J Korean Med Sci.
2005 Apr;20(2):307-312. 10.3346/jkms.2005.20.2.307.
Antinociceptive Interactions between Intrathecal Gabapentin and MK801 or NBQX in Rat Formalin Test
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Anesthesiology and Pain Medicine, Chonnam National University, Medical School, Gwangju, Korea. mhyoon@chonnam.ac.kr
- KMID: 1095209
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2005.20.2.307
Abstract
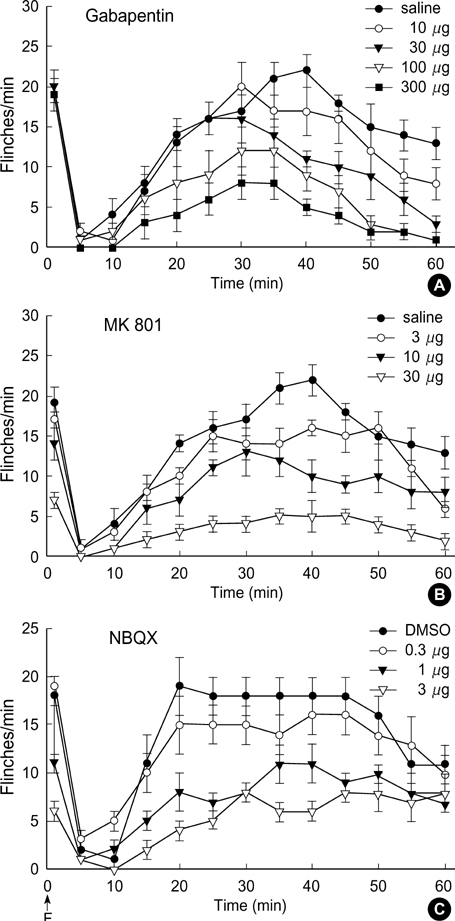
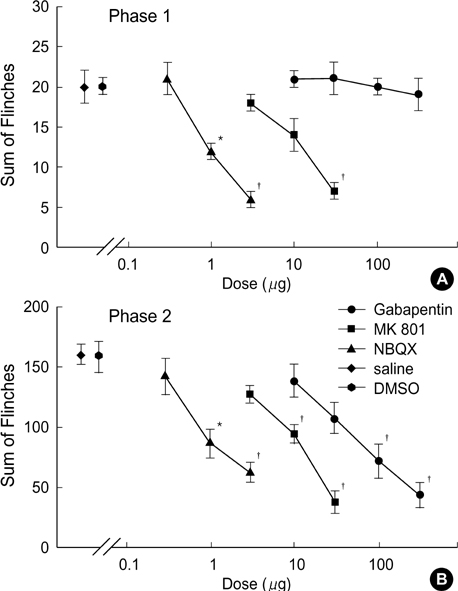
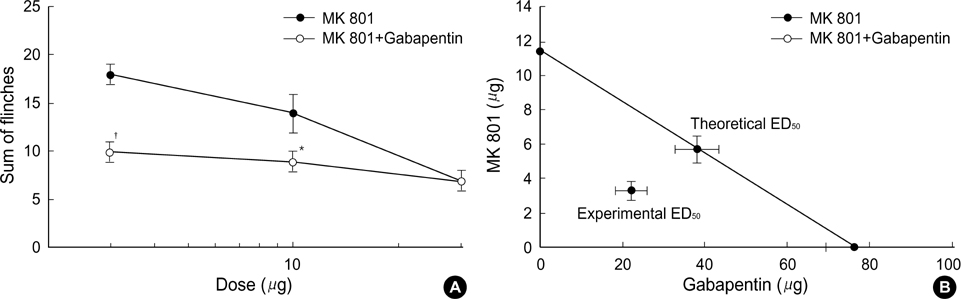
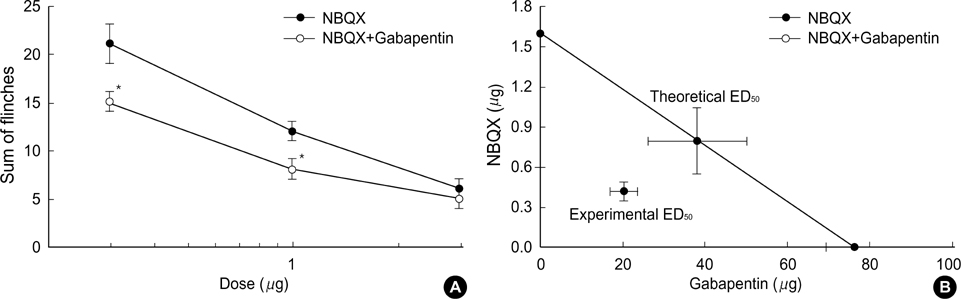
- Antagonists for spinal N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) and amino-hydroxy-methtyl-isoxazolepropionate (AMPA) receptors are effective in attenuating acute nociception or injury-induced hyperalgesia. The antinociception of spinal gabapentin is developed in injury-induced hyperalgesia without affecting acute nociception. The authors evaluated the effects of intrathecal gabapentin, NMDA antagonist (MK801) and AMPA antagonist (NBQX) in the formalin test which shows injury-induced hyperalgesia as well as acute pain. We further assessed the interactions between gabapentin and either MK801 or NBQX. Male Sprague-Dawley rats were implanted with intrathecal catheters. To evoke pain, 50 microliter of 5% formalin solution was injected into the hindpaw. The interaction was investigated by a fixed dose analysis or an isobolographic analysis. MK801 and NBQX suppressed flinching responses during phase 1 of the formalin test, while gabapentin had little effect on phase 1. All three agents decreased the phase 2 flinching response. A fixed dose analysis in phase 1 showed that gabapentin potentiated the antinociceptive effect of MK801 and NBQX. Isobolographic analysis in phase 2 revealed a synergistic interaction after coadministration of gabapentin-MK801 or gabapentin-NBQX. Correspondingly, spinal gabapentin with NMDA or AMPA antagonist may be useful in managing acute pain and injury-induced hyperalgesia.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Amines/administration & dosage/*pharmacology
Analgesics/*pharmacology
Animals
Cyclohexanecarboxylic Acids/administration & dosage/*pharmacology
Dizocilpine Maleate/*pharmacology
Drug Interactions
Excitatory Amino Acid Antagonists/*pharmacology
Hyperalgesia/drug therapy
Injections, Spinal
Male
Quinoxalines/*pharmacology
Rats
Rats, Sprague-Dawley
Receptors, AMPA/drug effects/physiology
Receptors, N-Methyl-D-Aspartate/drug effects/physiology
Research Support, Non-U.S. Gov't
gamma-Aminobutyric Acid/administration & dosage/*pharmacology
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
