Yonsei Med J.
2010 Sep;51(5):661-671. 10.3349/ymj.2010.51.5.661.
Acute Stress and Chronic Stress Change Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor (BDNF) and Tyrosine Kinase-Coupled Receptor (TrkB) Expression in Both Young and Aged Rat Hippocampus
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Medical Psychology, Institute of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Binzhou Medical College, Yantai, Shandong, China.
- 2Gaomi People's Hospital, Weifang, Shandong, China.
- 3Department of Medical Psychology, Shandong University Medical School, Jinan, Shandong, China.
- 4Institute of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Binzhou Medical University, Yantai, Shandong, China. becky6280@hotmail.com
- KMID: 1071416
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2010.51.5.661
Abstract
- PURPOSE
The purpose of this study is to explore the dynamic change of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) mRNA, protein, and tyrosine kinase-coupled receptor (TrkB) mRNA of the rat hippocampus under different stress conditions and to explore the influence of senescence on the productions expression.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
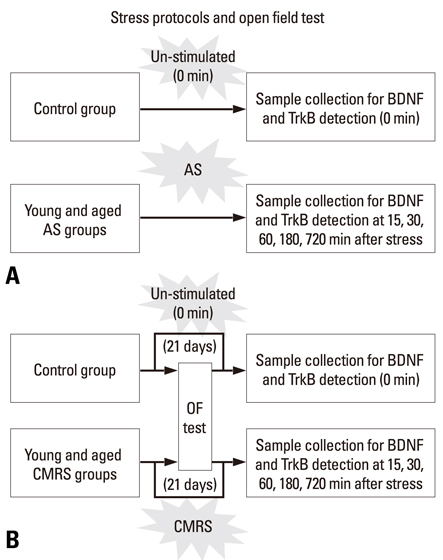
