Korean J Radiol.
2007 Dec;8(6):556-560. 10.3348/kjr.2007.8.6.556.
Hemoperitoneum Caused by Hepatic Necrosis and Rupture Following a Snakebite: a Case Report with Rare CT Findings and Successful Embolization
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiology, Asan Foundation, GangNeung Asan Hospital, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Gangneung, Korea. smjung@gnah.co.kr
- 2Department of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery, Asan Foundation, GangNeung Asan Hospital, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Gangneung, Korea.
- 3Department of General Surgery, Asan Foundation, GangNeung Asan Hospital, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Gangneung, Korea.
- KMID: 1089446
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2007.8.6.556
Abstract
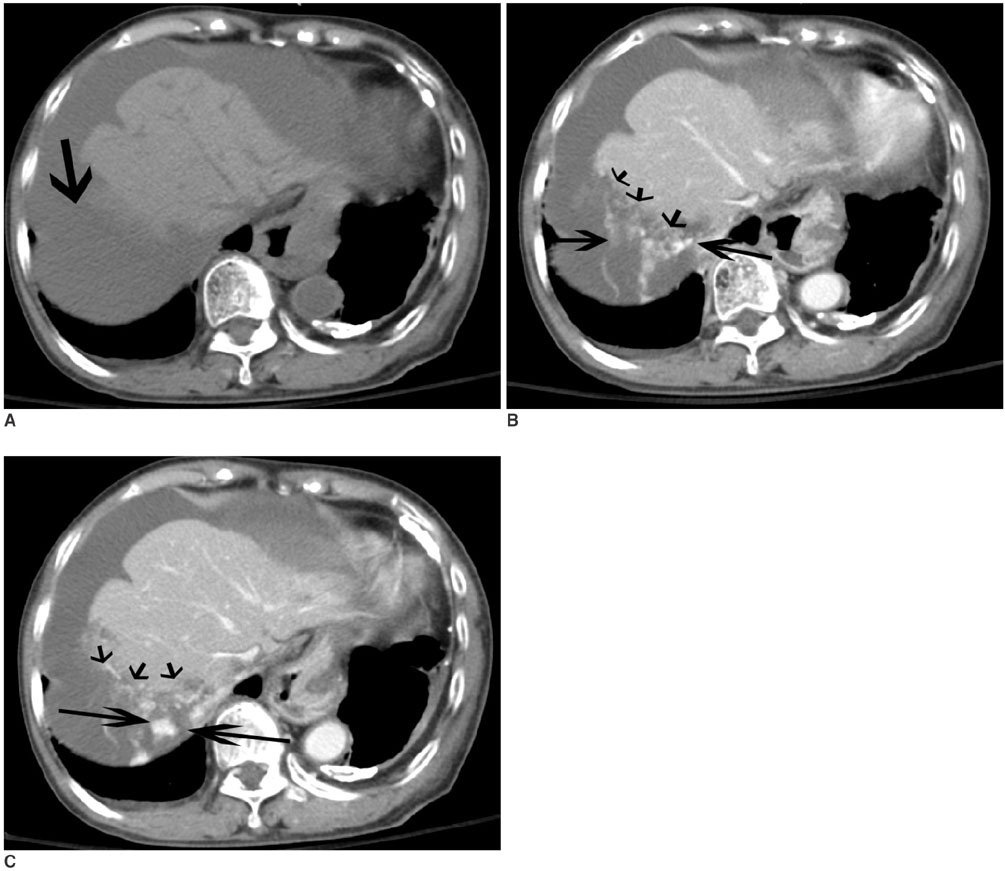
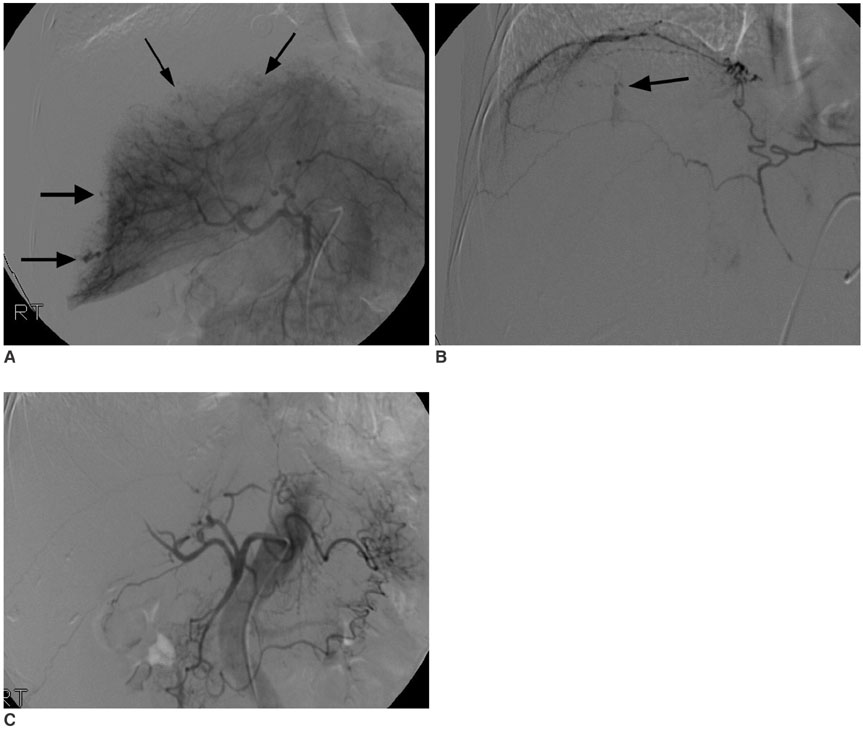
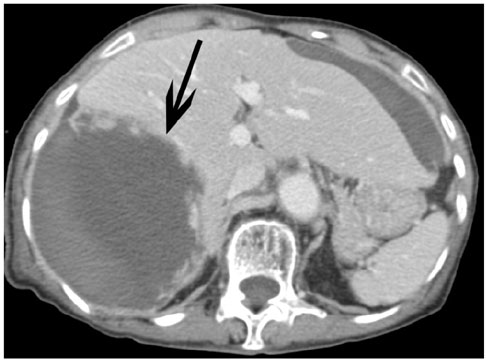
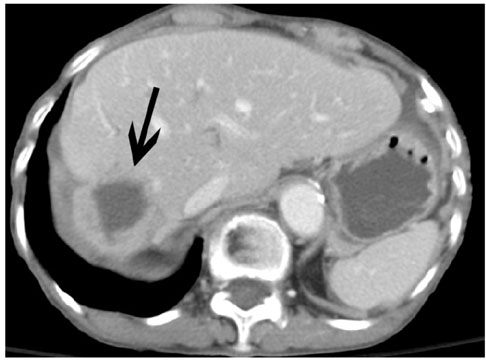
- We report the computed tomographic and angiographic findings in the case of a recently obtained successful clinical outcome after embolization of the hepatic artery in the case of a snakebite causing hemoperitoneum associated with hepatic necrosis and rupture with active bleeding.
MeSH Terms
-
Aged, 80 and over
Contrast Media/administration & dosage
Embolization, Therapeutic/*methods
Female
Fibrin Foam/therapeutic use
Follow-Up Studies
Hemoglobins
Hemoperitoneum/*etiology/therapy
Hemorrhage/etiology/therapy
Hepatic Artery/radiography
Humans
Korea
Liver/*injuries/pathology/radiography
Massive Hepatic Necrosis/complications/*etiology/therapy
Radiographic Image Enhancement/methods
Rupture, Spontaneous
Snake Bites/*complications
Tomography, X-Ray Computed/*methods
Treatment Outcome
Viper Venoms/adverse effects
Figure
Reference
-
