J Korean Acad Nurs.
2010 Feb;40(1):127-138. 10.4040/jkan.2010.40.1.127.
Development of a Structural Equation Model for Children's Adaptation in Divorced Families
- Affiliations
-
- 1College of Nursing Science, Kyung Hee University, Seoul, Korea. sunghshin@khu.ac.kr
- KMID: 1125572
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2010.40.1.127
Abstract
- PURPOSE
This study was designed to develop and test a structural model for children's adaptation in divorced families. The hypothetical model was constructed based on the Family Resilience Model by McCubbin and McCubbin.
METHODS
Data were collected using self-report questionnaires from 219 children (3-6th grade) in divorced families. The children attended one of 22 community agencies, 8 after-school programs, 3 elementary schools in three cities in South Korea. The collected data were analyzed using LISREL program to test the hypothetical model.
RESULTS
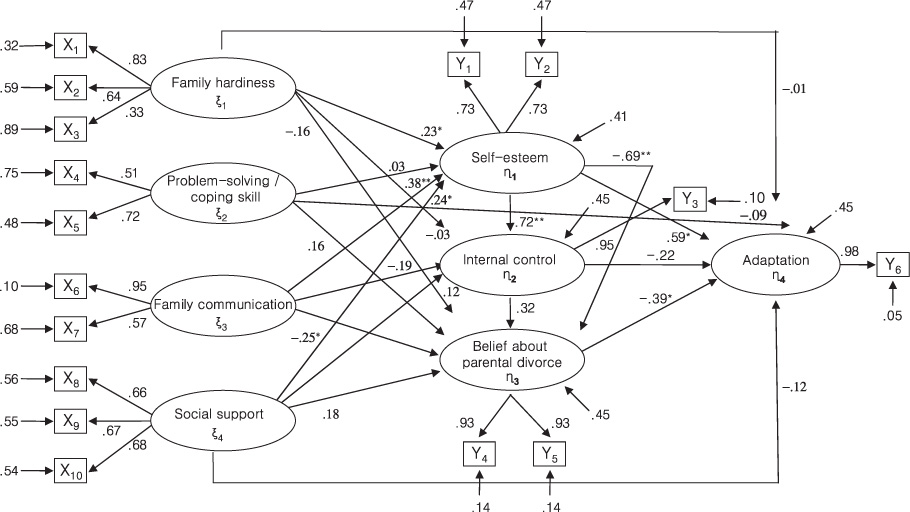
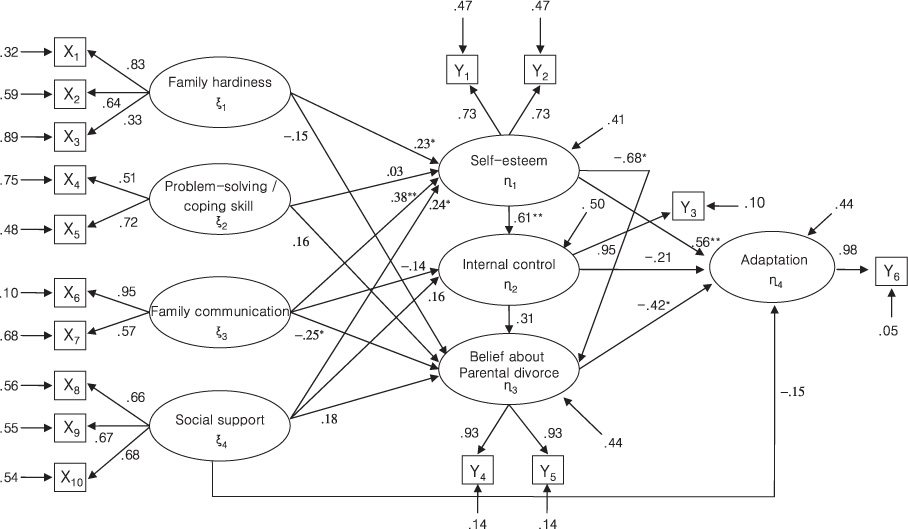
The modified model was constructed by deleting four paths in accordance with the statistical and theoretical criteria. Compared to the hypothetical model, the revised one had a better fit to the data. Self-esteem, and beliefs about parental divorce had direct effects, and family communication and internal control had indirect effects on children's adaptation in divorced families. These variables explained 56% of the variance in children's adaptation.
CONCLUSION
The modified model was supported by empirical data. This model could be applied to family nursing interventions with divorced families or any other suffering family transition. When working with children experiencing parental divorce, it is important for nurses to enhance children's self-esteem, family communication and to decrease children's negative beliefs about parental divorce to help in their adaptation.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Mental Distress of Children in Kirogi Families
Sung Hee Shin, Heeseung Choi, Mi Ja Kim
J Korean Acad Psychiatr Ment Health Nurs. 2014;23(4):208-216. doi: 10.12934/jkpmhn.2014.23.4.208.
