Korean J Ophthalmol.
2007 Sep;21(3):163-168. 10.3341/kjo.2007.21.3.163.
Relations between Age, Weight, Refractive Error and Eye Shape by Computerized Tomography in Children
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Ophthalmology, Inha University College of Medicine, Incheon, Korea. DrMYs@inha.ac.kr
- KMID: 1099033
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3341/kjo.2007.21.3.163
Abstract
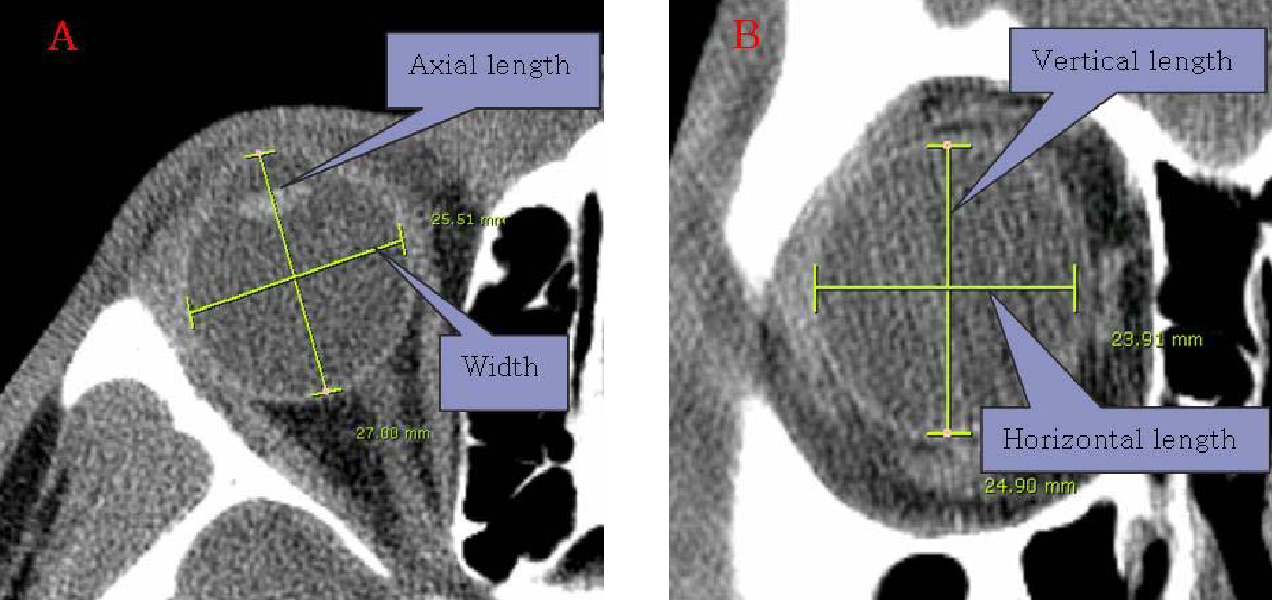
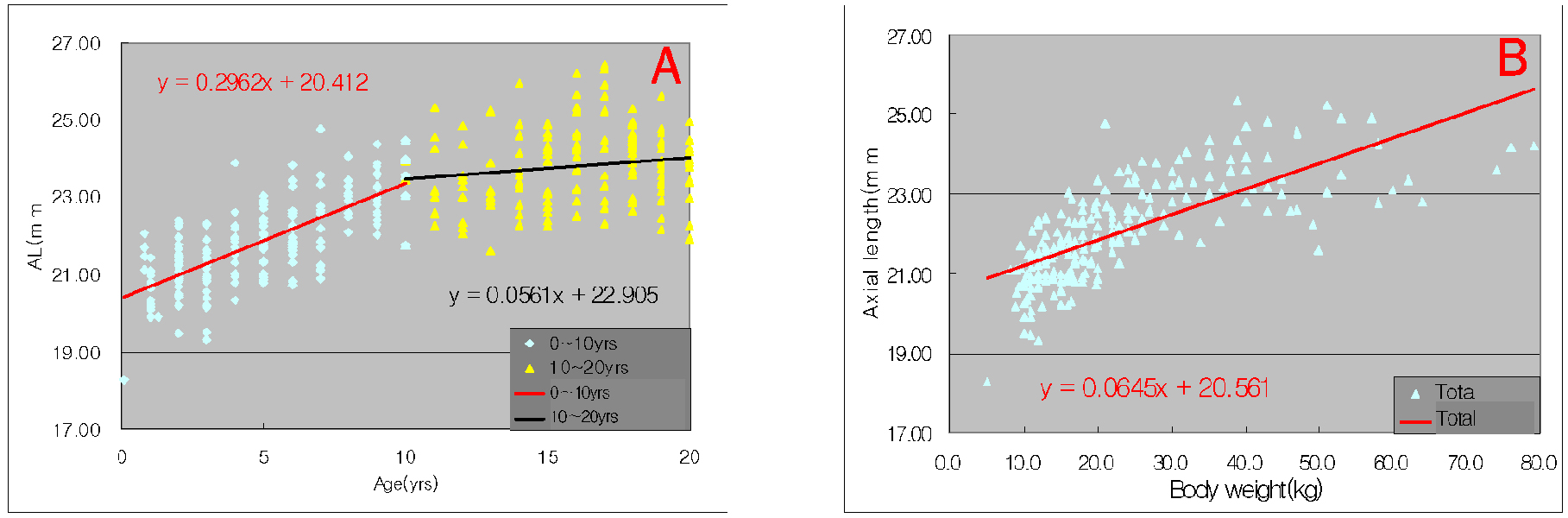
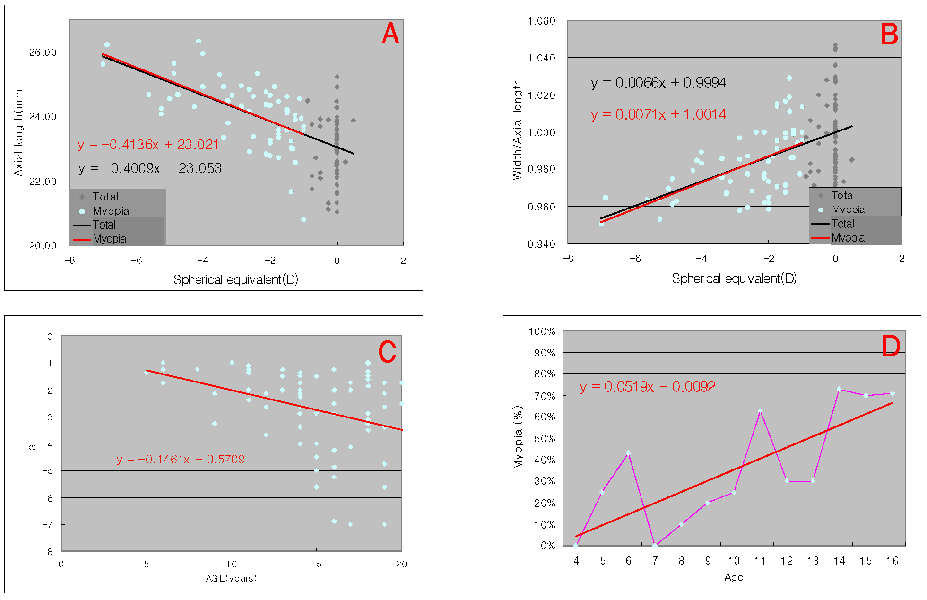
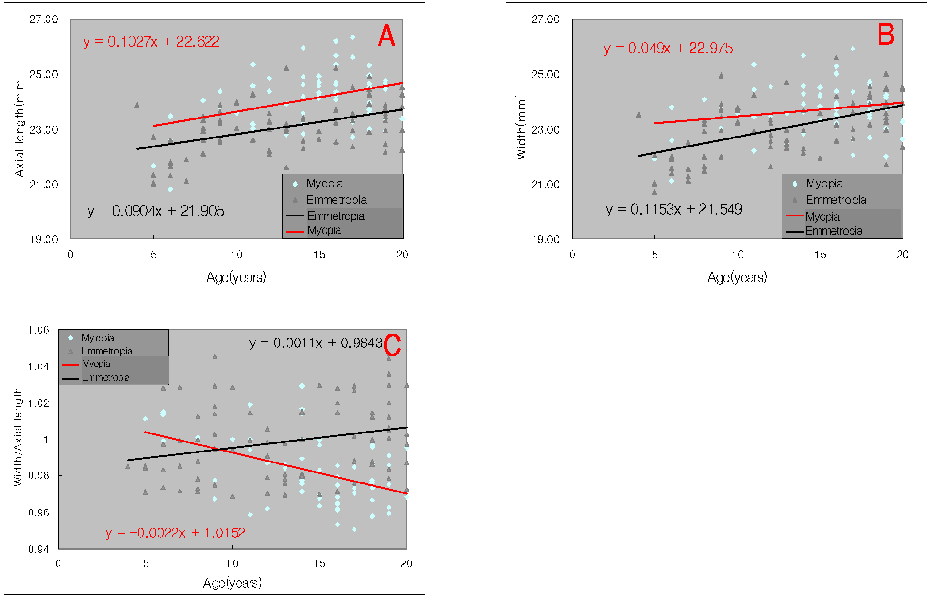
- PURPOSE: To investigate relationships between age, weight, refractive error, and morphologic changes in children's eyes by computerized tomography (CT). METHODS: Of the 772 eyes of 386 patients under the age of 20 years, who visited our Department of Ophthalmology between January 2005 to August 2006 and underwent CT of the orbit, 406 eyes of 354 patients with clear CT images and normal eyeball contour were enrolled in the present retrospective study. The axial lengths, widths, horizontal and vertical lengths, refractive errors, and body weight of eyes were measured, and relationship between these parameters were investigated. RESULTS: Axial length was found to correlate significantly with eye width (r=0.914), and in emmetropic eyes and myopic eyes, axial lengths and widths were found to increase as age and body weight increased. Axial lengths increased rapidly until age 10, and then increased slowly. In emmetropic eyes, widths / axial lengths increased with age, but in myopic eyes these decreased as age or severity of myopia increased. Moreover, as age increased, the myopic