Korean J Lab Med.
2010 Apr;30(2):178-184. 10.3343/kjlm.2010.30.2.178.
Comparison of Nine Different Qualitative HBsAg Assay Kits
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Laboratory Medicine, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea. yeongsik@catholic.ac.kr
- 2Department of Pediatrics, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea. jh00mn@catholic.ac.kr
- KMID: 1096805
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3343/kjlm.2010.30.2.178
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
Qualitative hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg) assay kits are still commonly used in Korea where hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection is endemic. The accurate determination of HBsAg plays a crucial role in the diagnosis and prevention of HBV infection, especially in endemic areas. The aim of this study was to compare the detection sensitivities of 9 qualitative HBsAg assay kits.
METHODS
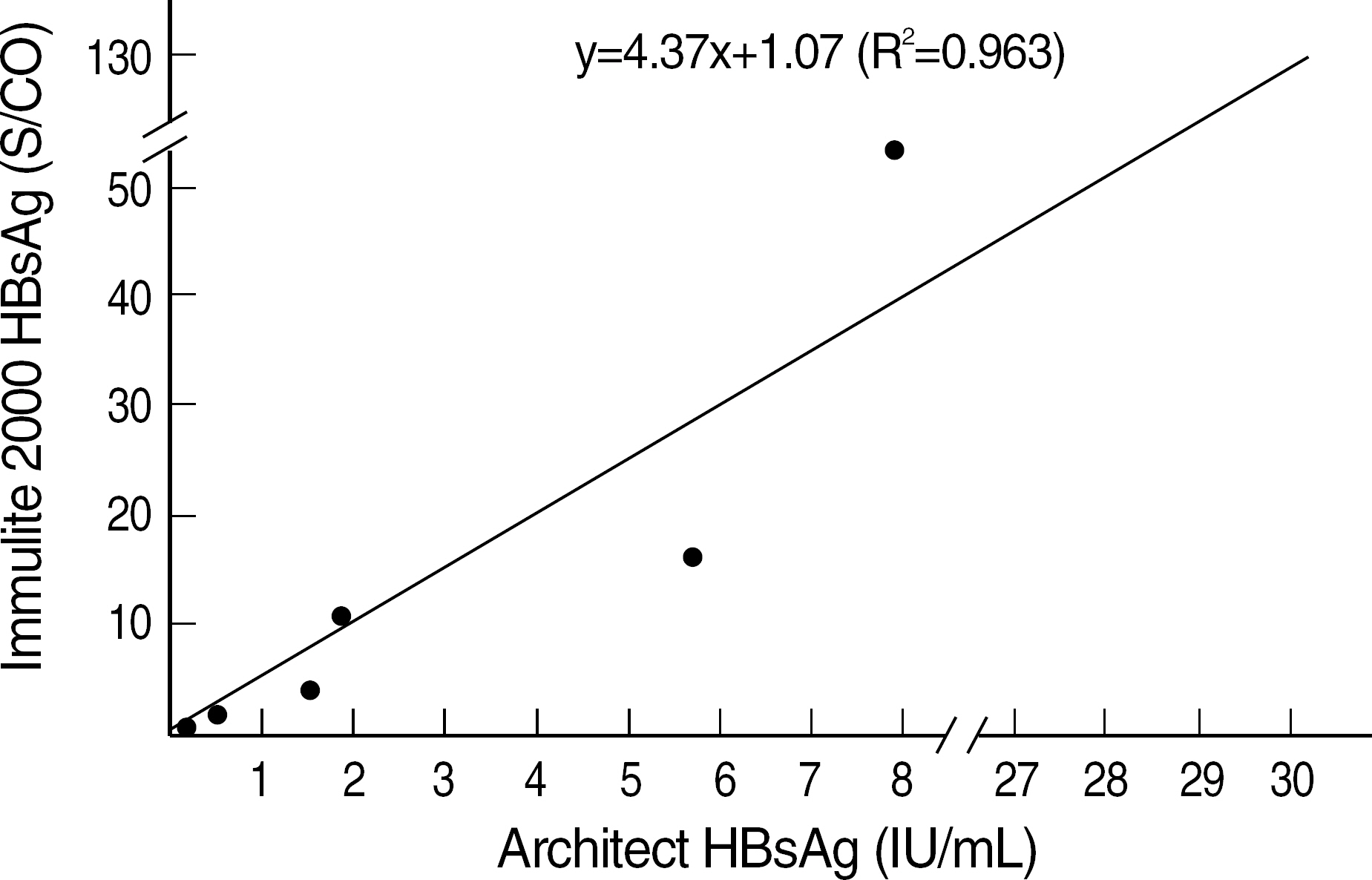
