J Vet Sci.
2006 Sep;7(3):249-255. 10.4142/jvs.2006.7.3.249.
Characterization of HC58cDNA, a putative cysteine protease from the parasite Haemonchus contortus
- Affiliations
-
- 1College of Veterinary Medicine, Nanjing Agricultural University, Jiangsu 210095, P R China. cimuleke@yahoo.com
- KMID: 1089909
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4142/jvs.2006.7.3.249
Abstract
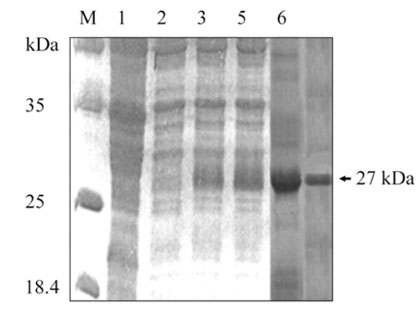
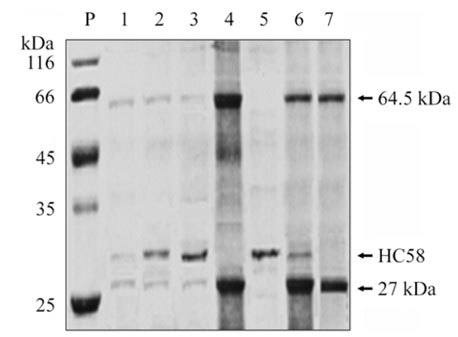
- Because of the complexity of the cathepsin B-like (CBL) family, an information on the biological and biochemical characteristics of individual CBL genes is lacking. In this study, we investigated the degradative effects of the recombinant HC58 protein isolated from Haemonchus contortus parasites on protein substrates over a broad pH range in vitro. This protein, which hydrolyzed the synthetic peptide substrates Z-FR-AMC and Z-RR-AMC, had characteristics of the cysteine protease class of proteins. In the acidic pH range, the isolated protein actively degraded hemoglobin (Hb), the heavy chain of goat immunoglobulin G, and azocasein. By contrast, it degraded fibrinogen in the alkaline pH range. These activities were strongly inhibited in the presence of the cysteine protease inhibitor E-64. While the protein digested Hb, it did not induce the agglutination of erythrocytes from its natural host. These results suggest that the HC58 protein may play a role in the nutrition of this parasite.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Animals
Caseins/metabolism
Cathepsin B/antagonists&inhibitors/*genetics/isolation & purification/*metabolism
Cysteine Proteinase Inhibitors/pharmacology
DNA, Complementary/genetics
Goat Diseases/*parasitology
Goats
Haemonchiasis/parasitology/*veterinary
Haemonchus/*enzymology/genetics/isolation & purification
Hemagglutination Tests/veterinary
Hemoglobins/metabolism
Hydrogen-Ion Concentration
Immunoglobulin G/metabolism
Leucine/analogs & derivatives/pharmacology
RNA, Helminth/chemistry/genetics
Recombinant Proteins/genetics/metabolism
Reverse Transcriptase Polymerase Chain Reaction/veterinary
Figure
Reference
-
1. Baig S, Damian RT, Peterson DS. A novel cathepsin B active site motif is shared by helminth blood feeders. Exp Parasitol. 2002. 101:83–89.
Article2. Bradford MM. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976. 72:248–254.
Article3. Chomczynski P, Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987. 162:156–159.
Article4. Geldhof P, Claerebout E, Knox DP, Jagneessens J, Vercruysse J. Proteinases released in vitro by the parasitic stages of the bovine abomasal nematode Ostertagia ostertagi. Parasitology. 2000. 121:639–647.5. Hartman D, Donald DR, Nikolaou S, Savin KW, Hasse D, Presidente PJA, Newton SE. Analysis of developmentally regulated genes of the parasite Haemonchus contortus. Int J Parasitol. 2001. 31:1236–1245.
