Korean J Radiol.
2008 Jul;9(Suppl):S22-S25. 10.3348/kjr.2008.9.s.s22.
A Narrow Internal Auditory Canal with Duplication in a Patient with Congenital Sensorineural Hearing Loss
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiology, Chung-Ang University Hospital, College of Medicine, Chung-Ang University, Seoul, Korea. hyeonyu@cau.ac.kr
- 2Department of Otolaryngology and Head and Neck Surgery, Chung-Ang University Hospital, College of Medicine, Chung-Ang University, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 1100098
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2008.9.s.s22
Abstract
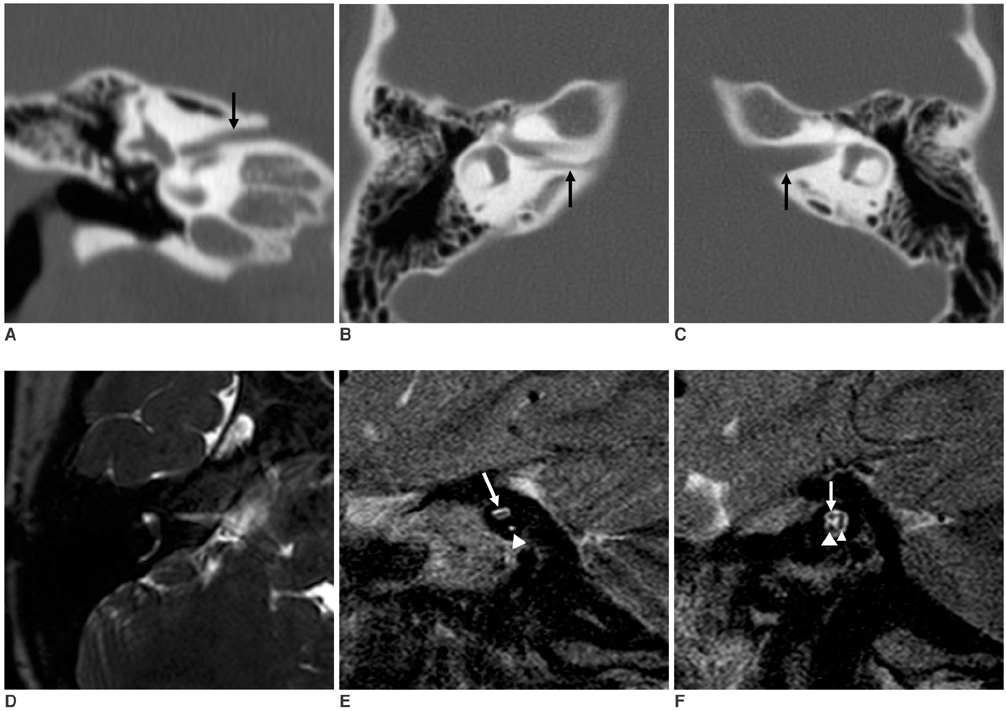
- A narrow internal auditory canal (IAC) with duplication is a rare anomaly of the temporal bone. It is associated with congenital sensorineural hearing loss. Aplasia or hypoplasia of the vestibulocochlear nerve may cause the hearing loss. We present an unusual case of an isolated narrow IAC with duplication that was detected by a CT scan. In this case, the IAC was divided by a bony septum into an empty stenotic inferoposterior portion and a large anterosuperior portion containing the facial nerve that was clearly delineated on MRI.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Duplicated Internal Auditory Canal: High-Resolution CT and MRI Findings
Linsheng Wang, Lihong Zhang, Xian Li, Xiang Guo
Korean J Radiol. 2019;20(5):823-829. doi: 10.3348/kjr.2018.0065.
Reference
-
1. Yates JA, Patel PC, Millman B, Gibson WS. Isolated congenital internal auditory canal atresia with normal facial nerve function. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 1997. 41:1–8.2. Ferreira T, Shayestehfar B, Lufkin R. Narrow, duplicated internal auditory canal. Neuroradiology. 2003. 45:308–310.3. Jackler RK, Luxford WM, House WF. Congenital malformations of the inner ear: a classification based on embryogenesis. Laryngoscope. 1987. 97:2–14.4. Winslow CP, Lepore ML. Imaging quiz case 1. Bilateral agenesis of lateral semicircular canals with hypoplasia of the left internal auditory canal (IAC). Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 1997. 123:12361238–1239.5. Cho YS, Na DG, Jung JY, Hong SH. Narrow internal auditory canal syndrome: parasaggital reconstruction. J Laryngol Otol. 2000. 114:392–394.6. Casselman JW, Offeciers FE, Govaerts PJ, Kuhweide R, Geldof H, Somers T, et al. Aplasia and hypoplasia of the vestibulocochlear nerve: diagnosis with MR imaging. Radiology. 1997. 202:773–781.7. Demir OI, Cakmakci H, Erdag TK, Men S. Narrow duplicated internal auditory canal: radiological findings and review of the literature. Pediatr Radiol. 2005. 35:1220–1223.8. Vilain J, Pigeolet Y, Casselman JW. Narrow and vacant internal auditory canal. Acta Otorhinolaryngol Belg. 1999. 53:67–71.9. Valvassori GE, Pierce RH. The normal internal auditory canal. Am J Roentgenol Radium Ther Nucl Med. 1964. 92:1232–1241.10. Roberto M, Ettorre GC, Iurato S. Stenosis of the internal auditory canal. J Laryngol Otol. 1979. 93:1211–1216.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Significance of a Hypoplastic Bony Canal for the Cochlear Nerve in Patients with Sensorineural Hearing Loss: CT and MRI Findings
- A Case with the Bilateral Narrow Bony Cochlear Nerve Canals Associated with Near Normal Hearing Thresholds
- A Case of Jugular Bulb Diverticulum Invading the Internal Auditory Canal
- Stem Cell Therapy for Sensorineural Hearing Loss, Still Alive?
- Sensorineural Hearing Loss: Causes and Hearing Rehabilitation