Reference
-
1. Achenbach TM. Manual for the child behavior checklist 4-18 and 1990 profile. 1991. Burlington, VT: University of Vermont, Department of Psychiatry.2. Amato L, Keith B. Parental divorce and the well-being of children: A meta-analysis. Psychological Bulletin. 1991. 110:26–46.3. Amato PR. Children's adjustment to divorce: Theories, hypotheses and empirical support. Journal of Marriage and the Family. 1993. 02. 55:23–38.4. Bae BR. Lisrel structural equation model: Interative Lisrel. 2005. 2nd ed. Seoul: Chunglam Publishing.5. Bae J. Causal relationships between school adjustment of middle school students and related variables. Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing. 2008. 38:454–464.6. Barens H, Olson DH. Parent-adolescent communication, family inventories. 1982. Minneapolis, MN: University of Minnesota Press.7. Cho SA. Differences in risk factors and protective factors according to the level of psychological maladjustment of children of divorce. 2004. Daegu: Keimyung University;Unpublished master's thesis.8. Coopersmith S. Coopersmith self-esteem inventory. 1975. Palo Alto, CA: Consulting Psychologists Press.9. Dubow EF, Ulman DG. Assessing social support in elementary school children: The survey of children's social support. Journal of Clinical Child Psychology. 1989. 1:52–64.10. Emery R. Postdivorce family life for children: Postdivorce family. 1999. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage.11. Han MH. The relation of stress and perceived social support to problem behavior. 1996. Seoul: Seoul National University;Unpublished doctoral dissertation.12. Han SS, Kim KM. Influencing factors on self-esteem in adolescents. Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing. 2006. 36:37–44.13. Hetherington EM. Cowan PA, Hetherington EM, editors. The role of individual differences and family relationships in children's coping with divorce and remarriage. Family transitions. 1991. Hillsdale, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates;163–192.14. Hetherington M, Stanley-Hogan M. The adjustment of children with divorced parents: A risk and resiliency perspective. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry. 1999. 40:129–140.15. Jeon BJ. Self-esteem: A test of its measurability. Yonsei Nonchong. 1974. 1:107–130.16. Joo SH. Study of the factors that influence child's adaptation after divorce in child's point of view. 2004. Seoul: Sungkyunkwan University;Unpublished doctoral dissertation.17. Kelly JB. Children's adjustment in conflicted marriage and divorce: A decade review of research. Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry. 2000. 39:963–972.18. Kim SK, Kang MH. The path-analysis among riskprotective factors on the resilience of children from divorced family. Korean Journal of Child Studies. 2005. 26:261–278.19. A report of population and households. Korea National Statistical Office. 2009. Retrieved December 10, 2009. from http://kosis.kr/metadata/main.jsp?c_id=1962004.20. Kurdek LA, Berg B. Children's beliefs about parental divorce scale: Psychometric characteristics and concurrent validity. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology. 1987. 55:712–718.21. Lee YA. A study of perceived family adaptation in patient with chronic renal failure. 1995. Seoul: Yonsei University;Unpublished doctoral dissertation.22. Leske JS, Jiricka MK. Impact of family demands and family strengths and capabilities on family well-being and adaptation after critically injury. American Journal of Critical Care. 1998. 7:383–392.23. Lin SI. Coping and adaptation in family of children with cerebral palsy. Exceptional Children. 2000. 66:201–217.24. McCubbin MA, McCubbin HI. Danielson CB, Bisell BH, Fry PW, editors. Families coping with illness: The resiliency model of family stress, adjustment and adaptation. Families, health, and illness: Perspectives on coping and intervention. 1993. St. Louis, MO: Mosby;21–63.25. McCubbin MA, McCubbin HI, Thompson AI. McCubbin HI, Thompson AI, MaCubbin MA, editors. Family hardiness index (FHI). Family assessment: Resiliency, coping and adaptation-Inventory for research and practice. 1986. Madison, WI: University of Wisconsin;239–305.26. McCubbin HI, Olson D, Larsen A. McCubbin HI, Thompson AI, MaCubbin MA, editors. Family crisis oriented personal evaluation scales (F-COPES). Family assessment: Resiliency, coping and adaptation-Inventory for research and practice. 1981. Madison, WI: University of Wisconsin;455–507.27. Min HY. Circumplex model and parent-adolescent communication. 1990. Seoul: Yonsei University;Unpublished master's thesis.28. Min HY. The Influence of the perceived controllability of stress situation and locus of control on children's coping behaviors with hassles. 1999. Seoul: Seoul National University;Unpublished doctoral dissertation.29. Nam YO, Kim JH. A study on the factors influencing school resilience of adolescents in the alcoholic families. Korean Journal of Youth Studies. 2003. 10:199–221.30. Oh KJ, Lee HL, Hong KY, Ha EH. K-CBCL: Korean children behavior check list. 1997. Seoul: Chungangjucksung Publication.31. Rosenberg M. Society and the adolescent self-image. 1965. Princeton, NJ: Princeton University Press.32. Sandler I, Kim L, Tein J. Locus of Control as Stress moderator and mediator in child of divorce. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology. 1997. 25:145–155.33. Sim MK. Testing of resiliency model of families of children with cancer. 2004. Seoul: Yonsei University;Unpublished doctoral dissertation.34. Stolberg AL, Mahler J. Enhancing treating gains in a school-based intervention for children of divorce through skill building, parental involvement and transfer procedures. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology. 1994. 62:147–156.35. Walsh F. Strengthening family resilience. 1998. New York, NY: Guilford.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Influence of Resiliency Factors on Adaptation in Families of Children with Cancer
- Structural Equation Model for Caregiving Experience of Families Providing Care for Family Members with Mental Disorders
- How Job Stress and Psychological Adaptation Predicting Interpersonal Needs Among Female Migrant Manufacturing Workers in China: A Structural Equation Model
- An Analysis on the Pathway between Family Stress and Adaptation in Families with Mentally Handicapped Children
- A Comparative Study of Health State and School Adaptation between Children in Divorced Family and in Normal Family