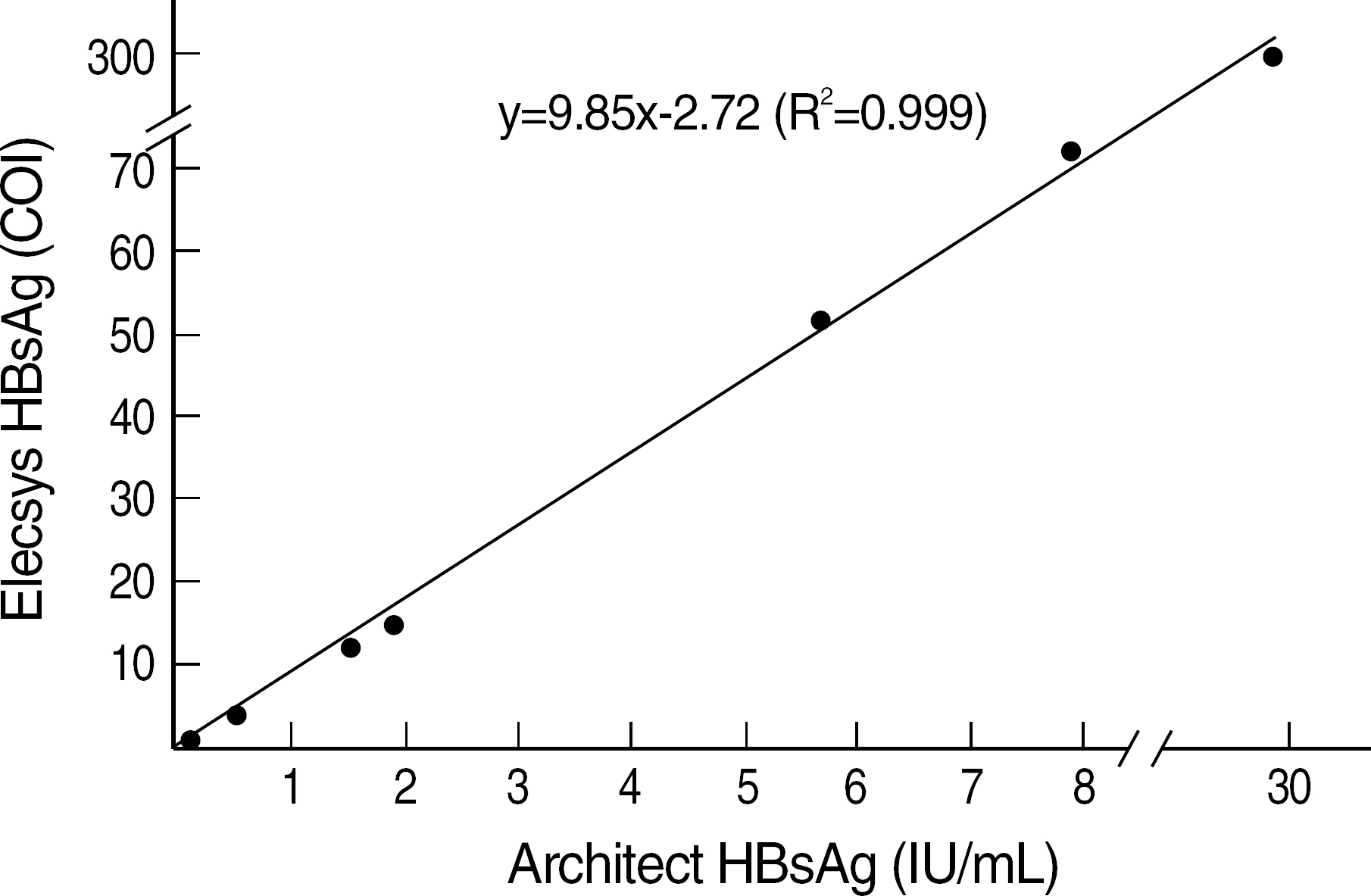
Seven pooled sera with HBsAg concentration ranging from 0.14 IU/mL to 29.96 IU/mL were prepared. The HBsAg concentration of each pooled serum was determined by a quantitative HBsAg assay, Architect HBsAg (Abbott Laboratories, Ireland). The fully automated immunoassay kits included Elecsys HBsAg (Roche Diagnostics, Germany) and Immulite 2000 HBsAg (DPC, USA) and the rapid tests included 5 immunochromatographic assay (ICA) kits and 2 reverse passive hemagglutination assay (RPHA) kits.
RESULTS
Elecsys HBsAg (Roche Diagnostics) showed positive result in pooled serum with HBsAg concentration of 0.14 IU/mL, but Immulite 2000 HBsAg (DPC) showed negative result in the same concentration. Although ICA kits showed variable results among different assay kits, all of them showed negative results in pooled sera with HBsAg concentration of < or =1.89 IU/mL. Two RPHA kits showed negative results in pooled sera with HBsAg concentration of < or =7.98 IU/mL.
