Clin Orthop Surg.
2009 Jun;1(2):118-121. 10.4055/cios.2009.1.2.118.
Fracture of a Polyethylene Tibial Post in a Scorpio Posterior-Stabilized Knee Prosthesis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Korea University College of Medicine, Guro Hospital, Seoul, Korea. osman@korea.ac.kr
- KMID: 1122643
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4055/cios.2009.1.2.118
Abstract
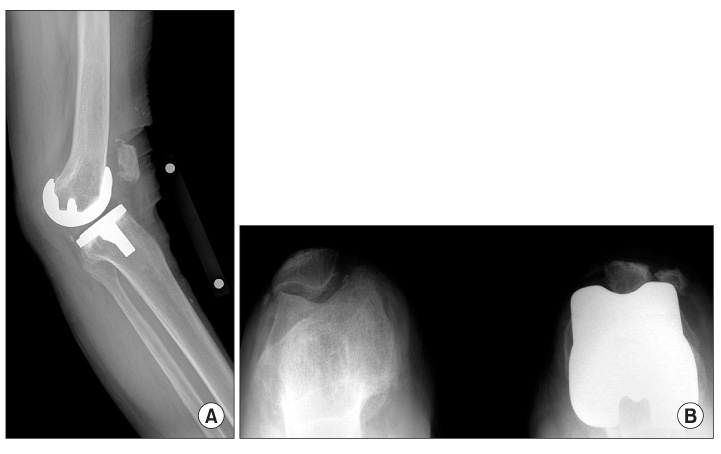
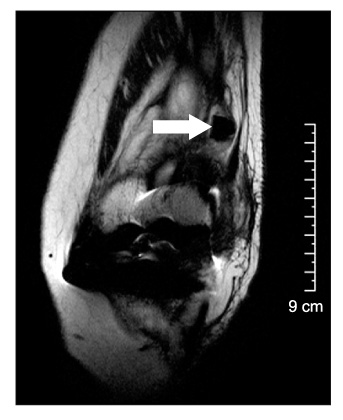
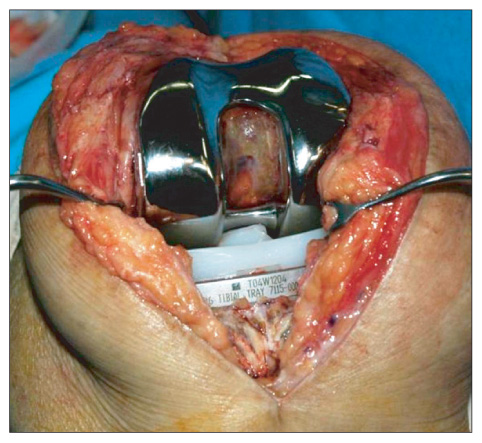
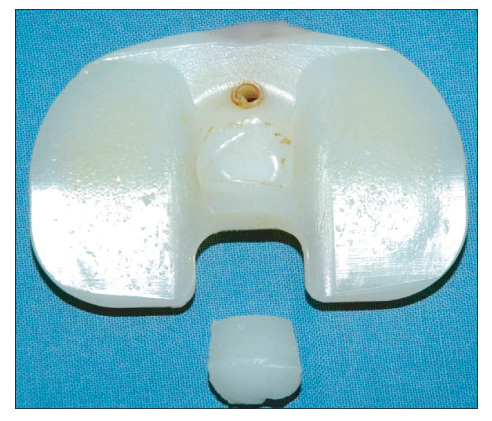
- We report the case of a polyethylene tibial post fracture in a 72-year-old woman 14 months after a Scorpio posterior-stabilized (PS) total knee arthroplasty. The polyethylene wear was found around the fracture site of the post, especially over the anterior aspect of the post base. The failure mechanism of the post fracture in the present case was anterior impingement with excessive wear over the base of the anterior aspect of the tibial post, which became a stress-riser of post and cam articulation. This is the first report of a polyethylene tibial post fracture of a Scorpio PS prosthesis.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Kelly MA, Clarke HD. Long-term results of posterior cruciate-substituting total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2002. (404):51–57.
Article2. Thadani PJ, Vince KG, Ortaaslan SG, Blackburn DC, Cudiamat CV. ten- to 12-year followup of the Insall-Burstein I total knee prosthesis. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2000. (380):17–29.3. Callaghan JJ, O'Rourke MR, Goetz DD, Schmalzried TP, Campbell PA, Johnston RC. Tibial post impingement in posterior-stabilized total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2002. (404):83–88.
Article4. Banks SA, Harman MK, Hodge WA. Mechanism of anterior impingement damage in total knee arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2002. 84:Suppl 2. 37–42.
Article5. Mestha P, Shenava Y, D'Arcy JC. Fracture of the polyethylene tibial post in posterior stabilized (Insall Burstein II) total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2000. 15(6):814–815.
Article6. Clarke HD, Math KR, Scuderi GR. Polyethylene post failure in posterior stabilized total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2004. 19(5):652–657.
Article7. Chiu YS, Chen WM, Huang CK, Chiang CC, Chen TH. Fracture of the polyethylene tibial post in a NexGen posterior-stabilized knee prosthesis. J Arthroplasty. 2004. 19(8):1045–1049.
Article8. Li G, Papannagari R, Most E, et al. Anterior tibial post impingement in a posterior stabilized total knee arthroplasty. J Orthop Res. 2005. 23(3):536–541.
Article9. Babis GC, Trousdale RT, Morrey BF. The effectiveness of isolated tibial insert exchange in revision total knee arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2002. 84(1):64–68.
Article10. Engh GA, Koralewicz LM, Pereles TR. Clinical results of modular polyethylene insert exchange with retention of total knee arthroplasty components. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2000. 82(4):516–523.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Recurrent Dislocation of the Posterior-Stabilized Total Knee Prosthesis
- Breakage of the Implant after Total Knee Replacement: Cases Report
- Dislocation of Tibial Insert after Fixed Bearing TKA using Minimal Invasive Surgery: A Case Report
- Advantage of Minimal Anterior Knee Pain and Long-term Survivorship of Cemented Single Radius Posterior-Stabilized Total Knee Arthroplasty without Patella Resurfacing
- The Effect of Tibial Posterior Slope on Contact Force and Ligaments Stresses in Posterior-Stabilized Total Knee Arthroplasty-Explicit Finite Element Analysis