1. Chippaux JP. Snake-bites: appraisal of the global situation. Bull World Health Organ. 1988. 76:515–524.2. White J. Dart R, editor. Overview of venomous snakes of the world. Medical Toxicology. 2004a. Lippincott: Williams and Wilkins;1543–1559.3. Rathod K, Sheth R, Chavhan G, Asrani A, Raut A. Hemoperitoneum complicating snake bite: rare CT features. Abdom Imaging. 2003. 28:820–821.4. Iwakiri R, Fujimoto K, Hirano M, Hisatsugu T, Nojiri I, Sakemi T. Snake-strike-induced ischemic colitis with colonic stricture complicated by disseminated intravascular coagulation. South Med J. 1995. 88:1084–1085.5. Rosenthal R, Meier J, Koelz A, Müller C, Wegmann W, Vogelbach P. Intestinal ischemia after buchmaster (Lachesis muta) snakebite- a case report. Toxicon. 2002. 40:217–220.6. Lee BC, Hwang SH, Bae JC, Kwon SB. Brainstem infarction following Korean viper bite. Neurology. 2001. 56:1244–1245.7. Nunes JO, Turner MA, Fulcher AS. Abdominal imaging feature of HELLP syndrome: A 10-year retrospective review. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2005. 185:1205–1210.8. Lee JW, Seu JH, Rhee IK, Jin I, Kawamura Y, Park W. Purification and characterization of brevinase, a heterogeneous two-chain fibrinolytic enzyme from the venom of Korean snake, Agkistrodon blomhoffii brevicaudus. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1999. 260:665–670.9. Li ZY, Wu XW, Yu TF, Lian EC. Purification and characterization of lupus anticoagulant like protein form Agkistrodon halys brevicaudus venom. Thromb Haemost. 1996. 76:791–797.10. Xu X, Wang Y, Wei C, Zhu X. Study on the action mechanism of hemorrhagin I from Agkidtrodon acutus venom. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1996. 391:361–366.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Hepatic Hemangioma Rupture Caused by Blunt Trauma
- Spontaneous hepatic haemangioma rupture and hemoperitoneum: a double problem with a single stage interventional radiology solution
- Gelatin Sponge Particle Embolization of Spontaneously Ruptured Intrahepatic Arterial Aneurysms in a Patient with Polyarteritis Nodosa: A Case Report
- Embolotherapy of Ruptured Gastroepiploico-Colic Communicating Artery with Median Arcuate Ligament Syndrome: A Case Report
- Hepatic Rupture Caused by Hemolysis, Elevated Liver Enzyme, and Low Platelet Count Syndrome: A Case Report with Computed Tomographic and Conventional Angiographic Findings