CONCLUSIONS
Although ICAs were more sensitive than RPHAs, they had variable sensitivities for HBsAg and were less sensitive than the automated immunoassay kits. Therefore, ICAs and RPHAs should be used with caution in the screening tests for HBsAg and their sensitivities need to be improved.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1.Lee WM. Hepatitis B virus infection. N Engl J Med. 1997. 337:1733–45.
Article2.Lee DH., Kim JH., Nam JJ., Kim HR., Shin HR. Epidemiological findings of hepatitis B infection based on 1998 National Health and Nutrition Survey in Korea. J Korean Med Sci. 2002. 17:457–62.
Article3.Cha YJ., Kum DG., Kim SW., Kim TY., Kim JR., Kim HS, et al. Annual report on external quality assessment in immunoserology in Korea (2001). J Clin Pathol Qual Control. 2002. 24:27–38. (차영주, 금동길, 김성원, 김신규, 김재룡, 김현숙등. 면역혈청검사신빙도조사결과보고(2001).임상병리와정도관리 2002; 24: 27-38.).4.Cha YJ., Kum DG., Kim SW., Kim TY., Kim JR., Kim HS, et al. Annual report on external quality assessment in immunoserology in Korea (2002). J Lab Med Qual Assur. 2003. 25:51–71. ((차영주, 금동길, 김성원,김신규, 김재룡, 김현숙등. 면역혈청검사신빙도조사결과보고(2002). 임상검사와정도관리 2003;25:51-71.).5.Cha YJ., Kwon SY., Kum DG., Kim SW., Kim TY., Kim JR, et al. Annual report on external quality assessment in immunoserology in Korea (2003). J Lab Med Qual Assur. 2004. 26:47–69. (차영주, 권소영, 금동길,김성원, 김신규, 김재룡등. 면역혈청검사신빙도조사결과보고(2003). 임상검사와정도관리 2004;26:47-69.).6.Cha YJ., Kwon SY., Kum DG., Kim SW., Kim TY., Kim JR, et al. Annual report on external quality assessment in immunoserology in Korea (2004). J Lab Med Qual Assur. 2005. 27:37–57. (차영주, 권소영, 금동길,김성원, 김신규, 김재룡등. 면역혈청검사신빙도조사결과보고(2004). 임상검사와정도관리 2005;27:37-57.).7.Cha YJ., Kwon SY., Kim TY., Kim JR., Kim HS., Park MH, et al. Annual report on external quality assessment in immunoserology in Korea (2005). J Lab Med Qual Assur. 2006. 28:41–61. (차영주, 권소영, 김신규,김재룡, 김현숙, 박명희등. 면역혈청검사신빙도조사결과보고(2005). 임상검사와정도관리 2006;28:41-61.).8.Cha YJ., Kwon SY., Kim TY., Kim JR., Kim HS., Park MH, et al. Annual report on external quality assessment in immunoserology in Korea (2006). J Lab Med Qual Assur. 2007. 29:45–64. (차영주, 권소영, 김신규,김재룡, 김현숙, 박명희등. 면역혈청검사신빙도조사결과보고(2006). 임상검사와정도관리 2007;29:45-64.).9.Cha YJ., Kwon SY., Kim TY., Kim JR., Kim HS., Park MH, et al. Annual report on external quality assessment in immunoserology in Korea (2007). J Lab Med Qual Assur. 2008. 30:49–74. (차영주, 권소영, 김신규,김재룡, 김현숙, 박명희등. 면역혈청검사신빙도조사결과보고(2007). 임상검사와정도관리 2008;30:49-74.).10.Cha YJ., Kwon SY., Kim TY., Kim JR., Kim HS., Park MH, et al. Annual report on external quality assessment in immunoserology in Korea (2008). J Lab Med Qual Assur. 2009. 31:49–72. (차영주, 권소영, 김신규,김재룡, 김현숙, 박명희등. 면역혈청검사신빙도조사결과보고(2008). 임상검사와정도관리 2009;31:49-72.).11.WHO Working Group on Hepatitis and HIV Diagnostic Kits. Report of a WHO collaborative study to assess the suitability of a candidate replacement International standard for HBsAg and a reference panel for HBsAg and to calibrate the candidate standard in IU. WHO/BS/03.1987. Geneva: World Health Organization. 2003.12.Cha YJ., Yang JS., Chae SL. Evaluation of indigenously manufactured immunochromatographic assay systems for rapid detection of hepatitis B surface antigen and antibody. Korean J Lab Med. 2006. 26:52–7. 차영주, 양주석, 채석래. 국내에서생산되는면역크로마토그래피법을이용한 B형간염표면항원 및 항체 검사 제품의 평가. 대한진단검사의학회지 2006;26:52-7.).
