J Vet Sci.
2010 Dec;11(4):341-344. 10.4142/jvs.2010.11.4.341.
Novel insertion mutation of ABCB1 gene in an ivermectin-sensitive Border Collie
- Affiliations
-
- 1Veterinary Laboratory Medicine, College of Veterinary Medicine, Chungbuk National University, Cheongju 361-763, Korea. sigol@cbnu.ac.kr
- 2Eden Canine Training Center, Asan 336-912, Korea.
- KMID: 1072184
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4142/jvs.2010.11.4.341
Abstract
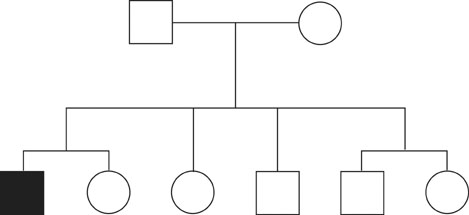
- P-glycoprotein (P-gp) is encoded by the ABCB1 gene and acts as an efflux pump for xenobiotics. In the Border Collie, a nonsense mutation caused by a 4-base pair deletion in the ABCB1 gene is associated with a premature stop to P-gp synthesis. In this study, we examined the full-length coding sequence of the ABCB1 gene in an ivermectin-sensitive Border Collie that lacked the aforementioned deletion mutation. The sequence was compared to the corresponding sequences of a wild-type Beagle and seven ivermectin-tolerant family members of the Border Collie. When compared to the wild-type Beagle sequence, that of the ivermectin-sensitive Border Collie was found to have one insertion mutation and eight single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) in the coding sequence of the ABCB1 gene. While the eight SNPs were also found in the family members' sequences, the insertion mutation was found only in the ivermectin-sensitive dog. These results suggest the possibility that the SNPs are species-specific features of the ABCB1 gene in Border Collies, and that the insertion mutation may be related to ivermectin intolerance.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Ameyaw MM, Regateiro F, Li T, Liu X, Tariq M, Mobarek A, Thornton N, Folayan GO, Githang'a J, Indalo A, Ofori-Adjei D, Price-Evans DA, McLeod HL. MDR1 pharmacogenetics: frequency of the C3435T mutation in exon 26 is significantly influenced by ethnicity. Pharmacogenetics. 2001. 11:217–221.
Article2. Bauer JW, Rouan F, Kofler B, Rezniczek GA, Kornacker I, Muss W, Hametner R, Klausegger A, Huber A, Pohla-Gubo G, Wiche G, Uitto J, Hintner H. A compound heterozygous one amino-acid insertion/nonsense mutation in the plectin gene causes epidermolysis bullosa simplex with plectin deficiency. Am J Pathol. 2001. 158:617–625.
Article3. Cascorbi I, Gerloff T, Johne A, Meisel C, Hoffmeyer S, Schwab M, Schaeffeler E, Eichelbaum M, Brinkmann U, Roots I. Frequency of single nucleotide polymorphisms in the P-glycoprotein drug transporter MDR1 gene in white subjects. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2001. 69:169–174.
Article4. Cordon-Cardo C, O'Brien JP, Casals D, Rittman-Grauer L, Biedler JL, Melamed MR, Bertino JR. Multidrug-resistance gene (P-glycoprotein) is expressed by endothelial cells at blood-brain barrier sites. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1989. 86:695–698.
Article5. Desalle R, Williams AK, George M. Isolation and characterization of animal mitochondrial DNA. Methods Enzymol. 1993. 224:176–204.6. Fromm MF. The influence of MDR1 polymorphisms on P-glycoprotein expression and function in humans. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2002. 54:1295–1310.
Article7. Geyer J, Döring B, Godoy JR, Leidorf R, Moritz A, Petzinger E. Frequency of the nt230 (del4) MDR1 mutation in Collies and related dog breeds in Germany. J Vet Pharmacol Ther. 2005. 28:545–551.
Article8. Hoffmeyer S, Burk O, von Richter O, Arnold HP, Brockmöller J, Johne A, Cascorbi I, Gerloff T, Roots I, Eichelbaum M, Brinkmann U. Functional polymorphisms of the human multidrug-resistance gene: multiple sequence variations and correlation of one allele with P-glycoprotein expression and activity in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2000. 97:3473–3478.
