Yonsei Med J.
2011 Jan;52(1):113-120. 10.3349/ymj.2011.52.1.113.
The Correlation between Increased Serum Concentrations of Interleukin-6 Family Cytokines and Disease Activity in Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Rheumatology, Department of Internal Medicine, Institute for Immunology and Immunologic Disease, Brain Korea 21 Project for Medical Science, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. sookonlee@yuhs.ac
- KMID: 1106445
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2011.52.1.113
Abstract
- PURPOSE
This study was performed to determine whether the serum concentrations of interleukin (IL)-6 family cytokines are elevated in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and to investigate the relationship between IL-6 family cytokine levels and disease activity in RA patients.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
We obtained serum samples from 40 patients with RA and 40 age- and sex-matched healthy controls, and we assessed the clinical parameters of disease activity, including the 28-joint disease activity score (DAS28) and C-reactive protein (CRP) levels. Serum samples from five patients with high disease activity (DAS28 > 5.1) were also collected at the eighth week of treatment. Serum concentrations of IL-6, IL-11, and leukemia inhibitory factor (LIF) were measured using an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA).
RESULTS
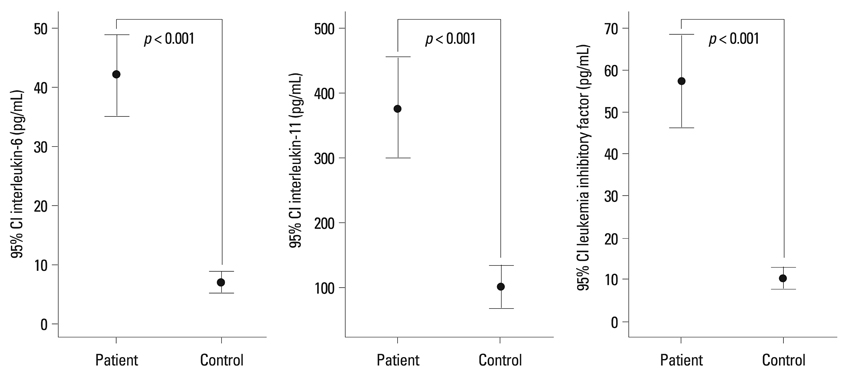
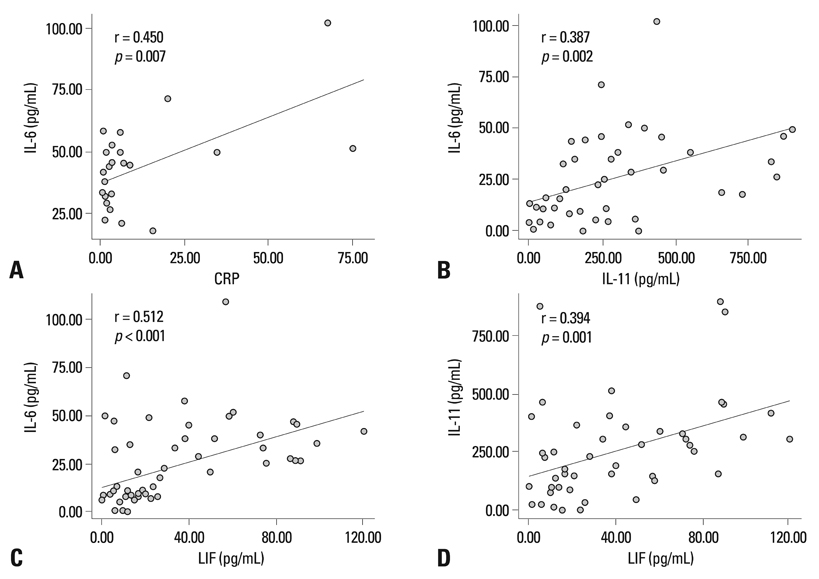
Serum concentrations of IL-6 family cytokines, including IL-6, IL-11, and LIF, were significantly elevated in patients with RA compared to those of healthy controls. Although there was no significant relationship between IL-6 family cytokine levels and DAS28, the IL-6 levels of patients with RA showed a significant correlation with CRP levels. After eight weeks of medical treatment in patients with high disease activity, a decrease in DAS28 was associated with a significant decrease in the serum concentrations of IL-6 and IL-11.
