J Korean Med Sci.
2007 Aug;22(4):660-666. 10.3346/jkms.2007.22.4.660.
Ultrasonographic Findings of the Shoulder in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis and Comparison with Physical Examination
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Hallym University Sacred Heart Hospital, Anyang, Korea. kimha@hallym.ac.kr
- KMID: 1127083
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2007.22.4.660
Abstract
- The objectives of this study were: 1) to identify the ultrasonographic (US) abnormalities and 2) to compare the findings of physical examination with US findings in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients with shoulder pain. We studied 30 RA patients. Physical examination was performed systemically as follows: 1) area of tenderness; 2) range of passive and active shoulder motion; 3) impingement tests; 4) maneuvers for determining the location of the tendon lesions. US investigations included the biceps, the supraspinatus, infraspinatus, and subscapularis tendons; the subacromial-subdeltoid bursa; and the glenohumeral and acromioclavicular joints. Thirty RA patients with 35 painful and 25 non-painful shoulders were examined. The range of motion affected the most by shoulder pain was abduction. The most frequent US finding of shoulder joint was effusion in the long head of the biceps tendon. Among the rotator cuff tendons, subscapularis was the most frequently involved. Tendon tear was also common among non-painful shoulders. Physical examination used for the diagnosis of shoulder pain had low sensitivity and specificity for detecting abnormalities in the rheumatoid shoulder joint. In conclusion, US abnormalities showed frequent tendon tears in our RA patients. Physical examination had low sensitivity and specificity for detecting rotator cuff tear in the rheumatoid shoulder joint.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Adolescent
Adult
Aged
Arthritis, Rheumatoid/complications/*ultrasonography
Female
Humans
Male
Middle Aged
Physical Examination/*methods
Reproducibility of Results
Rotator Cuff/pathology/ultrasonography
Shoulder/pathology/*ultrasonography
Shoulder Joint/*ultrasonography
Shoulder Pain/etiology/ultrasonography
Tendons/pathology/ultrasonography
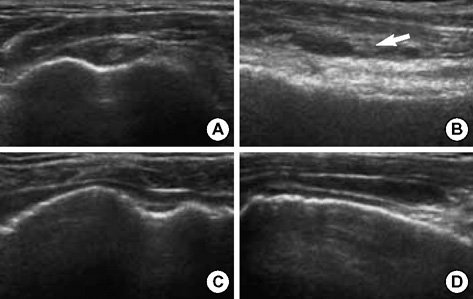
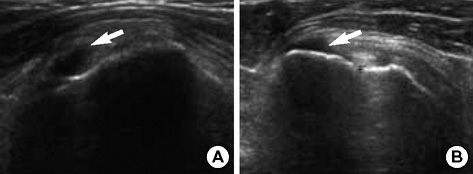
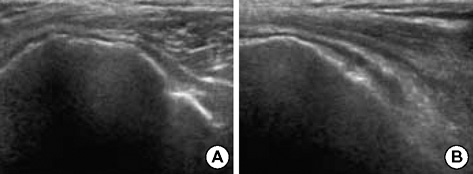
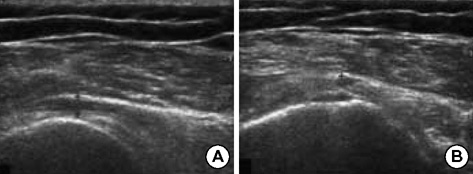
Figure
Reference
-
1. Alasaarela E, Suramo I, Tervonen O, Lahde S, Takalo R, Hakala M. Evaluation of humeral head erosions in rheumatoid arthritis: a comparison of ultrasonography, magnetic resonance imaging, computed tomography and plain radiography. Br J Rheumatol. 1998. 37:1152–1156.
Article2. Coari G, Paoletti F, Iagnocco A. Shoulder involvement in rheumatic diseases. Sonographic findings. J Rheumatol. 1999. 26:668–673.3. Norregaard J, Krogsgaard MR, Lorenzen T, Jensen EM. Diagnosing patients with longstanding shoulder joint pain. Ann Rheum Dis. 2002. 61:646–649.
