J Vet Sci.
2008 Dec;9(4):381-385. 10.4142/jvs.2008.9.4.381.
Serosurveillance for Japanese encephalitis, Akabane, and Aino viruses for Thoroughbred horses in Korea.
- Affiliations
-
- 1National Veterinary Research and Quarantine Service, Anyang 430-824, Korea. yangdk@nvrqs.go.kr
- 2Equine Hospital, Korea Racing Authority, Gwacheon 427-711, Korea.
- KMID: 1104913
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4142/jvs.2008.9.4.381
Abstract
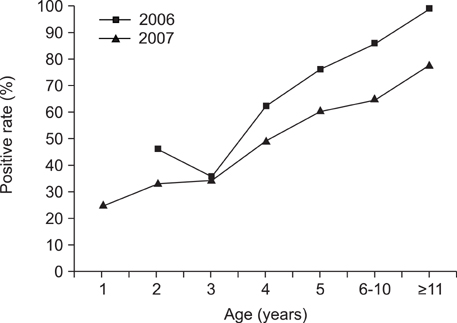
- Recent global warming trends may have a significant impact on vector-borne viral diseases, possibly affecting vector population dynamics and disease transmission. This study measured levels of hemagglutination-inhibition (HI) antibodies against Japanese encephalitis virus (JEV) and neutralizing antibodies against Akabane virus (AKAV) and Aino virus (AINV) for Thoroughbred horses in Korea. Blood samples were collected from 989 racehorses in several provinces, between October 2005 and March 2007. Sera were tested using either an HI assay or a virus neutralization test. Approximately half (49.7%; 492/989) of the horses tested were antibody-positive for JEV. The HI titer against JEV was significantly correlated with racehorse age (p < 0.05). Horses with an HI antibody titer of 1: 160 or higher accounted for 3.9% of the animals tested, indicating that vectors transmitting arthropod- borne viruses bit relatively few horses. In contrast, 3.8% (19/497) and 19.5% (97/497) of horse sera collected in March 2007 were positive against AKAV and AINV, respectively. The presence of antibodies against AKAV and AINV may indicate the multiplication of AKAV and AINV in these horses.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
Comparison of the antigenic relationship between Japanese encephalitis virus genotypes 1 and 3
Bo-Kyu Kang, Jeong-Min Hwang, Hyoungjoon Moon, Sang-Yoon Han, Jong-Man Kim, Dong-Kun Yang, Bong-Kyun Park, Daesub Song
Clin Exp Vaccine Res. 2016;5(1):26-30. doi: 10.7774/cevr.2016.5.1.26.Sero-surveillance of Getah Virus among Thoroughbred Horses in Korea
Hyun-Ye Jo, Dong-Kun Yang, Ha-Hyun Kim, Sung-Suk Choi, Kyung-Suk Kang, Sun-Ju Yang, Young-Jin Yang, In-Soo Cho
J Bacteriol Virol. 2015;45(3):235-241. doi: 10.4167/jbv.2015.45.3.235.
Reference
-
1. Clarke DH, Casals J. Techniques for hemagglutination and hemagglutination-inhibition with arthropod-borne viruses. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1958. 7:561–573.
Article2. Cybinski DH, StGeorge TD, Paull NI. Antibodies to Akabane virus in Australia. Aust Vet J. 1978. 54:1–3.
Article3. Davies FG, Jessett DM. A study of the host range and distribution of antibody to Akabane virus (genus bunyavirus, family Bunyaviridae) in Kenya. J Hyg (Lond). 1985. 95:191–196.
Article4. Ishibashi K, Shirakawa H, Uchinuno Y, Ogawa T. Seroprevalence survey of Aino virus infection in dairy cattle of Fukuoka, Japan in 1990. J Vet Med Sci. 1995. 57:1–4.
Article5. Konishi E, Shoda M, Ajiro N, Kondo T. Development and evaluation of an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for quantifying antibodies to Japanese encephalitis virus nonstructural 1 protein to detect subclinical infections in vaccinated horses. J Clin Microbiol. 2004. 42:5087–5093.
Article6. Konishi E, Shoda M, Kondo T. Prevalence of antibody to Japanese encephalitis virus nonstructural 1 protein among racehorses in Japan: indication of natural infection and need for continuous vaccination. Vaccine. 2004. 22:1097–1103.
