J Vet Sci.
2008 Jun;9(2):145-153. 10.4142/jvs.2008.9.2.145.
Variable number tandem repeat analysis of Mycobacterium bovis isolates from Gyeonggi-do, Korea
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Microbiology and the Brain Korea 21 Project for the Medical Sciences, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul 120-752, Korea. raycho@yuhs
- 2Gyeonggi-do Veterinary Service, Suwon 441-460, Korea.
- 3Department of Biomedical Laboratory Sciences, College of Health Sciences, Yonsei University, Wonju 220-710, Korea.
- 4The International Vaccine Institute, Seoul 151-600, Korea.
- KMID: 1106229
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4142/jvs.2008.9.2.145
Abstract
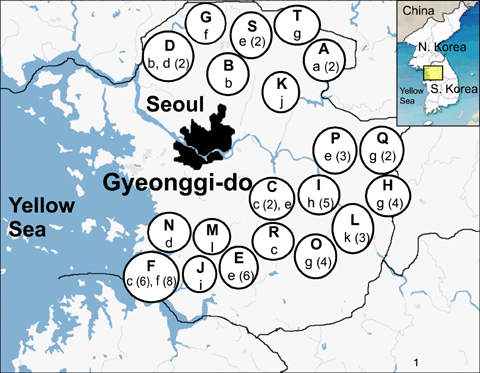
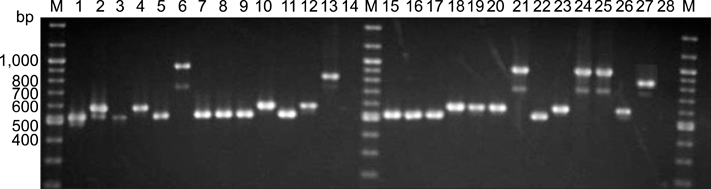
- Bovine tuberculosis (TB) is a major zoonosis that's caused by Mycobacterium bovis (M. bovis). Being able to detect M. bovis is important to control bovine TB. We applied a molecular technique, the variable number tandem repeat (VNTR) typing method, to identify and distinguish the M. bovis isolates from Gyeonggi-do, Korea. From 2003 to 2004, 59 M. bovis clinical strains were isolated from dairy cattle in Gyeonggi-do, Korea, and these cattle had tuberculosis-like lesions. Twenty-four published MIRUVNTR markers were applied to the M. bovis isolates and ten of them showed allelic diversity. The most discriminatory locus for the M. bovis isolates in Korea was QUB 3336 (h = 0.64). QUB 26 and MIRU 31 also showed high discriminative power (h = 0.35). The allelic diversity by the combination of all VNTR loci was 0.86. Six loci (MIRU 31, ETR-A and QUB-18, -26, -3232, -3336) displayed valuable allelic diversity. Twelve genotypes were identified from the 59 M. bovis isolates that originated from 20 cattle farms that were dispersed throughout the region of Gyenggi-do. Two genotypes [designation index (d.i.) = e, g] showed the highest prevalence (20% of the total farms). For the multiple outbreaks on three farms, two successive outbreaks were caused by the same genotype at two farms. Interestingly, the third outbreak at one farm was caused by both a new genotype and a previous genotype. In conclusion, this study suggests that MIRU-VNTR typing is useful to identify and distinguish the M. bovis isolates from Gyeonggi-do, Korea.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Mycobacterium bovis infection in a wild sow (Sus scrofa): the first case in Korea
Bok Kyung Ku, Bo-Young Jeon, Jae Myung Kim, Young-Boo Jang, Yunho Jang, So Yoon Yu, Jiro Kim, Oun Kyung Moon, Suk Chan Jung, Min Kwon Lee, Tae Nam Jeong
J Vet Sci. 2016;17(3):427-429. doi: 10.4142/jvs.2016.17.3.427.