Article4. Hermann KG, Backhaus M, Schneider U, Labs K, Loreck D, Zuhlsdorf S, Schink T, Fischer T, Hamm B, Bollow M. Rheumatoid arthritis of the shoulder joint: comparison of conventional radiography, ultrasound, and dynamic contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging. Arthritis Rheum. 2003. 48:3338–3349.
Article5. Naredo E, Aguado P, De Miguel E, Uson J, Mayordomo L, Gijon-Banos J, Martin-Mola E. Painful shoulder: comparison of physical examination and ultrasonographic findings. Ann Rheum Dis. 2002. 61:132–136.
Article6. Neer CS, Welsh RP. The shoulder in sports. Orthop Clin North Am. 1977. 8:583–591.
Article7. Hawkins RJ, Kennedy JC. Impingement syndrome in athletes. Am J Sports Med. 1980. 8:151–158.
Article8. Jobe FW, Jobe CM. Painful athletic injuries of the shoulder. Clin Orthop. 1983. 173:117–124.
Article9. Leroux JL, Thomas E, Bonnel F, Blotman F. Diagnostic value of clinical tests for shoulder impingement syndrome. Rev Rhum (Engl Ed). 1995. 62:423–428.10. Sheon RP, Moskowitz RW, Goldberg VM. Sheon RP, Moskowitz RW, Goldberg VM, editors. Upper limb disorders. Soft tissue rheumatic pain. 1987. Baltimore: Williams and Wilkins;79–129.11. Gilcreest EL. Dislocation and elongation of the long head of the biceps brachii. An analysis of 6 cases. Ann Surg. 1936. 104:118–138.12. Ptasznik R. van Holsbeeck MT, Introcaso JH, editors. Sonography of the shoulder. Musculoskeletal ultrasound. 2001. St. Louis: Mosby;464–516.13. Alasaarela EM, Alasaarela EL. Ultrasound evaluation of painful rheumatoid shoulders. J Rheumatol. 1994. 21:1642–1648.14. Naranjo A, Marrero-Pulido T, Ojeda S, Francisco F, Erausquin C, Rua-Figueroa I, Rodriguez-Lozano C, Hernandez-Socorro CR. Abnormal sonographic findings in the non-painful arthritic shoulder. Scand J Rheumatol. 2002. 31:17–21.15. Zehetgruber H, Lang T, Wurnig C. Distinction between supraspinatus, infraspinatus and subscapularis tendon tears with ultrasound in 332 surgically confirmed cases. Ultrasound Med Biol. 2002. 28:711–717.
Article16. Nelson MC, Leather GP, Nirschl RP, Pettrone FA, Freedman MT. Evaluation of the painful shoulder. A prospective comparison of magnetic resonance imaging, computerized tomographic arthrography, ultrasonography, and operative findings. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1991. 73:707–716.
Article17. Hermann KG, Backhaus M, Schneider U, Labs K, Loreck D, Zuhlsdorf S, Schink T, Fischer T, Hamm B, Bollow M. Rheumatoid arthritis of the shoulder joint: comparison of conventional radiography, ultrasound, and dynamic contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging. Arthritis Rheum. 2003. 48:3338–3349.
Article18. Strunk J, Lange U, Kurten B, Schmidt KL, Neeck G. Doppler sonographic findings in the long bicipital tendon sheath in patients with rheumatoid arthritis as compared with patients with degenerative diseases of the shoulder. Arthritis Rheum. 2003. 48:1828–1832.
Article19. Cofield RH. Current concepts review. Rotator cuff disease of the shoulder. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1985. 67:974–979.20. Bartolozzi A, Andreychik D, Ahmad S. Determinants of outcome in the treatment of rotator cuff disease. Clin Orthop. 1994. 308:90–97.
Article21. Smith AM, Sperling JW, Cofield RH. Rotator cuff repair in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2005. 87:1782–1787.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Ultrasonographic Evaluation of the Painful Hemiplegic Shoulder
- Ultrasonographic Findings in Rheumatoid Arthritis
- Analysis of Characteristics and Effect of Treatment for Shoulder Pain Patient Classified by Sonographic Findings
- Ultrasonographic and Physical Examination to Investigate the Cause of Painful Hemiplegic Shoulder
- Diagnosis and Treatment of Rheumatoid Shoulder