acquired immunity to hepatitis A virus in hepatitis B virus (HBV) carriers and in HBV- or hepatitis C virus-related chronic liver diseases in Thailand. J Viral Hepat. 2000; 7(Suppl 1):11–12.
Article25. Chu CM, Liaw YF. Increased incidence of fulminant hepatic failure in previously unrecognized HBsAg carriers with acute hepatitis independent of etiology. Infection. 2005; 33:136–139.
Article26. Sohn YM, Rho HO, Park MS, et al. The changing epidemiology of hepatitisA in children and the consideration of active immunization in Korea. Yonsei Med J. 2000; 41:34–39.27. Kim JH. Recent epidemiological status and vaccination of hepatitis A in Korea. J Korean Med Assoc. 2008; 51:110–118.
Article28. Iwarson S. Are we giving too many doses of hepatitis A and B vac-cines? Vaccine. 2002; 20:2017–2018.
Article29. Williams J, Bruden D, McMahon B, et al. Response to two doses of hepatitis A vaccine administered an average of 27 months apart. Antiviral Ther. 2000; 13:5.30. Landry P, Tremblay S, Darioli R, Genton B. Inactivated hepatitis A vaccine booster given at least 24 months after the primary dose. Vaccine. 2000; 19:399–402.31. Iwarson S, Lindh M, Widerström L. Excellent booster response 4–6 y after a single primary dose of an inactivated hepatitis A vaccine. Scand J Infect Dis. 2002; 34:110–111.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Positive seroconversion rate of hepatitis B antibody after hepatitis B vaccination by birth weight and gestational age
- The Seroconversion Rate of Hepatitis A Virus Vaccination among Patients with Hepatitis B Virus-Related Chronic Liver Disease in Korea
- A Seroepidemiologic Study of Hepatitis A Virus in the Healthy Children and Adolescent in Kyonggi-do Province
- Immunogenicity and Safety of Recombinant Hepatitis B Vaccine(Engerix B)
- Effect of Simultaneous Administration of Hepatitis B Vaccine with DPT and Oral Polio Vaccine