CONCLUSION
The serum concentrations of IL-6 family cytokines were significantly elevated in patients with RA, and they decreased with medical treatment. These findings suggest a possible role for IL-6 family cytokines in the pathogenesis of RA.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Hochberg MC, Silman AJ, Smolen JS, Weinblatt ME, Weisman MH. MacGregor AJ, Silman AJ, editors. Rheumatology. Classification and epidemiology. 2008. 4th ed. Spain: Mosby;755–762.2. McInnes IB, Schett G. Cytokines in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. Nat Rev Immunol. 2007. 7:429–442.
Article3. Brennan F, Beech J. Update on cytokines in rheumatoid arthritis. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2007. 19:296–301.
Article4. Szekanecz Z, Koch AE. Macrophages and their products in rheumatoid arthritis. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2007. 19:289–295.
Article5. Huber LC, Distler O, Tarner I, Gay RE, Gay S, Pap T. Synovial fibroblasts: key players in rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology. 2006. 45:669–675.
Article6. Nishimoto N, Kishimoto T. Interleukin 6: from bench to bedside. Nat Clin Pract Rheumatol. 2006. 2:619–626.
Article7. Madhok R, Crilly A, Watson J, Capell HA. Serum interleukin 6 levels in rheumatoid arthritis: correlations with clinical and laboratory indices of disease activity. Ann Rheum Dis. 1993. 52:232–234.
Article8. Knudsen LS, Christensen IJ, Lottenburger T, Svendsen MN, Nielsen HJ, Nielsen L, et al. Pre-analytical and biological variability in circulating interleukin 6 in healthy subjects and patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Biomarkers. 2008. 13:59–78.
Article9. Smolen JS, Beaulieu A, Rubbert-Roth A, Ramos-Remus C, Rovensky J, Alecock E, et al. Effect of interleukin-6 receptor inhibition with tocilizumab in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (OPTION study): a double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomised trial. Lancet. 2008. 371:987–997.10. Genovese MC, McKay JD, Nasonov EL, Mysler EF, da Silva NA, Alecock E, et al. Interleukin-6 receptor inhibition with tocilizumab reduces disease activity in rheumatoid arthritis with inadequate response to disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs: the tocilizumab in combination with traditional disease-modifying antirheumatic drug therapy study. Arthritis Rheum. 2008. 58:2968–2980.
Article11. Emery P, Keystone E, Tony HP, Cantagrel A, van Vollenhoven R, Sanchez A, et al. IL-6 receptor inhibition with tocilizumab improves treatment outcomes in patients with rheumatoid arthritis refractory to anti-tumour necrosis factor biologicals: results from a 24-week multicentre randomised placebo-controlled trial. Ann Rheum Dis. 2008. 67:1516–1523.
Article12. Kishimoto T, Akira S, Narazaki M, Taga T. Interleukin-6 family of cytokines and gp130. Blood. 1995. 86:1243–1254.
Article13. Wong PK, Campbell IK, Egan PJ, Ernst M, Wicks IP. The role of the interleukin-6 family of cytokines in inflammatory arthritis and bone turnover. Arthritis Rheum. 2003. 48:1177–1189.
Article14. Okamoto H, Yamamura M, Morita Y, Harada S, Makino H, Ota Z. The synovial expression and serum levels of interleukin-6, interleukin-11, leukemia inhibitory factor, and oncostatin M in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1997. 40:1096–1105.
Article15. Robak T, Gladalska A, Stepień H, Robak E. Serum levels of interleukin-6 type cytokines and soluble interleukin-6 receptor in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Mediators Inflamm. 1998. 7:347–353.16. Waring PM, Carroll GJ, Kandiah DA, Buirski G, Metcalf D. Increased levels of leukemia inhibitory factor in synovial fluid from patients with rheumatoid arthritis and other inflammatory arthritides. Arthritis Rheum. 1993. 36:911–915.
