Yonsei Med J.
2007 Oct;48(5):748-753. 10.3349/ymj.2007.48.5.748.
Endoscopic Laser Surgery for Subglottic Stenosis in Wegener's Granulomatosis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Otorhinolaryngology Head & Neck Surgery, Rabin Medical Center, Petah Tikva, and Sackler Faculty of Medicine, Tel Aviv University, Tel Aviv, Israel. asaf890@bezeqint.net
- 2Pulmonary Institute, Rabin Medical Center, Petah Tikva, and Sackler Faculty of Medicine, Tel Aviv University, Tel Aviv, Israel.
- 3Department of Pathology, Rabin Medical Center, Petah Tikva, and Sackler Faculty of Medicine, Tel Aviv University, Tel Aviv, Israel.
- KMID: 1122610
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2007.48.5.748
Abstract
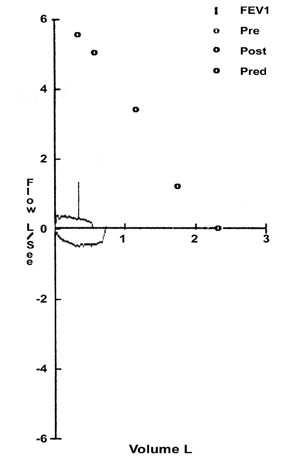
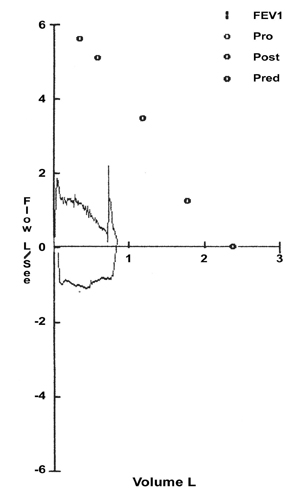
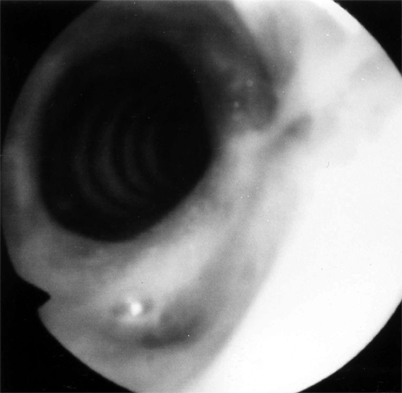
- PURPOSE: Wegener's granulomatosis (WG) is a rare multisystem inflammatory disease, which infrequently involves the subglottic area and trachea. Treatment usually involves the use of immunosuppressive agents with corticosteroids. Some patients, however, continue to have symptoms of airway obstruction after clinical remission following the standard therapeutic regimen. Objective: To investigate laser treatment for subglottic stenosis in five patients suffering from WG. MATERIALS AND METHODS: We endoscopically treated 5 patients with subglottic stenosis due to WG and airway obstruction by Nd:YAG and CO2 lasers. One of the patients had preoperative tracheostomy and after treatment was decannulated and could not breathe without dyspnea. Another patient required stenting of the subglottic area. RESULTS: All five patients were able to breathe without dyspnea after the treatment. Three patients were treated with an Nd:YAG laser but needed repeated laser treatment every four to six months, whenever they complained of dyspnea. The other two patients were treated with a CO2 laser; one of these patients had preoperative tracheostomy and was treated twice by CO2 laser and decannulated, with no further difficulty in breathing. The follow-up period was 1-5 years. CONCLUSIONS: Nd:YAG and CO2 lasers are recommended in the treatment of subglottic stenosis (SS) due to WG, particularly when the stenosis is in continuity or close proximity to the vocal cords.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. O'Devaney K, Ferlito A, Hunter BC, Devaney SL, Rinaldo A. Wegener's granulomatosis of the head and neck. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 1998. 107:439–445.2. Dedo HH, Sooy CD. Endoscopic laser repair of posterior glottic, subglottic and tracheal stenosis by division or micro-trapdoor flap. Laryngoscope. 1984. 2:445–450.
Article3. Walton EW. Giant-cell granuloma of the respiratory tract (Wegener's granulomatosis). Br Med J. 1958. 34:265–270.
Article4. DeRemee RA, McDonald TJ, Harrison EG, Coles DT. Wegener's granulomatosis.Anatomic correlates, a proposed classification. Mayo Clin Proc. 1976. 51:777–781.5. Arauz JC, Fonseca R. Wegener's granulomatosis appearing initially in the trachea. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 1982. 91:593–596.
Article6. McDonald TJ, Neel HB 3rd, DeRemee RA. Wegener's granulomatosis of the subglottis and the upper portion of the trachea. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 1982. 91:588–592.
Article7. Alaani A, Hogg RP, Drake Lee AB. Wegener's granulomatosis and subglottic stenosis: management of the airway. J Laryngol Otol. 2004. 118:786–790.
Article8. Nishiike S, Kato T, Nagai M, Konishi M, Sakata Y. Management and follow-up of localized Wegener's granulomatosis: a review of five cases. Acta Otolaryngol. 2004. 124:1103–1108.
Article9. Eliachar I, Chan J, Akst L. New approaches to the management of subglottic stenosis in Wegener's granulomatosis. Cleve Clin J Med. 2002. 69:Suppl 2. SII149–SII151.
Article10. Herridge MS, Pearson FG, Downey GP. Subglottic stenosis complicating Wegener's granulomatosis: surgical repair as a viable treatment option. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 1996. 111:961–966.
Article11. Crockett DM, Reynolds BN. Laryngeal laser surgery. Otolaryngol Clin North Am. 1990. 23:49–66.
Article12. Lebovics RS, Hoffman GS, Leavitt RY, Kerr GS, Travis WD, Kammerer W, et al. The management of subglottic stenosis in patients with Wegener's granulomatosis. Laryngoscope. 1992. 102:1341–1345.
Article13. Strong MS, Healy GB, Vaughan CW, Fried MP, Shapshay S. Endoscopic management of laryngeal stenosis. Otolaryngol Clin North Am. 1979. 12:797–805.14. Gluth MB, Shinners PA, Kasperbauer JL. Subglottic stenosis associated with Wegener's granulomatosis. Laryngoscope. 2003. 113:1304–1307.
Article15. Utzig MJ, Warzelhan J, Wertzel H, Berwanger I, Hasse J. Role of thoracic surgery and interventional bronchoscopy in Wegener's granulomatosis. Ann Thorac Surg. 2002. 74:1948–1952.
Article16. Stegeman CA, Tervaert JW, de Jong PE, Kallenberg CG. Dutch Co-Trimoxazole Wegener Study Group. Trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole (co-trimoxazole) for the prevention of relapses of Wegener's granulomatosis. N Engl J Med. 1996. 335:16–20.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Subglottic Stenosis in Wegener's granulomatosis: A Case Report
- Relapsing Polychondritis with Subglottic Stenosis Diagnosed after Tonsillectomy: A case report
- Localized Wegener's Granulomatosis in Maxillary Sinus
- A Case of Cortical Vein Thrombosis in Wegener's Granulomatosis
- A Case of Wegener's Granulomatosis Mimicking Behcet's Disease