J Vet Sci.
2007 Dec;8(4):323-327. 10.4142/jvs.2007.8.4.323.
Increased phosphorylation of caveolin-1 in the spinal cord of irradiated rats
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Veterinary Medicine, College of Applied Life Sciences, Cheju National University, Jeju 690-756, Korea. shint@cheju.ac.kr
- 2Applied Radiological Science Research Institute,Cheju National University, Jeju 690-756, Korea.
- 3Research Institute for Subtropical Agriculture and Biotechnology, Cheju National University, Jeju 690-756, Korea.
- 4Department of Biochemistry, College of Medicine, Cheju National University, Jeju 690-756, Korea.
- 5Department of Nuclear and Energy Engineering, College of Engineering, Cheju National University, Jeju 690-756, Korea.
- 6Department of Veterinary Anatomy, College of Veterinary Medicine, Chonnam National University, Gwangju 500-757, Korea.
- KMID: 1106210
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4142/jvs.2007.8.4.323
Abstract
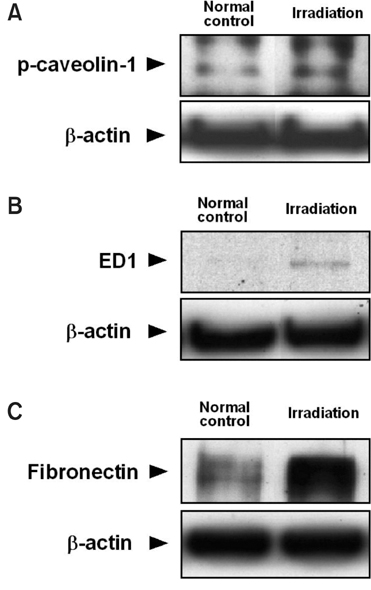
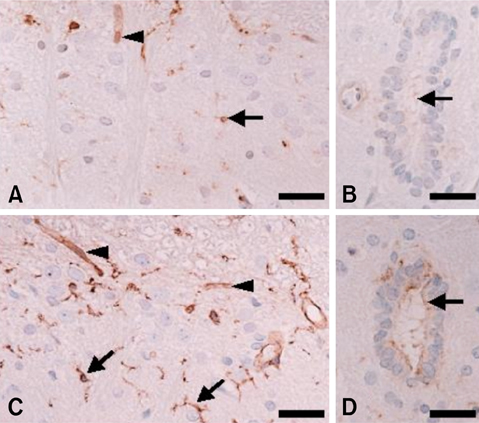
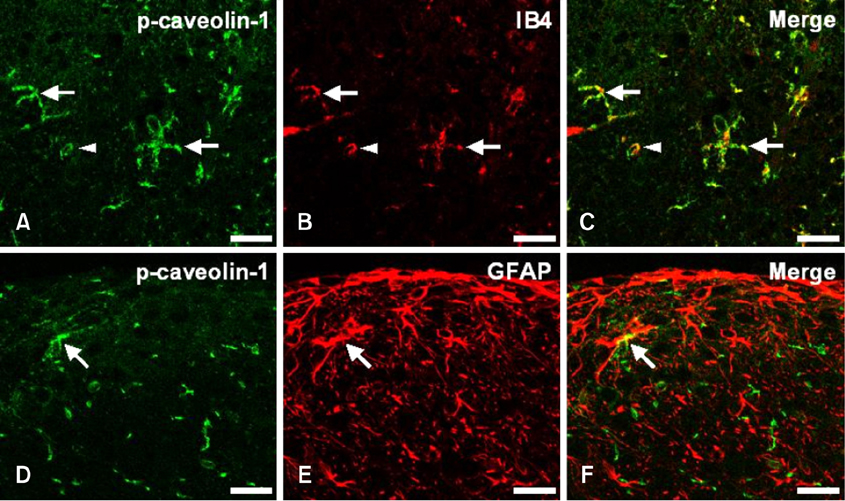
- Phosphorylation of caveolin-1 occurs during cell activation by various stimuli. In this study, the involvement of caveolin-1 in an irradiation injured spinal cord was examined by analyzing the phosphorylation of caveolin-1 in the spinal cord of rats after irradiation with a single dose of 15 Gray from a (60)Co gamma-ray source at 24 h post-irradiation (PI). A Western blot analysis showed that the phosphorylated form of caveolin-1 (p-caveolin-1) was expressed constitutively in the normal spinal cords and was significantly higher in the spinal cord of irradiated rats at 24 h PI. The increased expression of ED1, which is a marker of activated microglia/macrophages, was matched with that of p-caveolin-1. In the irradiated spinal cords, there was a higher level of p-caveolin-1 immunoreactivity in the isolectin B4-positive microglial, ependymal, and vascular endothelial cells, in which p-caveolin-1 was weakly and constitutively expressed in the normal control spinal cords. These results suggest that total body irradiation induces activation of microglial cells in the spinal cord through the phosphorylation of caveolin-1.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
The radioprotective effects of the hexane and ethyl acetate extracts of Callophyllis japonica in mice that undergo whole body irradiation
Jeongtae Kim, Changjong Moon, Heechul Kim, Jinwoo Jeong, Juyeon Lee, Jihoon Kim, Jin Won Hyun, Jae Woo Park, Mi Yeon Moon, Nam Ho Lee, Sung Ho Kim, Youngheun Jee, Taekyun Shin
J Vet Sci. 2008;9(3):281-284. doi: 10.4142/jvs.2008.9.3.281.