Article17. Arnett FC, Edworthy SM, Bloch DA, McShane DJ, Fries JF, Cooper NS, et al. The American Rheumatism Association 1987 revised criteria for the classification of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1988. 31:315–324.
Article18. Prevoo ML, van't Hof MA, Kuper HH, van Leeuwen MA, van de Putte LB, van Riel PL. Modified disease activity scores that include twenty-eight-joint counts. Development and validation in a prospective longitudinal study of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1995. 38:44–48.19. Smolen JS, Aletaha D. Activity assessments in rheumatoid arthritis. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2008. 20:306–313.
Article20. Zatarain E, Strand V. Monitoring disease activity of rheumatoid arthritis in clinical practice: contributions from clinical trials. Nat Clin Pract Rheumatol. 2006. 2:611–618.
Article21. Hermann JA, Hall MA, Maini RN, Feldmann M, Brennan FM. Important immunoregulatory role of interleukin-11 in the inflammatory process in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1998. 41:1388–1397.22. Walmsley M, Butler DM, Marinova-Mutafchieva L, Feldmann M. An anti-inflammatory role for interleukin-11 in established murine collagen-induced arthritis. Immunology. 1998. 95:31–37.23. Moreland L, Gugliotti R, King K, Chase W, Weisman M, Greco T, et al. Results of a phase-I/II randomized, masked, placebo-controlled trial of recombinant human interleukin-11 (rhIL-11) in the treatment of subjects with active rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Res. 2001. 3:247–252.24. Carroll GJ, Bell MC. Leukaemia inhibitory factor stimulates proteoglycan resorption in porcine articular cartilage. Rheumatol Int. 1993. 13:5–8.25. Campbell IK, Waring P, Novak U, Hamilton JA. Production of leukemia inhibitory factor by human articular chondrocytes and cartilage in response to interleukin-1 and tumor necrosis factor alpha. Arthritis Rheum. 1993. 36:790–794.
Article26. Straub RH, Müller-Ladner U, Lichtinger T, Schölmerich J, Menninger H, Lang B. Decrease of interleukin 6 during the first 12 months is a prognostic marker for clinical outcome during 36 months treatment with disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drugs. Br J Rheumatol. 1997. 36:1298–1303.27. Kopf M, Baumann H, Freer G, Feudenberg M, Lamers M, Kishimoto T, et al. Impaired immune and acute-phase responses in interleukin-6-deficient mice. Nature. 1994. 368:339–342.
Article28. Sasai M, Saeki Y, Ohshima S, Nishioka K, Mima T, Tanaka T, et al. Delayed onset and reduced severity of collagen-induced arthritis in interleukin-6-deficient mice. Arthritis Rheum. 1999. 42:1635–1643.
Article29. Xing Z, Gauldie J, Cox G, Baumann H, Jordana M, Lei XF, et al. IL-6 is an antiinflammatory cytokine required for controlling local or systemic acute inflammatory responses. J Clin Invest. 1998. 101:311–320.30. Cronstein BN. Interleukin-6--a key mediator of systemic and local symptoms in rheumatoid arthritis. Bull NYU Hosp Jt Dis. 2007. 65:Suppl 1. S11–S15.31. Yin TG, Schendel P, Yang YC. Enhancement of in vitro and in vivo antigen-specific antibody responses by interleukin 11. J Exp Med. 1992. 175:211–216.
Article32. Trepicchio WL, Bozza M, Pedneault G, Dorner AJ. Recombinant human IL-11 attenuates the inflammatory response through down-regulation of proinflammatory cytokine release and nitric oxide production. J Immunol. 1996. 157:3627–3634.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Serum Interleukin-10 Levels in Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients
- The Significance of IL-6 in Systemic Rheumatic Diseases: Systemic Lupus Erythematosus and Rheumatoid Arthritis
- Cytokines in rheumatoid arthritis
- beta-glucuronidase Activity in Rheumatoid Arthritis and Osteoarthritis
- Study on LD Isoenzyme Activity in Synovial Fluid of Joint Diseases