By using forced-swimming in 4degrees C cold ice water and 25degrees C warm water, young and aged male rats were randomly divided into acute stress (AS) and chronic mild repeated stress (CMRS) subgroups, respectively. BDNF productions and TrkB mRNA in the hippocampus were detected by using Western-blotting and reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR), separately, at 15, 30, 60, 180, and 720 min after the last stress session.
RESULTS
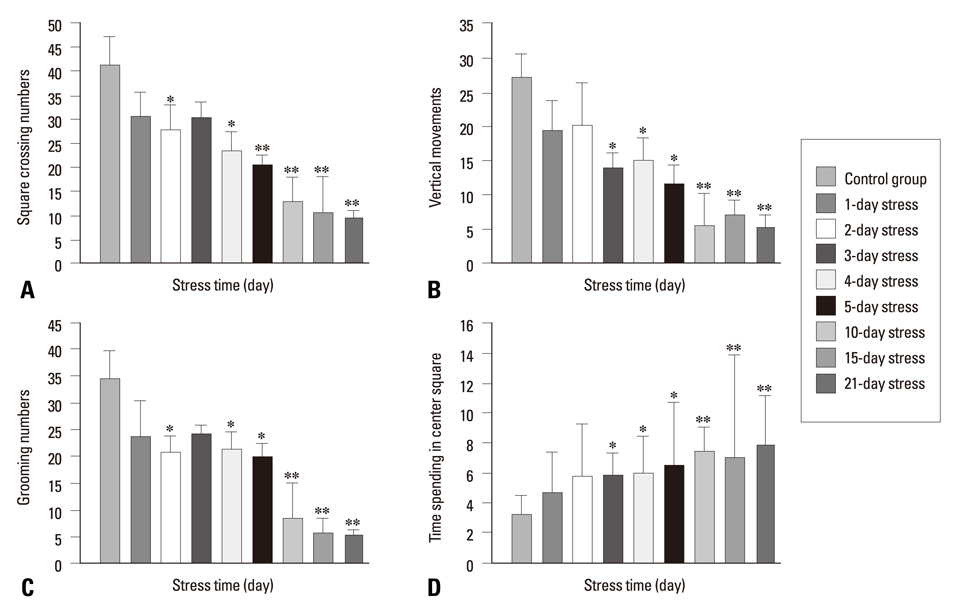
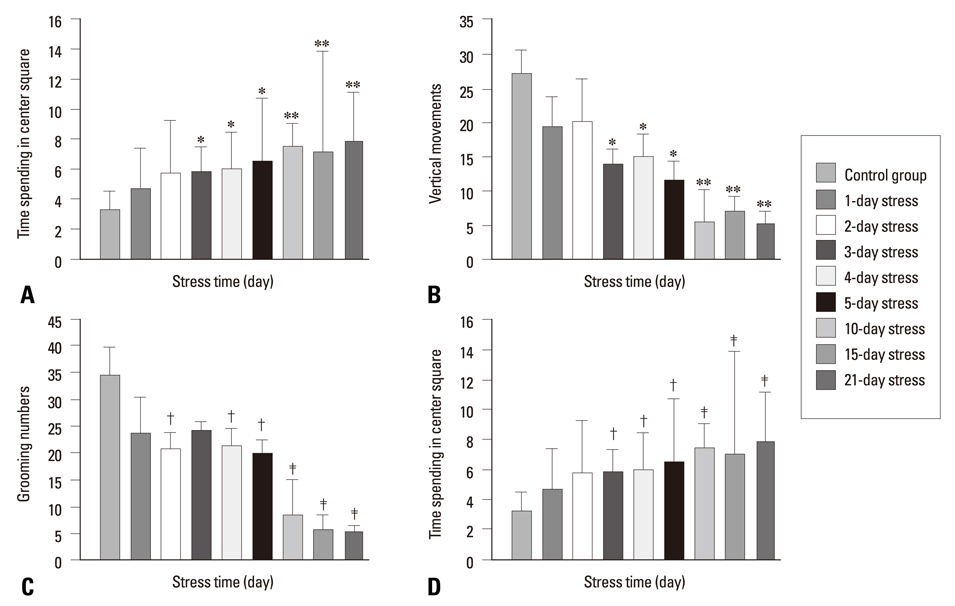
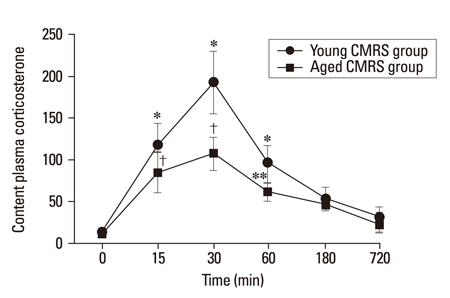
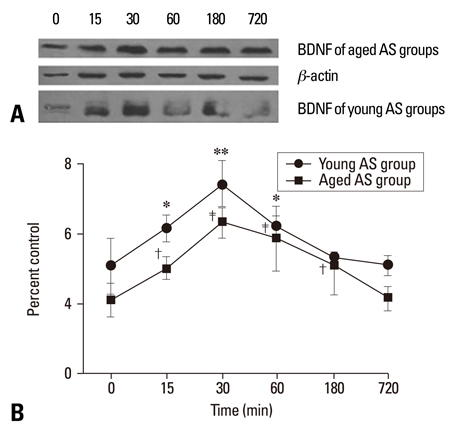
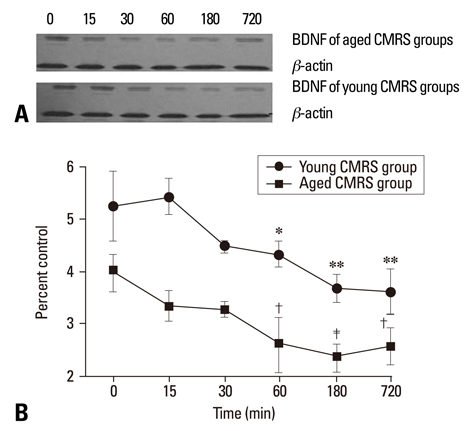
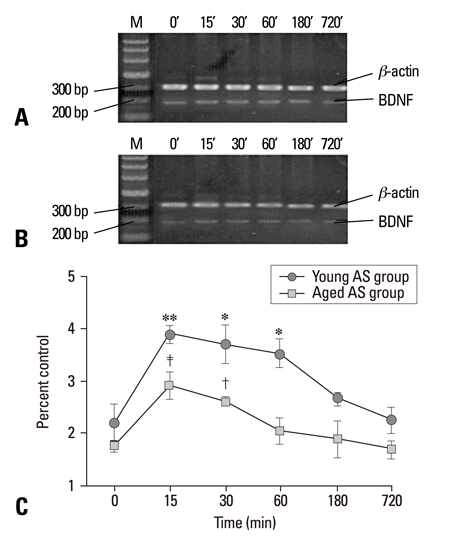
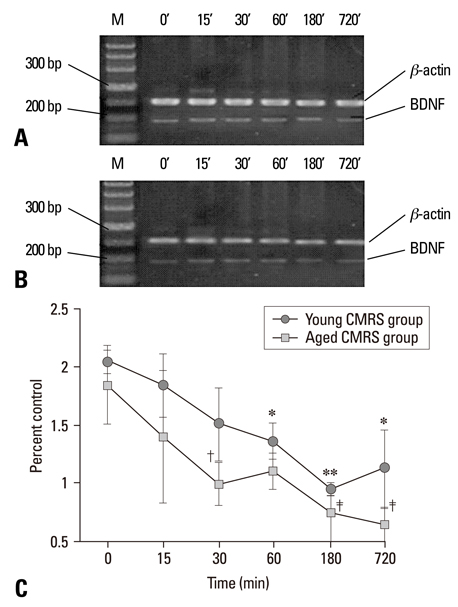
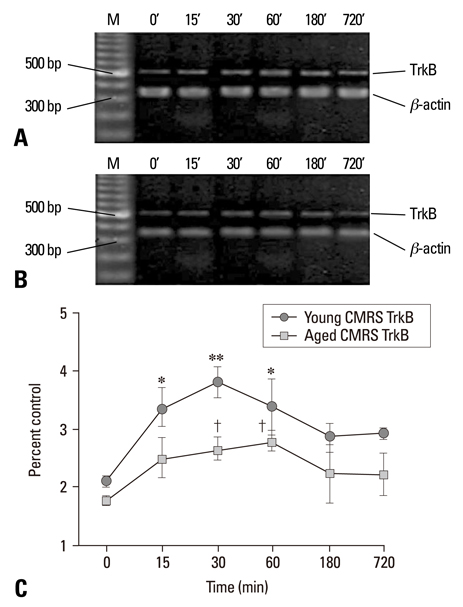
The short AS induced a significant increase in BDNF mRNA and protein in both age groups, but the changes in the young group were substantially greater than those of the aged group (p < 0.005). The CMRS resulted in a decrease in BDNF mRNA and protein, but a significant increase in TrkB mRNA in both young and age groups. The expression of BDNF mRNA and protein in the AS groups were higher than in the CMRS groups at 15, 30, and 60 min after stress.
CONCLUSION