Antinociceptive drug interaction between intrathecal vitamin E and gabapentin in the rat formalin test
Myoung-Joong Kim, Won Hyung Lee, Young-Kwon Ko, Boo Hwi Hong
Korean J Anesthesiol. 2012;63(5):447-453. doi: 10.4097/kjae.2012.63.5.447.Antinociceptive Effects of Intraperitoneal and Intrathecal Vitamin E in the Rat Formalin Test
Myoung Joong Kim, Boo Hwi Hong, En Ji Zhang, Young Kwon Ko, Won Hyung Lee
Korean J Pain. 2012;25(4):238-244. doi: 10.3344/kjp.2012.25.4.238.
Reference
-
1. Taylor CP, Gee NS, Su TZ, Kocsis JD, Welty DF, Brown JP, Dooley DJ, Boden P, Singh L. A summary of mechanistic hypotheses of gabapentin pharmacology. Epilepsy Res. 1998. 29:233–249.
Article2. Kaneko M, Mestre C, Sanchez EH, Hammond DL. Intrathecally administered gabapentin inhibits formalin-evoked nociception and the expression of Fos-like immunoreactivity in the spinal cord of the rat. J Pharmocol Exp Ther. 2000. 292:743–751.3. Shimoyama N, Shimoyama M, Davis AM, Inturrisi CE, Elliott KJ. Spinal gabapentin is antinociceptive in the rat formalin test. Neurosci Lett. 1997. 222:65–67.
Article4. Yoon MH, Yaksh TL. The effect of intrathecal gabapentin on pain behavior and hemodynamics on the formalin test in the rat. Anesth Analg. 1999. 89:434–439.
Article5. Yoon MH, Choi JI, Jeong SW. Spinal gabapentin and antinociception: mechanisms of action. J Korean Med Sci. 2003. 18:255–261.
Article6. Tolle TR, Berthele A, Schadrack J, Zieglgansberger W. Involvement of glutamatergic neurotransmission and protein kinase C in spinal plasticity and the development of chronic pain. Prog Brain Res. 1996. 110:193–206.7. Kolhekar R, Meller ST, Gebhart GF. N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor-mediated changes in thermal nociception: allosteric modulation at glycine and polyamine recognition sites. Neuroscience. 1994. 63:925–936.
Article8. Leem JW, Choi EJ, Park ES, Paik KS. N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) and non-NMDA glutamate receptor antagonists differentially suppress dorsal horn neuron responses to mechanical stimuli in rats with peripheral nerve injury. Neurosci Lett. 1996. 211:37–40.
Article9. Mori H, Mishina M. Structure and function of the NMDA receptor channel. Neuropharmacology. 1995. 34:1219–1237.
Article10. Hamada F, Noutsuka H, Hamada Y, Goto H. Comparison of the spinal anti-nociceptive effects of ES-242-1 and MK-801, two different NMDA antagonists, in rats. Neurosci Res. 2001. 40:61–66.
Article11. Huang W, Simpson RK Jr. Intrathecal treatment with MK-801 suppresses thermal nociceptive responses and prevents c-fos immunore-activity induced in rat lumbar spinal cord neurons. Neurol Res. 1999. 21:593–598.