Article7. Kurogi H, Akiba K, Inaba Y, Matumoto M. Isolation of Akabane virus from the biting midge Culicoides oxystoma in Japan. Vet Microbiol. 1987. 15:243–248.
Article8. Kwon HJ, Jang BJ, Lim YM, Lee CK, Jeon YS. Studies on Japanese encephalitis live vaccine. VII. Pathogenicity and immunogenicity of horses with Anyang strain of attenuated virus. Res Rep Natl Inst Vet Res. 1978. 20:29–34.9. Lee NS, Mun JB, Kim YH, Song KC. Studies on Japanese encephalitis. VI. Survey of incidence of the antibodies against Japanese encephalitis virus among domestic animals. Res Rep Natl Inst Vet Res. 1956. 4:21–38.10. Lee YT, Song JO, Park CH. Haemagglutination inhibition antibodies of Japanese encephalitis virus to bats. J Korean Soc Virol. 1991. 21:173–178.11. Lim SI, Kweon CH, Tark DS, Kim SH, Yang DK. Sero-survey on Aino, Akabane, Chuzan, bovine ephemeral fever and Japanese encephalitis virus of cattle and swine in Korea. J Vet Sci. 2007. 8:45–49.
Article12. Ministry of Agriculture and Forestry (MAF). Agricultural and Forestry Statistical Yearbook. 2007. Seoul: MAF;103.13. Ohashi S, Matsumori Y, Yanase T, Yamakawa M, Kato T, Tsuda T. Evidence of an antigenic shift among Palyam serogroup orbiviruses. J Clin Microbiol. 2004. 42:4610–4614.
Article14. Rhee YO, An SH, Jeon Y, Yoon YD, Park BK, Heo Y, Kim JM, Jang H, Kim YH, Sul DS, Song JB, Jung JK, Lee KH, Kim HP. The 1985 survey on horse diseases of veterinary importance in Korea. Korean J Vet Res. 1986. 26:87–92.15. Solomon T, Ni H, Beasley DW, Ekkelenkamp M, Cardosa MJ, Barrett AD. Origin and evolution of Japanese encephalitis virus in southeast Asia. J Virol. 2003. 77:3091–3098.
Article16. Sucharit S, Surathin K, Shrestha SR. Vectors of Japanese encephalitis virus (JEV): species complexes of the vectors. Southeast Asian J Trop Med Public Health. 1989. 20:611–621.17. Sugiura T, Shimada K. Seroepizootiological survey of Japanese encephalitis virus and Getah virus in regional horse race tracks from 1991 to 1997 in Japan. J Vet Med Sci. 1999. 61:877–881.
Article18. Widjaja S, Soekotjo W, Hartati S, Jennings GB, Corwin AL. Prevalence of hemagglutination-inhibition and neutralizing antibodies to arboviruses in horses of Java. Southeast Asian J Trop Med Public Health. 1995. 26:109–113.19. Yamanaka T, Tsujimura K, Kondo T, Yasuda W, Okada A, Noda K, Okumura T, Matsumura T. Isolation and genetic analysis of Japanese encephalitis virus from a diseased horse in Japan. J Vet Med Sci. 2006. 68:293–295.
Article20. Yang DK, Kim BH, Kweon CH, Kwon JH, Lim SI, Han HR. Biophysical characterization of Japanese encephalitis virus (KV1899) isolated from pigs in Korea. J Vet Sci. 2004. 5:125–130.
Article21. Yang DK, Kweon CH, Kim BH, Hwang IJ, Kang MI, So BJ, Cho KO. The seroprevalence of Japanese encephalitis virus in goats raised in Korea. J Vet Sci. 2007. 8:197–199.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Sero-survey on Aino, Akabane, Chuzan, bovine ephemeral fever and Japanese encephalitis virus of cattle and swine in Korea
- Apoptosis in Vero cells infected with Akabane, Aino and Chuzan virus
- Antiviral effect of 18-mer-peptide (1b-4/21-C12) on Japanese encephalitis virus and Akabane virus
- Serosurveillance for Japanese encephalitis virus infection among equines in India
- Detection of Neutralizing Antibody Against Japanese Encephalitis Virus in Wild Boars of Korea