population and severity also increased. CONCLUSIONS: The axial length was longer in case of myopia compared to emmetropia in all age groups and there was almost no difference in the increase rate of axial length by the age of myopia and emmetropia. However, the width was wider in case of myopia compared to emmetropia in all age groups and the increase rate of width in myopia by age was smaller than that of emmetropia. Myopia showed decreasing rate of width/axial length with increase of age, from 1.004 in 5 years to 0.971 in 20 years. However, emmetropia showed increasing rate of width/axial length with increase of age, from 0.990 in 5 years to 1.006 in 20 years.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Scammon RE. Harris JA, Jackson CM, Paterson DG, Scammon RE, editors. The measurement of body in childhood. Measurement of Man. 1930. Minneapolis: University of Minnesota Press;173–215.2. Tarkkanen A, Uusitalo R, Mianowicz J. Ultrasonographic biometry in congenital glaucoma. Acta Ophthalmol (Copenh). 1983. 61:618–623.3. Selovic A, Juresa V, Ivankovic D, et al. Relationship between axial length of the emmetropic eye and the age, body height, and body weight of schoolchildren. Am J Hum Biol. 2005. 17:173–177.4. Kim IT, Choi JB. Normal range of exophthalmos values on orbit computerized tomography in Koreans. Ophthalmologica. 2001. 215:156–162.5. Lee JS, Lim DW, Lee SH, et al. Normative measurements of Korean orbital structures revealed by computerized tomography. Acta Ophthalmol Scand. 2001. 79:197–200.6. Furuta M. Measurement of orbital volume by computed tomography: Especially on the growth of the orbit. Jpn J Ophthalmol. 2001. 