The results indicated that the up/down-regulation of BDNF and TrkB were affected by aging and the stimulus paradigm, which might reflect important mechanisms by which the hippocampus copes with stressful stimuli.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Animals
Blotting, Western
Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor/genetics/*metabolism
Corticosterone/blood
*Gene Expression Regulation
Hippocampus/*metabolism
Male
Radioimmunoassay
Random Allocation
Rats
Rats, Wistar
Receptor, trkB/genetics/*metabolism
Reverse Transcriptase Polymerase Chain Reaction
Stress, Physiological/genetics/*physiology
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
The changes of nociception and the signal molecules expression in the dorsal root ganglia and the spinal cord after cold water swimming stress in mice
Jing-Hui Feng, Su-Min Sim, Jung-Seok Park, Jae-Seung Hong, Hong-Won Suh
Korean J Physiol Pharmacol. 2021;25(3):207-216. doi: 10.4196/kjpp.2021.25.3.207.
Reference
-
1. Leibrock J, Lottspeich F, Hohn A, Hofer M, Hengerer B, Masiakowski P, et al. Molecular cloning and expression of brain-derived neurotrophic factor. Nature. 1989. 341:149–152.
Article2. Croll SD, Iq NY, Lindsay RM, Wiegand SJ. Expression of BDNF and trkB as a function of age and cognitive performance. Brain Res. 1998. 812:200–208.