Reference
-
1. Burger PC, Vogel FS, Green SB, Strike TA. Glioblastoma multiforme and anaplastic astrocytoma. Pathologic criteria and prognostic implications. Cancer. 1985. 56:1106–1111.
Article2. Damoiseaux JG, Döpp EA, Calame W, Chao D, MacPherson GG, Dijkstra CD. Rat macrophage lysosomal membrane antigen recognized by monoclonal antibody ED1. Immunology. 1994. 83:140–147.3. Fisher BJ, Scott C, Macdonald DR, Coughlin C, Curran WJ. Phase I study of topotecan plus cranial radiation for glioblastoma multiforme: results of Radiation Therapy Oncology Group Trial 9507. J Clin Oncol. 2001. 19:1111–1117.
Article4. Friedrich RE, Bartel-Friedrich S, Holzhausen HJ, Lautenschläger C. The effect of external fractionated irradiation on the distribution pattern of extracellular matrix proteins in submandibular salivary glands of the rat. J Craniomaxillofac Surg. 2002. 30:246–254.
Article5. Hwang SY, Jung JS, Kim TH, Lim SJ, Oh ES, Kim JY, Ji KA, Joe EH, Cho KH, Han IO. Ionizing radiation induces astrocyte gliosis through microglia activation. Neurobiol Dis. 2006. 21:457–467.
Article6. Kim H, Ahn M, Lee J, Moon C, Matsumoto Y, Koh CS, Shin T. Increased phosphorylation of caveolin-1 in the spinal cord of Lewis rats with experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Neurosci Lett. 2006. 402:76–80.
Article7. Kyrkanides S, Olschowka JA, Williams JP, Hansen JT, O'Banion MK. TNF alpha and IL-1beta mediate intercellular adhesion molecule-1 induction via microglia-astrocyte interaction in CNS radiation injury. J Neuroimmunol. 1999. 95:95–106.
Article8. Li S, Seitz R, Lisanti MP. Phosphorylation of caveolin by src tyrosine kinases. The alpha-isoform of caveolin is selectively phosphorylated by v-Src in vivo. J Biol Chem. 1996. 271:3863–3868.9. Milner R, Campbell IL. The extracellular matrix and cytokines regulate microglial integrin expression and activation. J Immunol. 2003. 170:3850–3858.
Article10. Ohnuma K, Yamochi T, Uchiyama M, Nishibashi K, Yoshikawa N, Shimizu N, Iwata S, Tanaka H, Dang NH, Morimoto C. CD26 up-regulates expression of CD86 on antigen-presenting cells by means of caveolin-1. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2004. 101:14186–14191.
Article11. Okamoto T, Schlegel A, Scherer PE, Lisanti MP. Caveolins, a family of scaffolding proteins for organizing "preassembled signaling complexes" at the plasma membrane. J Biol Chem. 1998. 273:5419–5422.
Article12. Veluthakal R, Chvyrkova I, Tannous M, McDonald P, Amin R, Hadden T, Thurmond DC, Quon MJ, Kowluru A. Essential role for membrane lipid rafts in interleukin-1beta-induced nitric oxide release from insulin-secreting cells: potential regulation by caveolin-1+. Diabetes. 2005. 54:2576–2585.
Article13. Volonté D, Galbiati F, Pestell RG, Lisanti MP. Cellular stress induces the tyrosine phosphorylation of caveolin-1 (Tyr(14)) via activation of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase and c-Src kinase. Evidence for caveolae, the actin cytoskeleton, and focal adhesions as mechanical sensors of osmotic stress. J Biol Chem. 2001. 276:8094–8103.
Article14. Wong CS, Van der Kogel AJ. Mechanisms of radiation injury to the central nervous system: implications for neuroprotection. Mol Interv. 2004. 4:273–284.
Article15. Zhang SX, Geddes JW, Owens JL, Holmberg EG. X-irradiation reduces lesion scarring at the contusion site of adult rat spinal cord. Histol Histopathol. 2005. 20:519–530.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Gamma-ray irradiation stimulates the expression of caveolin-1 and GFAP in rat spinal cord: a study of immunoblot and immunohistochemistry
- Changes of motor evoked potentials and spinal cord evoked potentials following spinal cord injury in rats
- Immunohistochemical study of caveolin-1 and -2 in the rat retina
- Increased expression of osteopontin in the spinal cords of Lewis rats with experimental autoimmune neuritis
- Differential expression of caveolins and myosin heavy chains in response to forced exercise in rats