Article9. Hori R, Okamura N, Aiba T, Tanigawara Y. Role of P-glycoprotein in renal tubular secretion of digoxin in the isolated perfused rat kidney. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1993. 266:1620–1625.10. Juliano RL, Ling V. A surface glycoprotein modulating drug permeability in Chinese hamster ovary cell mutants. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976. 455:152–162.
Article11. Kim KI, Lee JH, Li K, Zhang YP, Lee SS, Gongora J, Moran C. Phylogenetic relationships of Asian and European pig breeds determined by mitochondrial DNA D-loop sequence polymorphism. Anim Genet. 2002. 33:19–25.
Article12. Kim RB, Leake BF, Choo EF, Dresser GK, Kubba SV, Schwarz UI, Taylor A, Xie HG, McKinsey J, Zhou S, Lan LB, Schuetz JD, Schuetz EG, Wilkinson GR. Identification of functionally variant MDR1 alleles among European Americans and African Americans. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2001. 70:189–199.
Article13. Kunieda M, Tsuji T, Abbasi AR, Khalaj M, Ikeda M, Miyadera K, Ogawa H, Kunieda T. An insertion mutation of the bovine Fii gene is responsible for factor XI deficiency in Japanese black cattle. Mamm Genome. 2005. 16:383–389.
Article14. Li M, Hurren R, Zastawny RL, Ling V, Buick RN. Regulation and expression of multidrug resistance (MDR) transcripts in the intestinal epithelium. Br J Cancer. 1999. 80:1123–1131.
Article15. Litman T, Druley TE, Stein WD, Bates SE. From MDR to MXR: new understanding of multidrug resistance systems, their properties and clinical significance. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2001. 58:931–959.
Article16. Mealey KL. Canine ABCB1 and macrocyclic lactones: Heartworm prevention and pharmacogenetics. Vet Parasitol. 2008. 158:215–222.
Article17. Melaine N, Liénard MO, Dorval I, Le Goascogne C, Lejeune H, Jégou B. Multidrug resistance genes and P-glycoprotein in the testis of the rat, mouse, guinea pig, and human. Biol Reprod. 2002. 67:1699–1707.
Article18. Mickley LA, Lee JS, Weng Z, Zhan Z, Alvarez M, Wilson W, Bates SE, Fojo T. Genetic polymorphism in MDR-1: a tool for examining allelic expression in normal cells, unselected and drug-selected cell lines, and human tumors. Blood. 1998. 91:1749–1756.
Article19. Roulet A, Puel O, Gesta S, Lepage JF, Drag M, Soll M, Alvinerie M, Pineau T. MDR1-deficient genotype in Collie dogs hypersensitive to the P-glycoprotein substrate ivermectin. Eur J Pharmacol. 2003. 460:85–91.
Article20. Schaeffeler E, Eichelbaum M, Brinkmann U, Penger A, Asante-Poku S, Zanger UM, Schwab M. Frequency of C3435T polymorphism of MDR1 gene in African people. Lancet. 2001. 358:383–384.21. Thiebaut F, Tsuruo T, Hamada H, Gottesman MM, Pastan I, Willingham MC. Cellular localization of the multidrug-resistance gene product P-glycoprotein in normal human tissues. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1987. 84:7735–7738.
Article22. Vilà C, Savolainen P, Maldonado JE, Amorim IR, Rice JE, Honeycutt RL, Crandall KA, Lundeberg J, Wayne RK. Multiple and ancient origins of the domestic dog. Science. 1997. 276:1687–1689.
Article23. Wong LJ, Boles RG. Mitochondrial DNA analysis in clinical laboratory diagnostics. Clin Chim Acta. 2005. 354:1–20.
Article24. Yamamoto Y, Murata K, Matsuda H, Hosoda T, Tamura K, Furuyama J. Determination of the complete nucleotide sequence and haplotypes in the D-loop region of the mitochondrial genome in the oriental white stork, Ciconia boyciana. Genes Genet Syst. 2000. 75:25–32.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Presumptive Border Collie collapse in a dog: serial clinical observation and successful management
- The Impact of ABCB1 Gene Polymorphism on Steroid Responsiveness in Acute Rejection in Kidney Transplantation
- A Case of Cutaneous Larva Migrans Improved by Oral Ivermectin
- Perioral Dermatitis Successfully Treated with Topical Ivermectin
- Perioral Dermatitis Successfully Treated with Topical Ivermectin