Clin Orthop Surg.
2010 Mar;2(1):28-33. 10.4055/cios.2010.2.1.28.
Anti-TNF-alpha Therapy for Ankylosing Spondylitis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Kosin University Gospel Hospital, Busan, Korea. jhson@ns.kosinmed.or.kr
- KMID: 1110346
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4055/cios.2010.2.1.28
Abstract
-
BACKGROUND: This review evaluated the safety and efficacy of etanercept in patients with ankylosing spondylitis (AS).
METHODS
Of 59 patients with AS, this study reviewed 11 patients who were refractory to conventional therapy and treated with etanercept from September 2005 to January 2008. The mean follow-up duration was 13.6 months. The general improvement was evaluated by the Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Index (BASDAI), and adverse effects, complications and inflammatory markers were also assessed.
RESULTS
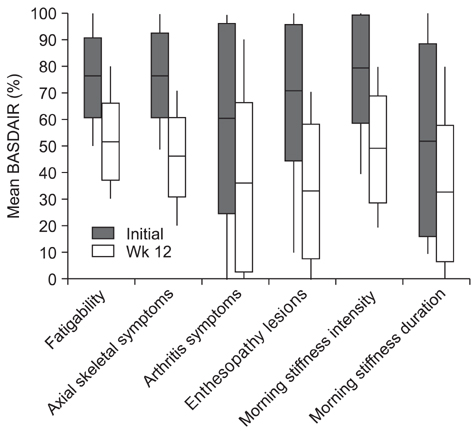
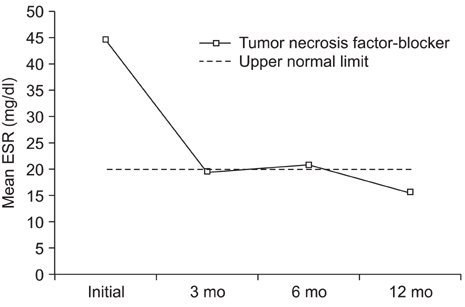
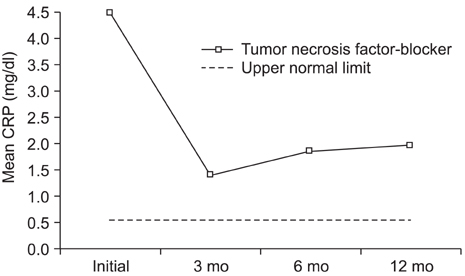
The mean BASDAI decreased from 7.1 +/- 1.6 before treatment to 4.2 +/- 1.8 at 3 months after the etanercept treatment (p = 0.001). The mean erythrocyte sedimentation rate and C-reactive protein were decreased significantly by the etanercept treatment. The greatest improvement in symptoms was enthesitis, followed by skin involvement and morning stiffness. There was a significant difference in the improvement in BASDAI along with the follow up duration (p = 0.04). A serious infection was observed as a complication in 1 case.
CONCLUSIONS
These results suggest that etanercept can induce significant improvement in most patients with less damage. A trial of tumor necrosis factor inhibition is indicated in all AS patients who do not achieve adequate disease control with disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs, such as methotrexate, leflunomide etc. The patients treated with etanercept should be educated about the possibility of infection and monitored closely.
MeSH Terms
-
Adult
Anti-Inflammatory Agents, Non-Steroidal/*administration & dosage/adverse effects
Antirheumatic Agents/*administration & dosage/adverse effects
Blood Sedimentation
C-Reactive Protein/analysis
Drug Administration Schedule
Female
Humans
Immunoglobulin G/*administration & dosage/adverse effects
Injections, Subcutaneous
Male
Middle Aged
Receptors, Tumor Necrosis Factor/*administration & dosage
Spondylitis, Ankylosing/diagnosis/*drug therapy
Tumor Necrosis Factor-alpha/*antagonists & inhibitors
Young Adult
Figure
Reference
-
1. Braun J, Brandt J, Listing J, Rudwaleit M, Sieper J. Biologic therapies in the spondyloarthritis: new opportunities, new challenges. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2003. 15(4):394–407.
Article2. Braun J, de Keyser F, Brandt J, Mielants H, Sieper J, Veys E. New treatment options in spondyloarthropathies: increasing evidence for significant efficacy of anti-tumor necrosis factor therapy. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2001. 13(4):245–249.
Article3. Davis JC Jr, van der Heijde DM, Braun J, et al. Efficacy and safety of up to 192 weeks of etanercept therapy in patients with ankylosing spondylitis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2008. 67(3):346–352.
Article4. van Eijk IC, Peters MJ, Serne EH, et al. Microvascular function is impaired in ankylosing spondylitis and improves after tumour necrosis factor alpha blockade. Ann Rheum Dis. 2009. 68(3):362–366.
Article5. Reed MR, Taylor AL. Tumor necrosis factor inhibitors in ankylosing spondylitis. Intern Med J. 2008. 38(10):781–789.6. Liu Y, Cortinovis D, Stone MA. Recent advances in the treatment of the spondyloarthropathies. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2004. 16(4):357–365.
Article7. Song JS. Review of tumor necrosis factor inhibitors on rheumatoid arthritis. J Korean Rheum Assoc. 2007. 14(1):1–14.
Article8. Chang J, Girgis L. Clinical use of anti-TNF-alpha biological agents: a guide for GPs. Aust Fam Physician. 2007. 36(12):1035–1038.9. Yun HR, Kim TJ, Kim TH, Choi HS, Bae SC. Anti-TNF-alpha therapy in rheumatic diseases with chronic hepatitis B virus infection. J Korean Rheum Assoc. 2007. 14(3):242–250.
Article10. Her MY, Sheen D, Kim TH. Treatment of ankylosing spondylitis. J Korean Rheum Assoc. 2006. 13(1):1–9.11. Howe CR, Gardner GC, Kadel NJ. Perioperative medication management for the patient with rheumatoid arthritis. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2006. 14(9):544–551.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Tumor Necrosis Factor-alpha Inhibitors-induced Pustular Psoriasis
- A Case of Varicelliform Zoster in a Patient Treated with Etanercept for Ankylosing Spondylitis
- Medical Treatment of Ankylosing Spondylitis
- Weight Gain and Improvement of Osteoporosis with Anti-TNF Therapy
- TNF Inhibitors and Uveitis in Ankylosing Spondylitis