Article3. Connor B, Dragunow M. The role of neuronal growth factors in neurodegenerative disorders of the human brain. Brain Res Rev. 1998. 27:1–39.
Article4. Hall J, Thomas KL, Everitt BJ. Rapid and selective induction of BDNF expression in the hippocampus during contextural learning. Nat Neurosci. 2000. 3:533–535.
Article5. Tafet GE, Bernardini R. Psychoneuroendocrinological links between chronic stress and depression. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2003. 27:893–903.6. McEwen BS. Stress and hippocampal plasticity. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1999. 22:105–122.
Article7. Aggleton JP, Vann SD, Oswald CJ, Good M. Identifying cortical inputs to the rat hippocampus that subserve allocentric spatial processes: a simple problem with a complex answer. Hippocampus. 2000. 10:466–474.
Article8. McEwen BS. Protective and damaging effects of stress mediators: central role of the brain. Dialogues Clin Neurosci. 2006. 8:367–381.
Article9. Adlard PA, Cotman CW. Voluntary exercise protects against stress-induced decreases in brain-derived neurotrophic factor protein expression. Neuroscience. 2004. 124:985–992.
Article10. Fuchikami M, Morinobu S, Kurata A, Yamamoto S, Yamawaki S. Single immobilization stress differentially alters the expression profile of transcripts of the brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) gene and histone acetylation at its promoters in the rat hippocampus. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2009. 12:73–82.
Article11. Ueyama T, Kawai Y, Nemoto K, Sekimoto M, Toné S, Senba E. Immobilization stress reduced the expression of neurotrophins and their receptors in the rat brain. Neurosci Res. 1997. 28:103–110.
Article12. Lee T, Saruta J, Sasaquri K, Sato S, Tsukinoki K. Allowing animals to bite reverses the effects of immobilization stress on hippocampal neurotrophin expression. Brain Res. 2008. 1195:43–49.13. Gray JA. The psychology of fear and stress. 1987. New York: Cambridge University Press.14. de Cabo de la Vega C, Pujol A, Paz Viveros M. Neonatally administered naltrexone affects several behavioral responses in adult rats of both genders. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 1995. 50:277–286.
Article15. Sarkisova KYu, Kulikov MA. Prophylactic actions of the antioxidant agent AEKOL on behavioral (psychoemotional) disturbances induced by chronic stress in rats. Neurosci Behav Physiol. 2001. 31:503–508.16. Srisomsap C, Sawangareetrakul P, Subhasitanont P, Panichakul T, Keeratichamroen S, Lirdprapamongkol K, et al. Proteomic analysis of cholangiocarcinoma cell line. Proteomics. 2004. 4:1135–1144.
Article17. Beck KD, Luine VN. Food deprivation modulates chronic stress effects on object recognition in male rats: role of monoamines and amino acids. Brain Res. 1999. 830:56–71.18. Toth E, Gersner R, Wilf-Yarkoni A, Raizel H, Dar DE, Richter-Levin G, et al. Age-dependent effects of chronic stress on brain plasticity and depressive behavior. J Neurochem. 2008. 107:522–532.19. Fukumoto T, Morinobu S, Okamoto Y, Kagaya A, Yamawaki S. Chronic lithium treatment increases the expression of brain-derived neurotrophic factor in the rat brain. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2001. 158:100–106.
Article20. Gregus A, Wintink AJ, Davis AC, Kalynchuk LE. Effect of repeated corticosterone injections and restraint stress on anxiety and depression-like behavior in male rats. Behav Brain Res. 2005. 156:105–114.
Article21. Leverenz JB, Wilkinson CW, Wamble M, Corbin S, Grabber JE, Raskind MA, et al. Effect of chronic high-dose exogenous cortisol on hippocampal neuronal number in aged nonhuman primates. J Neurosci. 1999. 19:2356–2361.
Article22. McQuade R, Young AH. Future therapeutic targets in mood disorders: the glucocorticoid receptor. Br J Psychiatry. 2000. 177:390–395.