Article6. Hotez PJ, Cerami A. Secretion of a proteolytic anticoagulant by Ancylostoma hookworms. J Exp Med. 1983. 157:1594–1603.7. Jasmer DP, Roth J, Myler PJ. Cathepsin B-like cysteine proteases and Caenorhabditis elegans homologues dominate gene products expressed in adult Haemonchus contortus intestine. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 2001. 116:159–169.
Article8. Jasmer DP, Mitreva MD, McCarter JP. mRNA sequences for Haemonchus contortus intestinal cathepsin B-like cysteine proteases display an extreme in abundance and diversity compared with other adult mammalian parasitic nematodes. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 2004. 137:297–305.
Article9. Knox DP, Redmond DL, Jones DG. Characterization of proteinases in extracts of adult Haemonchus contortus, the ovine abomasal nematode. Parasitology. 1993. 106:395–404.
Article10. Lourenco EV, Pereira SR, Faca VM, Coelho-Castelo AAM, Mineo JR, Roque-Barreira MC, Greene LJ, Panunto-Castelo A. Toxoplasma gondii micronemal protein MIC1 is a lactose-binding lectin. Glycobiology. 2001. 11:541–547.
Article11. Newton SE, Meeusen EN. Progress and new technologies for developing vaccines against gastrointestinal nematode parasites of sheep. Parasite Immunol. 2003. 25:283–296.
Article12. Newlands GFJ, Skuce PJ, Knox DP, Smith WD. Cloning and expression of cystatin, a potent cysteine protease inhibitor from the gut of Haemonchus contortus. Parasitology. 2001. 122:371–378.13. Pratt D, Armes LG, Hageman R, Reynolds V, Boisvenue RJ, Cox GN. Cloning and sequence comparisons of four distinct cysteine proteases expressed by Haemonchus contortus adult worms. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1992. 51:209–218.
Article14. Sajid M, Mckerrow JH, Hansell E, Mathieu MA, Lucas KD, Hsieh I, Greenbaum D, Bogyo M, Salter JP, Lim KC, Franklin C, Kim JH, Caffrey CR. Functional expression and characterization of Schistosoma mansoni cathepsin B and its trans-activation by an endogenous asparaginyl endopeptidase. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 2003. 131:65–75.
Article15. Sajid M, Mckerrow JH. Cysteine proteases of parasitic organisms. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 2002. 120:1–21.
Article16. Shompole S, Jasmer DP. Cathepsin B-like cysteine proteases confer intestinal cysteine protease activity in Haemonchus contortus. J Biol Chem. 2001. 276:2928–2934.
Article17. Skuce PJ, Redmond DL, Liddell S, Stewart EM, Newlands GFJ, Smith WD, Knox DP. Molecular cloning and characterization of gut-derived cysteine proteinases associated with a host protective extract from Haemonchus contortus. Parasitology. 1999. 119:405–412.
Article18. Stear MJ, Bishop SC, Doligalska M, Duncan JL, Holmes PH, Irvine J, McCririe L, McKeller QA, Sinski E, Murray M. Regulation of egg production, worm burden, worm length and worm fecundity by host responses in sheep infected with Ostertagia circumcincta. Parasite Immunol. 1995. 17:643–652.
Article19. Tort J, Brindley PJ, Knox D, Wolfe KH, Dalton JP. Proteinases and associated genes of parasitic helminths. Adv Parasitol. 1999. 43:161–266.
Article20. Williamson AL, Brindley PJ, Knox PK, Hotez PJ, Loukas A. Digestive proteases of blood-feeding nematodes. Trends Parasitol. 2003. 19:417–423.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Erratum: Characterization of HC58cDNA, a putative cysteine protease from the parasite Haemonchus contortus
- Characterization of proteases isolated from Kudoa septempunctata
- Fractionation of DNases Specific to Haemonchus contortus Intestine by Phenyl Sepharose Column
- Partial Purification and Characterization of a Cysteine Protease Inhibitor from the Plerocercoid of Spirometra erinacei
- Isolation and characterization of a 40 kDa cysteine protease from Gymnophalloides seoi adult worms