45:600–606.7. Navas RM, Parra R, Pacheco M, et al. Congenital bilateral microphthalmos after gestational syphilis. Indian J Pediatr. 2006. 73:935–936.8. Happle R, Daniels O, Koopman RJ. MIDAS syndrome (microphthalmia, dermal aplasia, and sclerocornea): an X-linked phenotype distinct from Goltz syndrome. Am J Med Genet. 1993. 47:710–713.9. Stromland K, Pinazo-Duran MD. Ophthalmic involvement in the fetal alcohol syndrome: clinical and animal model studies. Alcohol Alcohol. 2002. 37:2–8.10. Zaka-Ur-Rab S. Evaluation of relationship of ocular parameters and depth of anisometropic amblyopia with the degree of anisometropia. Indian J Ophthalmol. 2006. 54:99–103.11. Takei K, Sekine Y, Okamoto F, Hommura S. Measurement of axial length of eyes with incomplete filling of silicone oil in the vitreous cavity using x ray computed tomography. Br J Ophthalmol. 2002. 86:47–50.12. Hahn FJ, Chu WK. Ocular volume measured by CT scans. Neuroradiology. 1984. 26:419–420.13. Atchison DA, Jones CE, Schmid KL, et al. Eye shape in emmetropia and myopia. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2004. 45:3380–3386.14. Chau A, Fung K, Pak K, Yap M. Is eye size related to orbit size in human subjects? Ophthalmic Physiol Opt. 2004. 24:35–40.15. Zadnik K, Manny RE, Yu JA, et al. Ocular component data in schoolchildren as a function of age and gender. Optom Vis Sci. 2003. 80:226–236.16. Mutti DO, Mitchell GL, Jones LA, et al. Axial growth and changes in lenticular and corneal power during emmetropization in infants. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2005. 46:3074–3080.17. Larsen JS. Axial length of the emmetropic eye and its relation to the head size. Acta Ophthalmol (Copenh). 