Article23. Hassan AH, Patchev VK, von Rosenstiel P, Holsboer F, Almeida OF. Plasticity of hippocampal corticosteroid receptors during aging in the rat. FASEB J. 1999. 13:115–122.
Article24. Korte SM. Corticosteroids in relation to fear, anxiety and psychopathology. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2001. 25:117–142.
Article25. Powers SK, LOCKE And M, Demirel HA. Exercise, heat shock proteins, and myocardial protection from I-R injury. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2001. 33:386–392.26. Sousa N, Lukoyanov NV, Madeira MD, Almeida OF, Paula-Barbosa MM. Reorganization of the morphology of hippocampal neurites and synapses after stress-induced damage correlates with behavioral improvement. Neuroscience. 2000. 97:253–266.27. Cosi C, Spoerri PE, Comelli MC, Guidolin D, Skaper SD. Glucocorticoids depress activity-dependent expression of BDNF mRNA in hippocampal neurons. Neuroreport. 1993. 4:527–530.28. Makino S, Kaneda T, Nishiyama M, Asaba K, Hashimoto K. Lack of decrease in hypothalamic and hippocampal glucocorticoid receptor mRNA during starvation. Neuroendocrinology. 2001. 74:120–128.
Article29. Lauterborn J, Berschauer R, Gall C. Cell-specific modulation of basal and seizure-induced neurotrophin expression by adrenalectomy. Neuroscience. 1995. 68:363–378.
Article30. Marmigére F, Givalois L, Rage F, Arancibia S, Tapia-Arancibial L. Rapid induction of BDNF expression in the hippocampus during immobilization stress challenge in adult rats. Hippocampus. 2003. 13:646–655.
Article31. Rage F, Givalois L, Marmigére F, Tapia-Arancibia L, Arancibia S. Immobilization stress rapidly modulates BDNF mRNA expression in the hypothalamus of adult male rats. Neuroscience. 2002. 112:309–318.
Article32. Lupien SJ, de Leon M, de Santi S, Convit A, Tarshish C, Nair NP, et al. Cortisol levels during human aging predict hippocampal atrophy and memory deficits. Nat Neurosci. 1998. 1:69–73.
Article33. Hibberd C, Yau JL, Seckl JR. Glucocorticoids and the ageing hippocampus. J Anat. 2000. 197:553–562.
Article34. Bremner JD. Stress and brain atrophy. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets. 2006. 5:503–512.
Article35. Smith MA, Makino S, Kvetnansky R, Post RM. Stress and glucocorticoids affect the expression of brain-derived neurotrophic factor and neurotrophin-3 mRNAs in the hippocampus. J Neurosci. 1995. 15:1768–1777.
Article36. Thoenen H. Neurotrophins and activity-dependent plasticity. Prog Brain Res. 2000. 128:183–191.
Article37. Yamasaki Y, Shigeno T, Furukawa Y, Furukawa S. Reduction in brain-derived neurotrophic factor protein level in the hippocampal CA1 dendritic field precedes the delayed neuronal damage in the rat brain. J Neurosci Res. 1998. 53:318–329.
Article38. Yamada K, Mizuno M, Nabeshima T. Role for brain-derived neurotrophic factor in learning and memory. Life Sci. 2002. 70:735–744.
Article39. McAllister AK, Katz LC, Lo DC. Neurotrophins and synaptic plasticity. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1999. 22:295–318.
Article40. Nibuya M, Takahashi M, Russell DS, Duman RS. Repeated stress increases catalytic TrkB mRNA in rat hippocampus. Neurosci Lett. 1999. 267:81–84.
Article41. Tsukinoki K, Saruta J, Sasaguri K, Miyoshi Y, Jinbu Y, Kusama M, et al. Immobilization stress induces BDNF in rat submandibular glands. J Dent Res. 2006. 85:844–848.
Article42. Fujihara H, Sei H, Morita Y, Ueta Y, Morita K. Short-term sleep disturbance enhances brain-derived neurotrophic factor gene expression in rat hippocampus by acting as internal stressor. J Mol Neurosci. 2003. 21:223–232.43. Grundy PL, Patel N, Harbuz MS, Lightman SL, Sharples PM. Glucocorticoids modulate BDNF mRNA expression in the rat hippocampus after traumatic brain injury. Neuroreport. 2000. 11:3381–3384.
