Korean J Lab Med.
2011 Jan;31(1):1-8. 10.3343/kjlm.2011.31.1.1.
Utility of ELISA Optical Density Values and Clinical Scores for the Diagnosis of and Thrombosis Prediction in Heparin-induced Thrombocytopenia
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Laboratory Medicine, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. lukekhk@snu.ac.kr
- 2Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 1096652
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3343/kjlm.2011.31.1.1
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
Heparin-induced thrombocytopenia (HIT) is an adverse drug reaction caused by antibodies to the heparin/platelet factor 4 (PF4) complex, resulting in thrombocytopenia and prothrombotic state. HIT diagnosis is challenging and depends on clinical presentation and laboratory tests. We investigated the usefulness of clinical scores and heparin/PF4 ELISA optical density (OD) as a diagnostic marker and thrombosis predictor in HIT.
METHODS
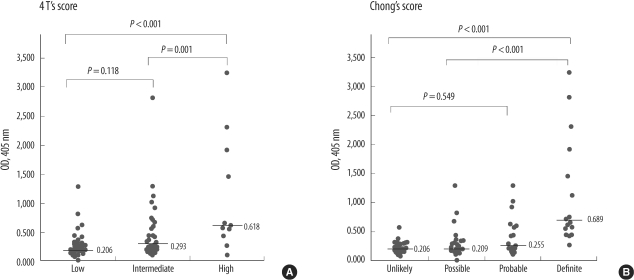
We analyzed 92 patients with suspected HIT. The heparin/PF4 antibody was measured using a commercial ELISA kit (GTI, USA). For each patient, the 4 T's score and Chong's score were calculated.
RESULTS
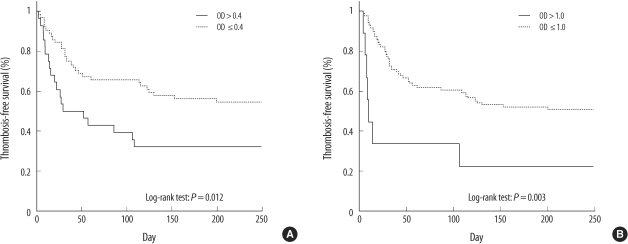
Of the 92 patients, 28 were anti-heparin/PF4-seropositive. The 4 T's score and Chong's score showed good correlation (r=0.874). The 4 T's score and OD values showed good performance for diagnosis of the definite and unlikely HIT groups; however, OD levels showed better sensitivity (93.8%) than the 4 T's score used alone (62.5%). Of the 92 patients, 26 developed thrombosis. The OD values were significantly higher in patients with thrombosis than in those without thrombosis (0.52 vs. 0.22, P<0.001). Patients with high OD values (OD>0.4) had an increased risk of thrombosis (adjusted odds ratio 9.44 [3.35-26.6], P<0.001) and a shorter 250-day thrombosis-free survival (32.1% vs. 54.7%, P=0.012).
CONCLUSIONS
ELISA OD values in combination with clinical scoring can improve the diagnosis of and thrombosis prediction in HIT. More attention should be paid to the use of clinical scores and OD values as thrombosis predictors in HIT.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Adolescent
Adult
Aged
Aged, 80 and over
Antibodies/adverse effects/analysis
Area Under Curve
Child
Child, Preschool
Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay/*methods
Female
Heparin/immunology
Humans
Infant
Male
Middle Aged
Platelet Factor 4/immunology
Risk
Sensitivity and Specificity
Survival Analysis
Thrombocytopenia/chemically induced/*diagnosis/mortality
Thrombosis/*diagnosis/etiology
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Thrombocytopenia caused by low-dose heparin supplementation of parenteral nutrition solution
Eunyoung Lee, Jeong-Ok Lee, Yoojoo Lim, Ji-Yeon Kim, Hyun Kyung Kim, Soo-Mee Bang
Blood Res. 2013;48(2):160-163. doi: 10.5045/br.2013.48.2.160.
Reference
-
1. Greinacher A, Warkentin TE. Recognition, treatment, and prevention of heparin-induced thrombocytopenia: review and update. Thromb Res. 2006; 118:165–176. PMID: 16139874.