1979. 57:76–83.18. Zadnik K, Mutti DO, Mitchell GL, et al. Normal eye growth in emmetropic schoolchildren. Optom Vis Sci. 2004. 81:819–828.19. Herse P, Yao W. Variation of corneal thickness with age in young New Zealanders. Acta Ophthalmol (Copenh). 1993. 71:360–364.20. Shimmyo M, Orloff PN. Corneal thickness and axial length. Am J Ophthalmol. 2005. 139:553–554.21. Siu A, Herse P. The effect of age on human corneal thickness. Statistical implications of power analysis. Acta Ophthalmol (Copenh). 1993. 71:51–56.22. Tong L, Saw SM, Siak JK, et al. Corneal thickness determination and correlates in Singaporean schoolchildren. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2004. 45:4004–4009.23. Goh WS, Lam CS. Changes in refractive trends and optical components of Hong Kong Chinese aged 19-39 years. Ophthalmic Physiol Opt. 1994. 14:378–382.24. van Rens GH, Arkell SM. Refractive errors and axial length among Alaskan Eskimos. Acta Ophthalmol (Copenh). 1991. 69:27–32.25. Saw SM, Chua WH, Gazzard G, et al. Eye growth changes in myopic children in Singapore. Br J Ophthalmol. 2005. 89:1489–1494.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Effect of Age Wearing Prescription Glasses on Changes of Refractive Error in Accommodative Esotropia
- Relationship between Uncorrected Visual Acuity and Refractive Error in Visual Acuity Test of Children
- A survey of the Refractive State of Elementary School Children in Rural Area
- Long-term Changes in the Spherical Equivalent and Axial Length in Bilateral High-hyperopia Children
- Second-Eye Refractive Error Depending on the Reflection Rate of First-Eye Refractive Error in Cataract Surgeries