Reference
-
1. Allix C, Walravens K, Saegerman C, Godfroid J, Supply P, Fauville-Dufaux M. Evaluation of the epidemiological relevance of variable-number tandem-repeat genotyping of Mycobacterium tuberculosis and comparison of the method with IS6110 restriction fragment length polymorphism analysis and spoligotyping. J Clin Microbiol. 2006. 44:1951–1962.
Article2. Alito A, Morcillo N, Scipioni S, Dolmann A, Romano MI, Cataldi A, van Soolingen D. The IS6110 restriction fragment length polymorphism in particular multidrug-resistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis strains may evolve too fast for reliable use in outbreak investigation. J Clin Microbiol. 1999. 37:788–791.
Article3. Cowan LS, Mosher L, Diem L, Massey JP, Crawford JT. Variable-number tandem repeat typing of Mycobacterium tuberculosis isolates with low copy numbers of IS6110 by using mycobacterial interspersed repetitive units. J Clin Microbiol. 2002. 40:1592–1602.
Article4. Domenech P, Barry CE III, Cole ST. Mycobacterium tuberculosis in the post-genomic age. Curr Opin Microbiol. 2001. 4:28–34.5. Frothingham R, Meeker-O'Connell WA. Genetic diversity in the Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex based on variable numbers of tandem DNA repeats. Microbiology. 1998. 144:1189–1196.
Article6. Heersma HF, Kremer K, van Embden JD. Computer analysis of IS6110 RFLP patterns of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Methods Mol Biol. 1998. 101:395–422.7. Hilty M, Diguimbaye C, Schelling E, Baggi F, Tanner M, Zinsstag J. Evaluation of the discriminatory power of variable number tandem repeat (VNTR) typing of Mycobacterium tuberculosis strains. Vet Microbiol. 2005. 109:217–222.
Article8. Kamerbeek J, Schouls L, Kolk A, van Agterveld M, van Soolingen D, Kuijper S, Bunschoten A, Molhuizen H, Shaw R, Goyal M, van Embden JDA. Simultaneous detection and strain differentiation of Mycobacterium tuberculosis for diagnosis and epidemiology. J Clin Microbiol. 1997. 35:907–914.
Article9. Kremer K, van Soolingen D, Frothingham R, Haas WH, Hermans PWM, Martín C, Palittapongarnpim P, Plikaytis BB, Riley LW, Yakrus MA, Musser JM, van Embden JD. Comparison of methods based on different molecular epidemiological markers for typing of Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex strains: interlaboratory study of discriminatory power and reproducibility. J Clin Microbiol. 1999. 37:2607–2618.
Article10. Le Flèche P, Fabre M, Denoeud F, Koeck JL, Vergnaud G. High resolution, on-line identification of strains from the Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex based on tandem repeat typing. BMC Microbiol. 2002. 2:37.11. Mazars E, Lesjean S, Banuls AL, Gilbert M, Vincent V, Gicquel B, Tibayrenc M, Locht C, Supply P. High-resolution minisatellite-based typing as a portable approach to global analysis of Mycobacterium tuberculosis molecular epidemiology. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2001. 98:1901–1906.
Article12. O'Reilly LM, Daborn CJ. The epidemiology of Mycobacterium bovis infections in animals and man: a review. Tuber Lung Dis. 1995. 76:Suppl 1. 1–46.13. Perumaalla VS, Adams LG, Payeur J, Baca D, Ficht TA. Molecular fingerprinting confirms extensive cow-to-cow intra-herd transmission of a single Mycobacterium bovis strain. Vet Microbiol. 1999. 70:269–276.
Article14. Roring S, Brittain D, Bunschoten AE, Hughes MS, Skuce RA, van Embden JDA, Neill SD. Spacer oligotyping of Mycobacterium bovis isolates compared to typing by restriction fragment length polymorphism using PGRS, DR and IS6110 probes. Vet Microbiol. 1998. 61:111–120.
Article15. Roring S, Scott A, Brittain D, Walker I, Hewinson G, Neill S, Skuce R. Development of variable-number tandem repeat typing of Mycobacterium bovis: comparison of results with those obtained by using existing exact tandem repeats and spoligotyping. J Clin Microbiol. 2002. 40:2126–2133.