Article13.Whang DH., Um TH. Comparison of immunochromatography assays and quantitative immunoassays for detecting HBsAg and anti-HBs. Korean J Lab Med. 2005. 25:186–91. (황동희 및 엄태현. B형간염항원및 항체 검사를위한 신속검사법과정량적 효소면역법의비교.대한진단검사의학회지 2005;25:186-91.).14.Lau DT., Ma H., Lemon SM., Doo E., Ghany MG., Miskovsky E, et al. A rapid immunochromatographic assay for hepatitis B virus screening. J Viral Hepat. 2003. 10:331–4.
Article15.National Committee for Clinical Laboratory Standards. Preparation and validation of commutable frozen human serum pools as secondary reference materials for cholesterol measurement procedures: approved guideline. NCCLS document C37-A. Wayne, PA: NCCLS;1999.16.Deguchi M., Yamashita N., Kagita M., Asari S., Iwatani Y., Tsuchida T, et al. Quantitation of hepatitis B surface antigen by an automated chemiluminescent microparticle immunoassay. J Virol Methods. 2004. 115:217–22.
Article17.Chen CH., Lee CM., Wang JH., Tung HD., Hung CH., Lu SN. Correlation of quantitative assay of hepatitis B surface antigen and HBV DNA levels in asymptomatic hepatitis B virus carriers. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2004. 16:1213–8.
Article18.Chen J., Wang Z., Guo Y., Peng J., Sun J., Ahmed CS, et al. Serum HBsAg changes in HBeAg positive chronic hepatitis B patients with continuous viral load reductions during treatment with adefovir or peg-interferon-alpha-2a. Antiviral Res. 2009. 81:88–91.19.Muhlbacher A., Weber B., Burgisser P., Eiras A., Cabrera J., Louisirirotchanakul S, et al. Multicenter study of a new fully automated HBsAg screening assay with enhanced sensitivity for the detection of HBV mutants. Med Microbiol Immunol. 2008. 197:55–64.
Article20.Moucari R., Mackiewicz V., Lada O., Ripault MP., Castelnau C., Martinot-Peignoux M, et al. Early serum HBsAg drop: a strong predictor of sustained virological response to pegylated interferon alfa-2a in HBeAg-negative patients. Hepatology. 2009. 49:1151–7.
Article21.Weber B., Dengler T., Berger A., Doerr HW., Rabenau H. Evaluation of two new automated assays for hepatitis B virus surface antigen (HBsAg) detection: IMMULITE HBsAg and IMMULITE 2000 HBs-Ag. J Clin Microbiol. 2003. 41:135–43.
Article22.Huh HJ., Chae SL., Cha YJ. Comparison study with enzyme immunoassay and chemiluminescence immunoassay for hepatitis B virus surface antigen detection. Korean J Lab Med. 2007. 27:355–9. (허희진,채석래, 차영주. 효소면역측정법과화학발광면역측정법을이용한B형간염표면항원검사의비교. 대한진단검사의학회지 2007;27:355-9.).
Article23.Rodella A., Galli C., Terlenghi L., Perandin F., Bonfanti C., Manca N. Quantitative analysis of HBsAg, IgM anti-HBc and anti-HBc avidity in acute and chronic hepatitis B. J Clin Virol. 2006. 37:206–12.
Article24.Chan HL., Wong VW., Tse AM., Tse CH., Chim AM., Chan HY, et al. Serum hepatitis B surface antigen quantitation can reflect hepatitis B virus in the liver and predict treatment response. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2007. 5:1462–8.
Article25.Kohmoto M., Enomoto M., Tamori A., Habu D., Takeda T., Kawada N, et al. Quantitative detection of hepatitis B surface antigen by chemiluminescent microparticle immunoassay during lamivudine treatment of chronic hepatitis B virus carriers. J Med Virol. 2005. 75:235–9.
Article26.Chen Y., Wu W. Determination of low level HBsAg in serum by microparticle enzyme immunoassay. Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int. 2002. 1:262–4.27.Sato K., Ichiyama S., Iinuma Y., Nada T., Shimokata K., Nakashima N. Evaluation of immunochromatographic assay systems for rapid detection of hepatitis B surface antigen and antibody, Dainascreen HBsAg and Dainascreen Ausab. J Clin Microbiol. 1996. 34:1420–2.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Evaluation of the Usefulness of Kobias HBsAg and Anti-HBs
- Comparison of Immunochromatography Assays and Quantitative Immunoassays for Detecting HBsAg and Anti-HBs
- True Hepatitis B Virus Surface Antigen Prevalence among Korean Blood Donors
- Evaluation of Genedia HBsAg Rapid and Genedia Anti-HBs Rapid for the Screening of HBsAg and Anti-HBs
- Evaluation of Diagnostic Kits for Hepatitis B Developed by LG Chemical Ltd