Article2. Chong BH, Chong JJ. Heparin-induced thrombocytopenia. Expert Rev Cardiovasc Ther. 2004; 2:547–559. PMID: 15225114.
Article3. Warkentin TE, Heddle NM. Laboratory diagnosis of immune heparin-induced thrombocytopenia. Curr Hematol Rep. 2003; 2:148–157. PMID: 12901146.4. Lo GK, Juhl D, Warkentin TE, Sigouin CS, Eichler P, Greinacher A. Evaluation of pretest clinical score (4 T's) for the diagnosis of heparin-induced thrombocytopenia in two clinical settings. J Thromb Haemost. 2006; 4:759–765. PMID: 16634744.
Article5. Greinacher A, Juhl D, Strobel U, Wessel A, Lubenow N, Selleng K, et al. Heparin-induced thrombocytopenia: a prospective study on the incidence, platelet-activating capacity and clinical significance of antiplatelet factor 4/heparin antibodies of the IgG, IgM, and IgA classes. J Thromb Haemost. 2007; 5:1666–1673. PMID: 17488345.
Article6. Warkentin TE, Sheppard JA, Moore JC, Moore KM, Sigouin CS, Kelton JG. Laboratory testing for the antibodies that cause heparin-induced thrombocytopenia: how much class do we need. J Lab Clin Med. 2005; 146:341–346. PMID: 16310517.
Article7. Zwicker JI, Uhl L, Huang WY, Shaz BH, Bauer KA. Thrombosis and ELISA optical density values in hospitalized patients with heparin-induced thrombocytopenia. J Thromb Haemost. 2004; 2:2133–2137. PMID: 15613017.
Article8. Warkentin TE, Greinacher A. Heparin-induced thrombocytopenia: recognition, treatment, and prevention: the Seventh ACCP Conference on Antithrombotic and Thrombolytic Therapy. Chest. 2004; 126:311S–337S. PMID: 15383477.9. Bakchoul T, Giptner A, Najaoui A, Bein G, Santoso S, Sachs UJ. Prospective evaluation of PF4/heparin immunoassays for the diagnosis of heparin-induced thrombocytopenia. J Thromb Haemost. 2009; 7:1260–1265. PMID: 19422442.
Article10. Bryant A, Low J, Austin S, Joseph JE. Timely diagnosis and management of heparin-induced thrombocytopenia in a frequent request, low incidence single centre using clinical 4T's score and particle gel immunoassay. Br J Haematol. 2008; 143:721–726. PMID: 19036016.
Article11. Janatpour KA, Gosselin RC, Dager WE, Lee A, Owings JT, Zhou J, et al. Usefulness of optical density values from heparin-platelet factor 4 antibody testing and probability scoring models to diagnose heparin-induced thrombocytopenia. Am J Clin Pathol. 2007; 127:429–433. PMID: 17276943.
Article12. Whitlatch NL, Perry SL, Ortel TL. Anti-heparin/platelet factor 4 antibody optical density values and the confirmatory procedure in the diagnosis of heparin-induced thrombocytopenia. Thromb Haemost. 2008; 100:678–684. PMID: 18841292.
Article13. Weiss BM, Shumway NM, Howard RS, Ketchum LK, Reid TJ. Optical density values correlate with the clinical probability of heparin induced thrombocytopenia. J Thromb Thrombolysis. 2008; 26:243–247. PMID: 17982734.
Article14. Warkentin TE, Sheppard JI, Moore JC, Sigouin CS, Kelton JG. Quantitative interpretation of optical density measurements using PF4-dependent enzyme-immunoassays. J Thromb Haemost. 2008; 6:1304–1312. PMID: 18489711.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Two Cases of Heparin-Induced Thrombocytopenia Diagnosed by Particle Gel Immunoassay
- The Management of Heparin-induced Thrombocytopenia with Thrombosis That Developed after Aortic Dissection Surgery
- The Management of Heparin-induced Thrombocytopenia with Thrombosis after Open Heart Surgery: A Case Report
- Heparin-induced Thrombocytopenia Type II after Free Flap Operation
- Dabigatran approaching the realm of heparin-induced thrombocytopenia