Article44. Scaccianoce S, Del Bianco P, Caricasole A, Nicoletti F, Catalani A. Relationship between learning, stress and hippocampal brain-derived neurotrophic factor. Neuroscience. 2003. 121:825–828.
Article45. Givalois L, Marmigère F, Rage F, Ixart G, Arancibia S, Tapia-Arancibia L. Immobilization stress rapidly and differentially modulates BDNF and TrkB mRNA expression in the pituitary gland of adult male rats. Neuroendocrinology. 2001. 74:148–159.
Article46. Nibuya M, Takahashi M, Russell DS, Duman RS. Repeated stress increases catalytic TrkB mRNA in rat hippocampus. Neurosci Lett. 1999. 267:81–84.
Article47. Murakami S, Imbe H, Morikawa Y, Kubo C, Senba E. Chronic stress, as well as acute stress, reduces BDNF mRNA expression in the rat hippocampus but less robustly. Neurosci Res. 2005. 53:129–139.48. Gutsmann-Conrad A, Pahlavani MA, Heydari AR, Richardson A. Expression of heat shock protein 70 decreases with age in hepatocytes and splenocytes from female rats. Mech Ageing Dev. 1999. 107:255–270.
Article49. Honma Y, Tani M, Takayama M, Yamamura K, Hasegawa H. Aging abolishes the cardioprotective effect of combination heat shock and hypoxic preconditioning in reperfused rat hearts. Basic Res Cardiol. 2002. 97:489–495.50. Alsbury S, Papageorgiou K, Latchman DS. Heat shock proteins can protect aged human and rodent cells from different stressful stimuli. Mech Ageing Dev. 2004. 125:201–209.
Article51. Lapchak PA, Araujo DM, Beck KD, Finch CE, Johnson SA, Hefti F. BDNF and trkB mRNA expression in the hippocampal formation of aging rats. Neurobiol Aging. 1993. 14:121–126.52. Schaaf MJ, de Jong J, de Kloet ER, Vreugdenhil E. Down-regulation of BDNF mRNA and protein in the rat hippocampus by corticosterone. Brain Res. 1998. 813:112–120.
Article53. Narisawa-Saito M, Nawa H. Differential regulation of hippocampal neurotrophins during aging in rats. J Neurochem. 1996. 67:1124–1131.54. Sihol M, Arancibia S, Perrin D, Maurice T, Alliot J, Tapia-Arancibia L. Effect of aging on brain-derived neurotrophic factor, proBDNF, and their receptors in the hippocampus of Lou/C rats. Rejuvenation Res. 2008. 11:1031–1040.55. Hosinger RM, Schnarr J, Henry P, Castelo VT, Fahnestock M. Quantitation of BDNF mRNA in human parietal cortex by competitive reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction: decreased levels in Alzheimer's disease. Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 2000. 76:347–354.
Article56. Hock C, Heese K, Hulette C, Rosenberg C, Otten U. Region-specific neurotrophin imbalances in Alzheimer disease: decreased levels of brain-derived neurotrophic factor and increased levels of nerve growth factor in hippocampus and cortical areas. Arch Neurol. 2000. 57:846–851.
Article57. Silhol M, Bonnichon V, Rage F, Tapia-Arancibia L. Age-related changes in brain-derived neurotrophic factor and tyrosine kinase receptor isoforms in the hippocampus and hypothalamus in male rats. Neuroscience. 2005. 132:613–624.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Expression of Neurotrophic Factors and Their Receptors in Rat Posterior Taste Bud Cells
- Isoflurane Induces Transient Anterograde Amnesia through Suppression of Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor in Hippocampus
- Alpha-Asarone, a Major Component of Acorus gramineus, Attenuates Corticosterone-Induced Anxiety-Like Behaviours via Modulating TrkB Signaling Process
- Effects of Peripheral Inflammation on Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor and TrkB in Rat Dorsal Root Ganglia and Spinal Cord
- Expression and Distribution of BDNF (Brain Derived Neurotrophic Factor) in the Rat Hypothalamus