Article16. Roring S, Scott AN, Glyn HR, Neill SD, Skuce RA. Evaluation of variable number tandem repeat (VNTR) loci in molecular typing of Mycobacterium bovis isolates from Ireland. Vet Microbiol. 2004. 101:65–73.
Article17. Selander RK, Caugant DA, Ochman H, Musser JM, Gilmour MN, Whittam TS. Methods of multilocus enzyme electrophoresis for bacterial population genetics and systematics. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1986. 51:873–884.
Article18. Serraino A, Marchetti G, Sanguinetti V, Rossi MC, Zanoni RG, Catozzi L, Bandera A, Dini W, Mignone W, Franzetti F, Gori A. Monitoring of transmission of tuberculosis between wild boars and cattle: genotypical analysis of strains by molecular epidemiology techniques. J Clin Microbiol. 1999. 37:2766–2771.
Article19. Skuce RA, McCorry TP, McCarroll JF, Roring SMM, Scott AN, Brittain D, Hughes SL, Hewinson RG, Neill SD. Discrimination of Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex bacteria using novel VNTR-PCR targets. Microbiology. 2002. 148:519–528.
Article20. Supply P, Mazars E, Lesjean S, Vincent V, Gicquel B, Locht C. Variable human minisatellite-like regions in the Mycobacterium tuberculosis genome. Mol Microbiol. 2000. 36:762–771.
Article21. Supply P, Lesjean S, Savine E, Kremer K, van Soolingen D, Locht C. Automated high-throughput genotyping for study of global epidemiology of Mycobacterium tuberculosis based on mycobacterial interspersed repetitive units. J Clin Microbiol. 2001. 39:3563–3571.
Article22. van Deutekom H, Supply P, de Haas PE, Willery E, Hoijng SP, Locht C, Coutinho RA, van Soolingen D. Molecular typing of Mycobacterium tuberculosis by mycobacterial interspersed repetitive unit-variable-number tandem repeat analysis, a more accurate method for identifying epidemiological links between patients with tuberculosis. J Clin Microbiol. 2005. 43:4473–4479.23. van Soolingen D, Hermans PWM, de Haas PEW, Soll DR, van Embden JDA. Occurrence and stability of insertion sequences in Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex strains: evaluation of an insertion sequence-dependent DNA polymorphism as a tool in the epidemiology of tuberculosis. J Clin Microbiol. 1991. 29:2578–2586.
Article24. van Soolingen D, Borgdorff MW, de Haas PE, Sebek MM, Veen J, Dessens M, Kremer K, van Embden JDA. Molecular epidemiology of tuberculosis in the Netherlands: a nationwide study from 1993 through 1997. J Infect Dis. 1999. 180:726–736.
Article25. van Soolingen D. Molecular epidemiology of tuberculosis and other mycobacterial infections: main methodologies and achievements. J Intern Med. 2001. 249:1–26.26. Wedlock DN, Skinner MA, de Lisle GW, Buddle BM. Control of Mycobacterium bovis infections and the risk to human populations. Microbes Infect. 2002. 4:471–480.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Single-nucleotide polymorphismbased epidemiological analysis of Korean Mycobacterium bovis isolates
- Frequency of Mycobacterium tuberculosis Among M. tuberculosis Complex Strains Isolated from Clinical Specimen
- Optimal Combination of VNTR Typing for Discrimination of Isolated Mycobacterium tuberculosis in Korea
- Molecular Typing of
Mycobacterium intracellulare Using Pulsed-Field Gel Electrophoresis, Variable-Number Tandem-Repeat Analysis, Mycobacteria Interspersed Repetitive-Unit-Variable-Number Tandem Repeat Typing, and Multilocus Sequence Typing: Molecular Characterization and Comparison of Each Typing Methods - Molecular fingerprinting of clinical isolates of Mycobacterium bovis and Mycobacterium tuberculosis from India by restriction fragment length polymorphism (RFLP)