Article12. Hunter JC, Singh L. Role of excitatory amino acid receptors in the mediation of the nociceptive response to formalin in the rat. Neurosci Lett. 1994. 174:217–221.
Article13. Kristensen JD, Karlsten R, Gordh T, Berge OG. The NMDA antagonist 3-(2-carboxypiperazin-4-yl) propyl-1-phosphonic acid (CPP) has antinociceptive effect after intrathecal injection in the rat. Pain. 1994. 56:59–67.14. Nishiyama T. Interaction between intrathecal morphine and glutamate receptor antagonists in formalin test. Eur J Pharmacol. 2000. 395:203–210.
Article15. Nishiyama T, Yaksh TL, Weber E. Effects of intrathecal NMDA and non-NMDA antagonists on acute thermal nociception and their interaction with morphine. Anesthesiology. 1998. 89:715–722.
Article16. Matthews EA, Dickenson AH. A combination of gabapentin and morphine mediates enhanced inhibitory effects on dorsal horn neuronal responses in a rat model of neuropathy. Anesthesiology. 2002. 96:633–640.
Article17. Yaksh TL, Rudy TA. Chronic catheterization of the spinal subarachnoid space. Physiol Behav. 1976. 17:1031–1036.
Article18. Yoon MH, Choi JI, Kwak SH. Characteristics of interactions between intrathecal gabapentin and either clonidine or neostigmine in the formalin test. Anesth Analg. 2004. 98:1374–1379.19. Tallarida RJ, Murray R.B.. Manual of pharmacologic calculations with computer programs. 1987. 2nd ed. New York: Springer-Verlag.20. Bryans JS, Davies N, Gee NS, Dissanayake VU, Ratcliffe GS, Horwell DC, Kneen CO, Morrell AI, Oles RJ, O'Toole JC, Perkins GM, Singh L, Suman-Chauhan N, O'Neill JA. Identification of novel ligands for the gabapentin binding site on the alpha2delta subunit of a calcium channel and their evaluation as anticonvulsant agents. J Med Chem. 1998. 41:1838–1845.21. Benoliel R, Tanaka M, Caudle RM, Iadarola MJ. Co-localization of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors and substance P (neurokinin-1) receptors in rat spinal cord. Neurosci Lett. 2000. 291:61–64.
Article22. Jansen KL, Faull RL, Dragunow M, Waldvogel H. Autoradiographic localisation of NMDA, quisqualate and kainic acid receptors in human spinal cord. Neurosci Lett. 1990. 108:53–57.
Article23. Yaksh TL. The spinal pharmacology of facilitation of afferent processing evoked by high-threshold afferent input of the postinjury pain state. Curr Opin Neurol Neurosurg. 1993. 6:250–256.24. Furuyama T, Kiyama H, Sato K, Park HT, Maeno H, Takagi H, Tohyama M. Region-specific expression of subunits of ionotropic glutamate receptors (AMPA-type, KA-type and NMDA receptors) in the rat spinal cord with special reference to nociception. Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 1993. 18:141–151.
Article25. Headley PM, Grillner S. Excitatory amino acids and synaptic transmission: the evidence for a physiological function. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1990. 11:205–211.
Article26. Cuesta MC, Arcaya JL, Cano G, Sanchez L, Maixner W, Suarez-Roca H. Opposite modulation of capsaicin-evoked substance P release by glutamate receptors. Neurochem Int. 1999. 35:471–478.
Article27. Cheng J, Pan H, Eisenach JC. Antiallodynic effect of intrathecal gabapentin and its interaction with clonidine in a rat model of postoperative pain. Anesthesiology. 2000. 92:1126–1131.
Article28. Hurley RW, Chatterjea D, Rose Feng M, Taylor CP, Hammond DL. Gabapentin and pregabalin can interact synergistically with naproxen to produce antihyperalgesia. Anesthesiology. 2002. 97:1263–1273.
Article29. Roerig SC, Fujimoto JM. Multiplicative interaction between intrathecally and intracerebroventricularly administered mu opioid agonists but limited interactions between delta and kappa agonists for antinociception in mice. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1989. 249:762–768.30. Gu Y, Huang LY. Gabapentin actions on N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor channels are protein kinase C-dependent. Pain. 2001. 93:85–92.31. Chen SR, Eisenach JC, McCaslin PP, Pan HL. Synergistic effect between intrathecal non-NMDA antagonist and gabapentin on allodynia induced by spinal nerve ligation in rats. Anesthesiology. 2000. 92:500–506.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Analysis of Interaction between Intrathecal Gabapentin with MK801, 5,7-DKA or NBQX in the Rat Formalin Test
- Effect of Serotonergic Receptors on the Antinociception of Intrathecal Gabapentin in the Formalin Test of Rats
- Antinociceptive drug interaction between intrathecal vitamin E and gabapentin in the rat formalin test
- Interaction between Intrathecal Gabapentin and Adenosine in the Formalin Test of Rats
- Effect of Spinal Adrenergic and Cholinergic Antagonists for Antinociception of Intrathecal Gabapentin